Low-volume injection molding permits the economical production of high quality on-demand products. It helps manufacturers precisely meet the minimum order requirements all while in minimum turnaround time.

Conventional techniques like injection molding were laborious and time-consuming. These processes tend to be employed for mass production of parts. Now, in today’s manufacturing industries, the demand for highly efficient and economical parts has been on the rise. Industries turned their focus on more effective, and economical production of parts. Here, volume injection molding steps into the market. This enables plastic part manufacturers to shape low-volume functional prototypes into mass-produced parts with inconsistent quality. Moreover, it advances the prototyping sectors by minimizing delays in quotes, unlike traditional manufacturing.
This article helps you learn about key aspects of low-volume plastic molding, plastics used, types, processes, benefits, limitations, and DFM analysis for your project.
What is Low Volume Injection Molding?
As the name implies, low volume injection molding is a multifaceted technique. It helps to smartly replicate low volume plastic molded parts for end use products. It’s a firm, intensive process that allows OEM manufacturers to supply plastic molded parts to industries like aerospace, automotive, and consumer electronics by meeting exact part specifications, all while in minimum time and time frame.
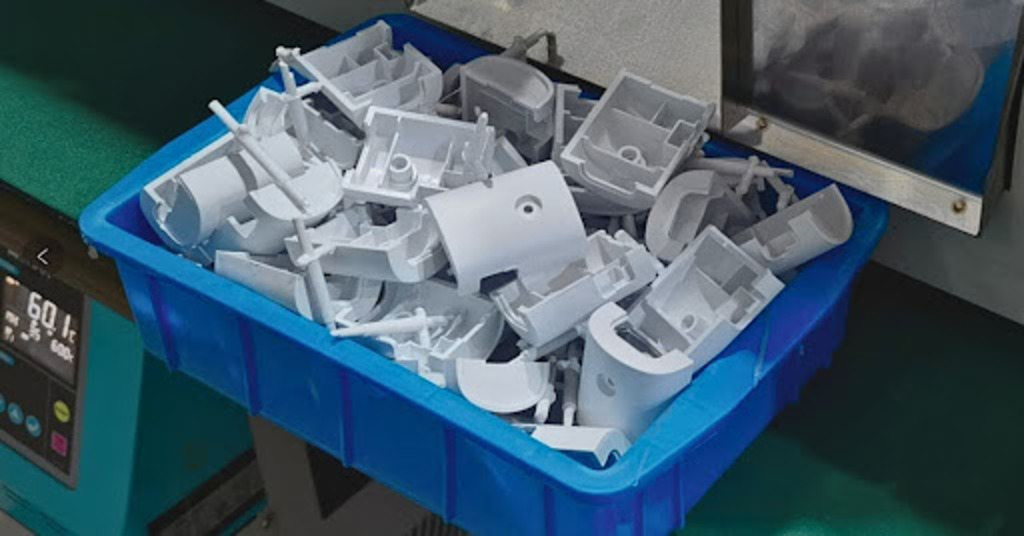

Low-volume injection molding
Usually, steel and aluminum molds are preferably used for fine production of low volume plastic parts. All the molds created by this technique can be machined or fabricated using prototyping allowing 3D printing and various designs.
Try Prolean Now!
Low Volume Vs. Traditional Injection Molding: Comparative Analysis
One simply employs small, while the other is for large volumes. Although both methods are known to be processed through high-pressure injection and used interchangeably. There are few distinctions between them. Let’s discuss these based on factors; including;
Production Volume
Based on production volume, the low-volume injection molding is specifically adapted to help businesses that require intricate exact specifications or limited prototyping. Moreover, it offers more customization possibilities for part manufacturing. These parts quantity range from a few hundred to a few thousand parts while traditional molding is geared towards mass productions that require tons of thousands to millions of parts. Injection molding has minimum possibilities for customization as it tends to employ bulk volumes
Mold Cost & Prototype Design
Usually, steel and aluminum molds are used to accommodate low volume plastic parts production. These molds are relatively simple in design, and provide ease of modification, thus permitting inexpensive, and fastidious production of parts. Among the two, the steel cost is higher than aluminum molds. Generally, these molds are designed through CNC machining and Electric Discharge Machining methods.
