“CNC milling brings precision and exactness to medical device manufacturing. It is used in the production of surgical instruments, dental implants, diagnosis equipment parts, and many more.”
CNC milling for medical devices addresses the soaring demands for top-tier, precision-driven medical equipment. This advanced machining technique supports the timely production of intricate medical components. The healthcare sector is continuously seeking reliability and perfection. Here, CNC milling ensures that medical parts, from implants to surgical instruments, are crafted with unparalleled precision. This article will explore how CNC milling crafts intricate details, ensuring that health devices meet the most stringent standards. As medical science progresses, so does the demand for state-of-the-art tools, and CNC milling is at the forefront of meeting these requirements.
Why CNC Milling for Medical Device Manufacturing?
Medical CNC milling
In medical manufacturing, every micron counts. The precision, reliability, and consistency required in this industry have very high standards. So, when the question arises – why choose CNC milling for medical device production? – the answer lies in its inherent benefits and its critical role in ensuring patient safety and medical efficacy.
1. Precision and Accuracy
One of the foremost reasons is the unmatched precision that CNC milling brings. Medical devices, whether surgical tools or implants, need to adhere to exact dimensions to function effectively.
- Micron-Level Tolerances: Many medical components require tolerances as tight as ±0.005 mm. CNC milling can consistently achieve these demanding standards and can easily avoid roughness.
- Repeatability: For mass-produced medical devices, every piece must match its predecessor. CNC milling guarantees this level of repeatability.
- Complex Geometries: Some medical parts (like implants) have intricate designs that other manufacturing methods cannot replicate. With CNC milling, even the most complex geometries are achievable.
2. Material Versatility
Medical devices employ a wide range of materials, from metals to polymers. CNC milling machines are adept at handling these diverse materials, ensuring optimal results every time. So, every medical grade material can be the desired shape & geometry with CNC milling.
3. Adherence to Medical Standards:
Medical devices are governed by stringent international standards due to their critical role. CNC milling ensures these standards are consistently met, guaranteeing safety and functionality. For instance, the ISO 13485 standard specifies quality management requirements where an organization must demonstrate its ability to provide medical devices and related services that consistently meet regulatory requirements. CNC milling’s precision and consistency support manufacturers in achieving and maintaining these certifications.
4. Cost-Effective Prototyping
Prototypes of medical devices are essential. Before full-scale production, CNC milling allows for rapid and cost-effective prototyping, ensuring that any design flaws are ironed out before mass production.
- Shorter Production Cycles: Faster production without compromising quality.
- Scalability: Transitioning from prototype to mass production is seamless.
- Reduced Waste: Efficient use of materials, leading to cost savings and environmental benefits.
- Customization: Can produce bespoke devices for specialized medical requirements.
5. Flexibility and Adaptability
As medical science evolves, the devices that accompany new treatments and techniques must adapt quickly. CNC milling’s computer-driven approach means that changes to a device’s design can be implemented soon, allowing for rapid iterations and adaptability in production.
Read More: CNC Milling Prototyping
CNC milling for the custom medical part
Key Applications of CNC Milling for Medical Devices
With its capabilities of creating intricate parts with exact precision, CNC milling has become a pivotal asset in producing these essential tools. Let’s delve into the key medical devices crafted using this sophisticated method.
1. Surgical Instruments
In medical manufacturing, the exactitude of CNC milling has become invaluable. Here’s a closer look at some of the surgical instruments it plays a role in crafting. CNC milling ensures that surgical tools retain their sharpness and precision, even after multiple sterilization processes.
- Scalpels: Precise blades crafted to offer surgeons a reliable tool for delicate operations.
- Forceps: Milled for a firm grip, ensuring tissue handling without damage.
- Hemostats: Used to stop bleeding by clamping blood vessels.
2. Orthopedic Implants
As we strive for solutions to age-related bone and joint issues, orthopedic implants have come to the fore. The demand for orthopedic implants is expected to rise with an aging global population. CNC-milled implants provide a solution that’s both efficient and patient-specific.
CNC-milled joint replacement
- Joint replacements: Including knee, hip, and shoulder joints. These parts must be custom-fitted for each patient, ensuring longevity and comfort.
- Bone plates: Used to stabilize fractured bones.
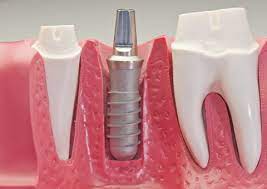
3. Dental Instruments and Implants
CNC milling of dental implants
Dental care hinges on personalized solutions for individual patients. Precision-crafted tools and implants are paramount for successful dental procedures. CNC milling ensures each dental piece is tailored perfectly.
Table: Dental instruments with CNC milling
| Device | Material Commonly Used | CNC Milling Advantage |
|---|---|---|
| Dental Drill | Stainless Steel | Precision in size and shape |
| Crowns | Ceramic, Metal Alloys | Customized fit |
4. Diagnostic Equipment
CNC-milled ultrasonic probe
The diagnostic equipment market is slated to grow at a CAGR of 6.5% through 2025, highlighting an increased demand for precision components. CNC milling contributes significantly to crafting and refining such essential equipment. Here are some key diagnostic tools:
- Ultrasound probes: These require precision milling to house intricate electronic components.
- MRI machine components: CNC milling aids in crafting specific parts for imaging machines.
5. Prosthetics and Exoskeletons
Mobility and quality of life are crucial for patients needing prosthetics. The blend of technology & healthcare exemplifies innovation as seen in exoskeletons. CNC milling ensures these devices fit perfectly and function seamlessly.
- Limb prosthetics: Tailored to fit the patient, ensuring natural movement.
- Exoskeleton parts: These assistive devices help people with mobility issues move better.
6. Robotic Surgery Components
Endoscope clamp made with CNC milling.
Robotic surgery has witnessed a significant surge in recent years. The components of these robotic systems. By 2024, over 4,000 robotic surgery systems are expected to be operational globally, emphasizing the importance of CNC-milled components in healthcare. Many of which are milled using CNC techniques, are:
- Arms: For precise surgical movements.
- Endoscopes: For better visualization during surgeries.
Standards in CNC Milling for Medical Devices
One of the most prominent entities that has laid down guidelines for medical device manufacturing is the International Organization for Standardization (ISO). The ISO 13485 standard, for instance, specifically relates to quality management systems for medical devices. This standard addresses the full spectrum of a device’s lifecycle, from design and development to production and post-market surveillance.
The Food and Drug Administration (FDA) also plays a pivotal role in the U.S. with its set of regulations. The FDA’s Quality System Regulation (QSR), outlined in 21 CFR Part 820, focuses on the methods used in, and the facilities and controls for, designing, manufacturing, packaging, labelling, storing, installing, and servicing of all finished devices intended for human use.
However, beyond these broad regulations, CNC milling for medical devices has its own set of nuanced standards to consider.
What is Meant by CNC Medical-grade Materials?
Different medical procedures and applications demand different materials. Titanium, for example, is favoured for its strength and biocompatibility in orthopedic implants. The ASTM (American Society for Testing and Materials) offers a wealth of material standards that influence CNC milling practices. For instance, ASTM F136 is the specification for wrought titanium-6 aluminum-4 vanadium ELI (Extra Low Interstitial) alloy for surgical implant applications.
Several criteria determine the classification of a material as “medical grade.” These include:
- Biocompatibility: The material should not induce an inflammatory or immunological response when in contact with body tissues.
- Sterilizeability: The material should be able to be sterilized without degrading, ensuring it’s free from any microorganisms before it’s used in medical procedures.
- Toxicity: The material must not release any toxic, carcinogenic, or mutagenic agents.
- Physical and Mechanical Properties: Depending on the application, the material might need specific strength, flexibility, or durability properties.
- Chemical Resistance: Some materials must resist bodily fluids, drugs, or other chemicals they might come in contact with.
Click here to download: Standard for medical device manufacturing and quality control
Try Prolean Now!
CNC Machinable Medical-Grade Materials
When it comes to manufacturing medical devices, the choice of material is paramount. The right material ensures the device’s safety, functionality, and durability. Thanks to advancements in CNC milling technology, a vast array of medical-grade materials can now be machined with impeccable precision, facilitating the development of medical devices that meet stringent health and safety standards.
What Are the Common Medical-grade materials?
Medical-grade materials commonly include certain plastics (like PEEK or medical-grade PVC), metals (like titanium or specific stainless steel alloys), and ceramics.
- Titanium and its Alloys
Titanium is a favorite in the medical field, Known for its robustness and biocompatibility. Its resistance to corrosion makes it an ideal choice for internal devices such as orthopedic implants. Furthermore, titanium’s strength-to-weight ratio is exceptional, ensuring that devices are both durable and lightweight.
- Stainless Steel
It is revered for its corrosion resistance and strength. Often found in surgical instruments and internal fixtures, stainless steel’s unique properties make it easy to sterilize, ensuring safe repeated use in medical environments.
- PEEK (Polyether Ether Ketone)
A high-performance plastic, PEEK is making waves in the medical device sector. Its biocompatibility combined with mechanical properties like resistance to wear makes it ideal for applications like spinal implants.
- Cobalt-Chromium Alloys
Cobalt-chromium alloys are typically used in dental and orthopedic implants, offering a blend of wear resistance and biocompatibility. Their strength and resistance to corrosion ensure longevity in the human body, making them a prime choice for critical applications.
- Tantalum
It is often found in radiographic markers due to its high density and visibility on X-ray, tantalum’s biocompatibility also makes it suitable for certain surgical implants. Its ability to foster bone ingrowth has opened new avenues in reconstructive surgery.
Medical grade titanium on use after CNC milling
Are there Any Challenges in Milling of Medical Grade Materials?
Machining these materials poses its own set of challenges. The CNC milling process needs to be tailored according to the material in question. For instance, while stainless steel may demand a certain milling speed and tool type, plastics like PEEK would require a different approach to prevent melting or warping.
As the medical industry continues to grow, so does the list of CNC machinable materials. Each material brings its own set of advantages to the table, catering to the diverse needs of this ever-evolving sector. As researchers continue to push the boundaries of medical science, there’s no doubt that the repertoire of CNC machinable materials will expand, offering even more tailored solutions for life-saving devices.