Moreover, an initial design to prototype is acquired for testing, and validating the product moldability before committing to volume production. In contrast, the complication of molds in conventional injection molding leads to more time consuming production of parts. Meanwhile, impacts the overall budget of production.
Low Volume Injection Molding Workflow
Let’s discuss low volume plastic molding process in detail;
1. Product Design & Mold Fabrication
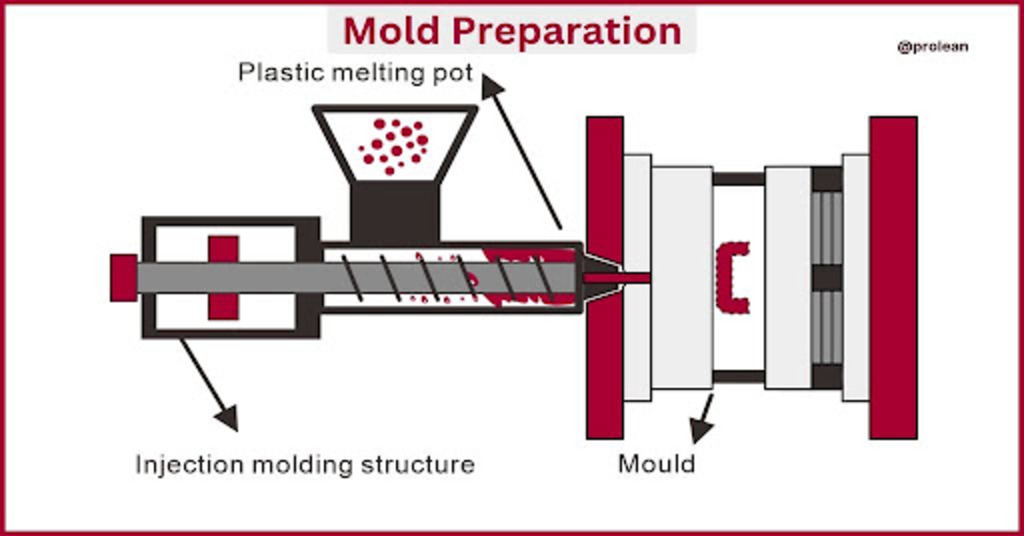
Mold Preparation
The initial step involves the CAD design for your intended parts. Ensure part specification in terms of wall thickness, draft angles, and parting lines to optimize design for low volume injection molding process. After virtual design, the next phase is to fabricate the mold. Unlike traditional molding which requires expensive steel molds, aluminum molds are widely used in low volume plastic molding. Aluminum molds help achieve tolerance down to +/- 0.005 inches. The ultimate material choice depends upon the stiffness, flexibility, thermal resistance, and stability of your mold. Once the 3D mold is printed, washed, and cured it. Now, you are ready to integrate this mold into the injection molding machine for part manufacturing.
2. Material selection
Commonly, thermoplastic resins or fillers are made based on price, chemical resistance, and functional requirements. Common materials include nylon, plastic, ABS, and polycarbonate, which must be considered to ensure the product meets its intended use. Factors such as mechanical strength, and thermal resistance, play a crucial role in material selection.
3. Molding Machine Setup
Engineers adjust the optimal parameters such as temperature, injection pressure, injection speed, and cycle time, based on the material chosen for the mold. It involves the following steps:
- Clamping involves securing the mold in the molding machine’s clamping unit. It ensures that the mold is held securely in its position and prevents premature injection.
- The injection stage involves thermoplastic melting and respectively being injected into the mold at high pressure to ensure the product’s integrity.
- Cooling & solidification allows the material to cool down and then solidify. The time for the cooling phase depends upon the material used.
- Ejection refers to the final phase of product development. It can be done manually or by using ejector pins. The subjective material solidifies and takes the shape of the mold. Then, it’s taken out from the molding machine. This is quite a crucial step, as a minute error could lead to the formation of bubbles, flashing, during ejection.
4. Surface Finishing
After the successful implementation of the aforementioned steps, post-processing is then initiated. Usually, in low volume plastic parts molding, the ejected parts further need trimming, polishing, and anodizing depending upon the end use application.