Challenges and Solutions in Medical CNC Milling
Precision, biocompatibility, and sterilization are just a few concerns milling operations face in this sector. Yet, the industry’s adaptive nature means it continually devises solutions, ensuring that medical devices are not only effective but safe.
Medical prototype created with CNC milling
The agility of CNC milling in the face of challenges stems largely from technological advancements, rigorous quality checks, and consistent research. Innovations in machine capabilities, materials, and software allow for the efficient addressing of issues that arise. This resilient and proactive approach safeguards the critical role of CNC-milled components in healthcare.
Table: Challenges and Solutions in Medical CNC Milling
| Challenge | Solution |
| Maintaining extreme precision and tight tolerances | Advanced CNC machines with enhanced accuracy and real-time monitoring. |
| Ensuring biocompatibility of milled parts | Usage of certified medical-grade materials and post-processing techniques. |
| Sterilization concerns | The development of milling techniques that support easy sterilization post-production. |
| Managing material waste and costs | Incorporating efficient tool paths and optimizing material utilization strategies. |
| Rapid production for urgent medical needs | Automated CNC setups and multi-axis machines for faster production cycle time.. |
| Consistency in mass production | Advanced quality control measures and real-time monitoring of milling processes. |
| Handling complex geometries of medical parts | Integration of high-end CAD/CAM software for intricate design execution. |
| Ensuring traceability and documentation | Comprehensive digital logging systems and automated tracking mechanisms. |
Summing Up
CNC milling for medical devices marks a convergence of technology and healthcare, ensuring that patients receive the best care possible. Through precise machining and adherence to rigorous standards, CNC milling guarantees that medical devices are safe, reliable, and efficient. As we move forward, it’s evident that this synergy between CNC technology and medical science will only deepen, heralding a new era of innovation in healthcare.
Experience the Best with Prolean’s Metal Milling Service for exceptional precision and adherence to medical standards. Our expertise ensures that your CNC milling for medical devices project will be handled accurately, making a difference in patient care.
Read more:
- CNC Milling for Automotive Parts
- CNC Milling for Aerospace
- CNC Milling: Definition, Process, Benefits & Applications
FAQs
What is the significance of CNC milling in medical device manufacturing?
CNC milling ensures high precision and customization essential for medical devices.
Are there specific materials used in CNC milling for medical parts?
Yes, biocompatible metals and plastics are typically used to ensure patient safety.
How does CNC milling guarantee sterility in medical devices?
While milling ensures cleanliness, devices undergo post-milling sterilization.
What are the challenges faced in medical CNC milling?
Miniaturization and working with specific materials are primary challenges.
How do Prolean’s CNC milling services stand out?
Prolean offers state-of-the-art equipment, materials expertise, and medical standards adherence.
Are there regulatory standards for CNC-milled medical devices?
Yes, FDA regulations and ISO 13485 are key benchmarks for quality and safety.
References













Way cool! Some extremely valid points! I appreciate you
writing this post and the rest of the website is very good.
Thanks for your kind words!
I was roaming around internet and found this. So, well described regarding the manufacturing of medical devices. Does The ASTM (American Society for Testing and Materials) standard works world-wide ?
The ASTM standards, while developed in the United States, are indeed used worldwide, especially in industries where international trade is common. Many companies and governments globally adopt ASTM standards for their operations and regulations.
Other widely recognized standards include:
ISO (International Organization for Standardization): A global network of national standards bodies with members from over 160 countries.
EN (European Norm): Standards that are used throughout the European Union.
JIS (Japanese Industrial Standards): Used in Japan and in many international markets for Japanese products.
DIN (Deutsches Institut für Normung): German standards that are highly regarded in engineering and often adopted internationally.
BS (British Standards): Developed by the BSI Group, these are used in the UK and in many places that follow British regulatory models.
These standards ensure that materials, products, processes, and services are fit for their purpose.
Thanks for these wonderful insights! Can you specify which surface finishing techniques is most bio-compatible for titanium parts?
When it comes to titanium parts, especially those used in biomedical applications such as implants and medical devices, biocompatibility is a crucial factor. The most biocompatible surface finishing techniques for titanium include:
Anodizing: This process enhances the natural oxide layer on titanium, improving its corrosion resistance and biocompatibility. Anodized titanium is often used in dental and orthopedic implants due to its excellent tissue compatibility and ability to promote bone osseointegration.
Passivation: In this process, titanium parts are treated to remove surface contaminants and improve corrosion resistance, which is essential for biocompatibility. Passivation forms a protective oxide layer that reduces ion release from the titanium, thereby enhancing its biocompatibility.
Electropolishing: This technique smooths and polishes the titanium surface, reducing the risk of bacterial adhesion and biofilm formation. A smoother surface also minimizes the wear and tear of moving parts, important for implantable devices.
CNC milling can create dental crown? amazing. Doesn’t the size and precision restrict the overall quality.
CNC milling can create aerospace parts with tolerance tight as 0.00125 mm
No CNC milling is capable of handling micro machining with extremely tight tolerances.