Design Considerations For Low Volume Injection Molding

Injection mold designing
There are some basic design considerations that one must keep an eye on for better manufacturing, some of them are explained briefly:
- Simple Yet Attractive Part Geometry: Designs parts with plane, and simple geometry and avoids complex features. Choosing a better surface finish than necessary puts a bad impression on the product. The polishing must be done through diamond buff up to 2 Ra or 600 grits stone. Make sure that the chosen finish matches alongwith the part functions.
- Uniform wall thickness: It allows the design to be uniform through all aspects without compromising quality. Thin walls are preferred in low volume injection molding to make the final product look fine and adequate. The thickness of the wall may vary from 0.04 to 0.14 inches.
- Blunt corners: The sharp corners are avoided because they create a lot of stress and affect part integrity.
- Appropriate Draft Angles: The appropriate addition of draft angles in low volume plastic molding must be taken into account. These angles are notably important to give sharp edges to the parts. Therefore, according to the rule of thumb draft angle of 1 to 2 degrees is recommended.
- Gate location: It places gates in areas that minimize aesthetic effects and focus on major things like near corners or parting lines. A multi-cavity mold is more efficient than a single mold tool as it enables the quick testing of the particular product.
Try Prolean Now!
Materials used in Low Volume Injection Molding
A wide range of thermoplastic materials due to their peculiar properties used as Injection Molding Materials. Some commonest types include;
- Acrylic or PMMA: It’s a clear, light, and shatter-resistant plastic widely used in medical goods. It has a high strength and is remarkably resilient.
- Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS): ABS is a solid and flexible material with good impact resistance. It is highly reactive with a high solubility allowing it to be beneficial for industrial and consumer products.
- Polypropylene (PP): It is a chemically resistant plastic. It has a high strength to weight ratio allowing it to have excellent tensile ratios and strength.
- Polycarbonate (PC) has high strength and impact resistance. It requires an extremely high injection pressure of around 70-100 Mpa. It is a versatile thermoplastic with high impact resistance, transparency, and clarity and gives excellent electrical insulation. Learn more about our guide about: Polycarbonate Injection Molding Process Guide.
- Nylon (PA): It is solid and comes with high heat, abrasion, and fatigue resistance.
- Polyethylene (PE): It is generally used for low-volume products along with it, it also has good flexibility and toughness even at low temperatures.
- Polyether Ether Ketone (PEEK): is a highly versatile plastic widely used in injection molding. It shows high temperature resistance along with mechanical strength and stiffness.
Benefits of Low Volume Injection Molding
Low volume molding possesses several benefits when it comes to manufacturing parts in small and effective quality.
- It offers an affordable manufacturing process for plastic parts production.
- Low volume allows for the production of small batches of units of any product ranging from 100-10,000 pieces.
- Low volume injection molded plastic parts require aluminum molds for molding, as it is less hardened and easier to shape than steel. Aluminum can be melted at about 660.3 °C or 1220 °F, helping remove the annealing step from the part manufacturing process.
- As aluminum is used, flexible mold designs are readily available to create any product with remarkable strength, and dimensional stability.
- It takes a shorter lead time for production to build functional prototypes and parts in weeks instead of months.
- Tooling costs are specifically low in low volume molding and are considerably feasible for low costing budget projects.
Limitations of Low Volume Injection Molding
Although it offers several benefits, there are a few limitations of commencing low volume plastic molding;
- Tooling designs are major hindrances for low volume plastic molding parts. Therefore, sometimes, it is limited to a certain number of products only, especially for aluminum mold cases.
- Moreover, aluminum molds offer a shorter product life. It is less durable than hardened steel and, therefore, increases maintenance to poses more expenses to the budget.
- The intricate designs are somewhat difficult to achieve through low volume injection molding.
Methods of Low Volume Injection Molding
Low volume injection molding accommodates various methods for producing high-quality plastic parts. Here are some key industrial processes;
1. Rapid Prototyping with Injection Molding

Prototype injection molded Parts
Low volume injection molding effectively produces parts for rapid prototyping. These components allow designer engineers to design iterations, testing, and validations, offering quick and cost-effective production. It has a lead time of almost 1-3 days. Some common industry use cases are automotive, aerospace, consumer electronics, and medical devices.
2. On Demand Injection Molding
The process allows businesses to set their expenses for producing on demand plastic parts based on the required quantity of part orders. This results in less material wastage and minimizes the extra parts. Additionally, it’s also helpful for businesses experiencing multiple types of products to test from end users.
3. Short run injection molding
It is widely used in small batches of production ranging from 100 to 10,000 plastic units. It helps create limited-edition products and allows marketers to test demand, thus allowing for rapid and valuable feedback from consumers.
Applications of Low Volume Injection Molding
Low volume injection molding is a cost effective process that covers the needs of several manufacturing sectors including;
Automotive Industry
The automotive sector is primarily used to manufacture smaller components of engines and automobiles. Low-volume plastic parts are now considered an advancement to produce high-quality parts with great accuracy in the automotive industry. Learn more about our guide: Automotive Plastic Injection Molding: The Ultimate Guide.
Medical devices
Low volume injection molding allows engineers to manufacture stringent quality parts for medical implantable devices. This technique contributes to the vast production of tools which includes surgical instruments, and diagnostic equipment. Medical devices require delicate features thus this technique suits it best as it facilitates strength, and durability for these part’s requirements. Learn more about our guide on: Medical Injection Molding.
Consumer goods and electronics
It fulfills the demands of the consumer goods and electronic industries, it makes the product with clean finishing along with proper color and texturing. Applications that include housings, buttons, and gadgets require this technique up to a higher extent.
Try Prolean Now!
Injection Molding Services at Prolean
Prolean with a decade of experience provides high quality, and affordable injection molding services from a broad perspective. Our professional staff provides you with technical assistance in DFM in engineering analysis, the right selection of material, and the process intended for your requirements.
We utilize state-of-the-art machinery to turn your parts into the required specifications and shapes, all while having a minimal turnaround and a constrained budget. Whether you need to manufacture small-scale prototypes or mass production, Prolean has the facility to meet these requirements by ensuring stringent quality and value-added finishings.
Trust us to provide reliability and permanence for great customer service. Contact us now to get an instant quote for your project.
Read more:
- Efficient Hot Runner Injection Molding
- CNC Machining Vs. Injection Molding
- Common Injection Molding Defects
Summing Up
Low-volume injection molding has become a beneficial technique for producing parts for functional testing and product development. This technique has sped up product development. Low inventory requirements, minimum cycle time, and stringent quality parts are key features of this technique.
Moreover, it has revolutionized the industrial sectors. Many companies, like Tesla and Apple, may acquire low-volume injection molded parts. Although the process benefits designers in certain aspects, a few limitations are associated with this technique. For example, the manufactured parts may lead to risks of flashing and shrinkage. Therefore, outsourcing your project to reputable vendors can eliminate these potential risks for better product development. Moreover, companionship with reliable partners helps you achieve desired results according to your project demand.
FAQs
Q1. What are some alternatives to low-volume injection molding?
Here are some popular alternatives:
- 3D Printing
- CNC Machining
- Thermoforming
- Urethane Casting
Q2. How much does low volume injection molding cost?
Low volume injection molding for 100 parts, typically costs around $450 after considering equipment, mold design, injecting material costs, and service charges. It costs $4.5 to produce a plastic part.
Q3. How small can injection molding be?
Generally, there is no limitation in size for injection molding. It depends upon the injection molding machine. Specifically for low volume plastic parts, a thinner mold should be used for parts of around 1 mm of thickness due to compactness.
Q4. When to use low volume injection molding?
Low volume injection molding is preferably an economical choice for situations where you need to turn 10, 000 parts with inconsistent quality, and scalability.
Q5. What are the design guidelines for low-volume injection molding?
Keep your design simple. Avoid specifying an overly smooth finish and prioritize functionality. Include draft angles for easy part removal. Maintain consistent, moderate wall thickness to prevent warping. Use rounded corners instead of sharp edges for better safety.
Resources
- Hamid Kalami, Ruth Jill Urbani, (2019), Design and fabrication of a low-volume, high-temperature injection mold leveraging a ‘rapid tooling’ approach: DOI: 10.1007%2Fs00170-019-03799-8, Retrieved From Researchgate
- Ismet P. Ilyas, (2018), Development of a 3D Printed Rapid Plastic Injection Molding for Low Volume Production: Retrieved From: Researchgate

0 Comments