“Although laser cutters can cut several materials, the cutting parameters must be fixed with the specific material type and sheet thickness.”
The laser cutting process can cut, mark, engrave, and etch the materials to custom shape and size. But can it cut all materials? The answer is no. The materials need certain properties to make the laser cuts. However, there are enough Laser Cutting Materials to cover the diverse applications of numerous industries.
Materials like metals, alloys, and plastics & composites are suitable for laser cutting. They can be converted into designed geometry with powerful CNC laser machines. Furthermore, this article will elaborate on the six common materials in detail.
Can Laser Cut Any Materials?
The compatibility of any materials with the laser cutting method depends on the physical and chemical properties. Those materials are hard to cut, which poses a risk to workpieces and equipment safety. If the materials have low reflectivity, thermal conductivity, and chemical stability, they can be processed with laser cutting. Especially if the material is chemically unstable and produces hazardous fumes unsuitable for the laser beam.
The common materials for laser cutting are;
Metals & Alloys
- Steel
- Stainless Steel
- Aluminum
- Titanium
- Copper
- Brass
Plastics
- Acrylic
- PEEK
- Nylon
- Polyethylene, etc.
Try Prolean Now!
Laser Cutting Plastics
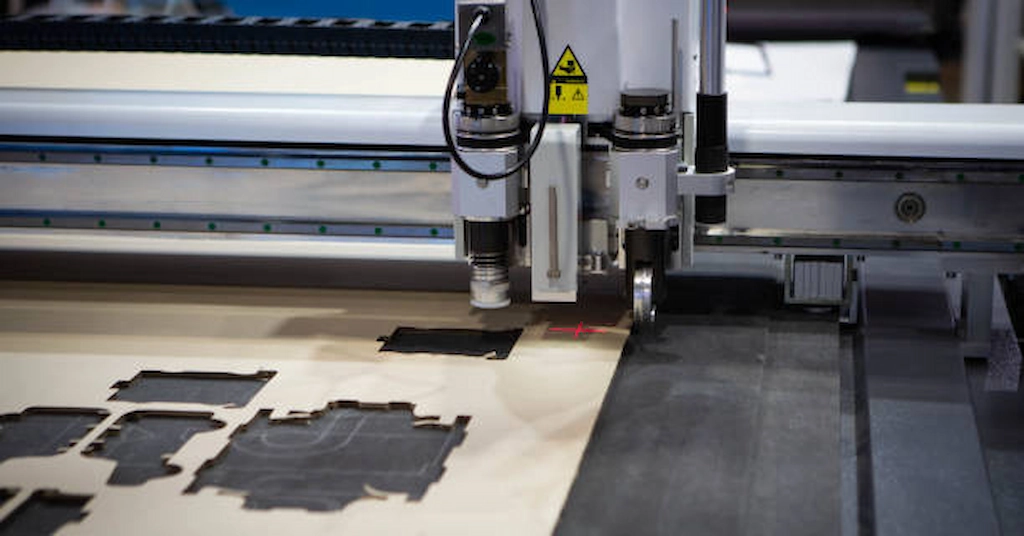
As previously said, not all plastics are laser cutting materials. The plastic needs to have the ability to absorb intense-laser energy without excessive melting or harmful emissions. Although many plastics are available for laser cut projects, Acrylic, PEEK, and Nylon are the most common in plastic laser cutting.
1. Acrylic Laser Cutting
Acrylic laser cutting
This high-strength and low-weight plastic is often considered an alternative to glass because of its excellent tensile strength and stiffness. Laser cutting to shape Acrylic produces clean, smooth, and polished cutting surfaces and edges.
Moreover, the Acrylic is elevated at some height from the work bed during the laser cut process to avoid material backlash. The recommended speed for laser cut acrylic is 20 to 55 mm/s, depending on the thickness of the sheet.
Application Examples of laser cutting acrylic are;
- Light fixtures & diffusers
- Indoor and outdoor signage
- Machine guards
- Frames for artistic pieces
- Furniture elements
- Prototypes for testing.
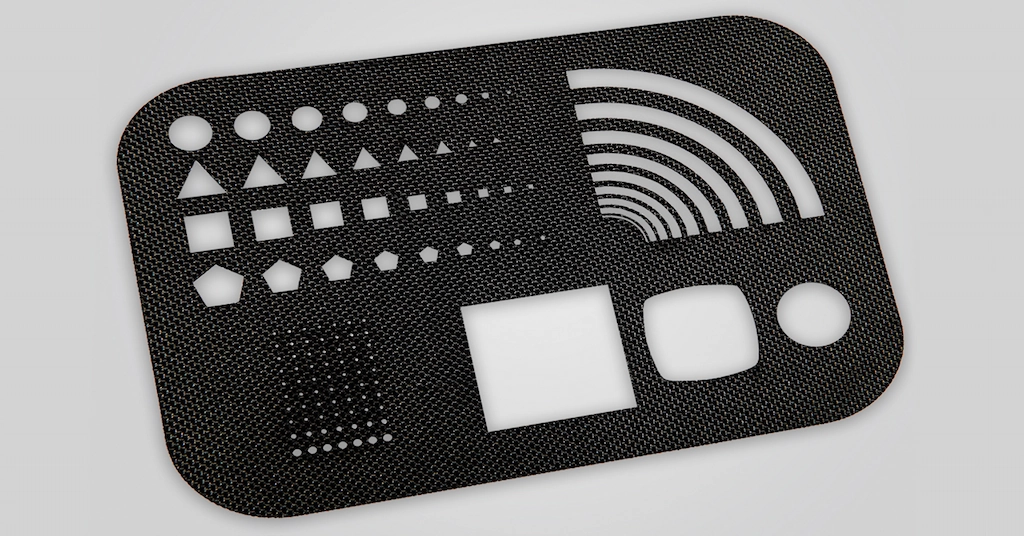
2. PEEK Laser Cutting
PEEK laser cut part
Polyether ether ketones (PEEK) are popular laser cutting materials among plastics. They are semicrystalline plastics with excellent mechanical strength, heat resistance, and dimensional stability. Their thermal resistance produces minimal heat around the lasering surface. Still, improper parameters and wrong combinations of laser power and thickness can cause excessive burns.
Consequently, Laser Cutting PEEK is fast and precise. It can operate with a speed of 50 to 60 mm/s, 1m in a minute approximately, and even higher.
Application Examples of PEEK laser cutting are;
- Aerospace engine components
- Electrical connectors
- Medical implants
- Seals & gaskets
- Electrical insulators at high temperature
- Pump & valve components.
3. Nylon Laser Cutting
Nylon laser cut parts
It is a synthetic homopolymer with a silky surface. The Laser Cutting Of Nylon converts properties like strength, resilience, abrasion resistance, and chemical inertness into functional components by giving them the designed shape or geometry. Although nylon cutting might leave rough cutting surfaces, it is as precise as other plastic laser cutting processes. Consequently, the speed for Nylon laser cutting is 15 to 25 mm/s
Here are some examples of Nylon laser-cut parts;
- Automotive interior parts
- Robotic components
- Cases for consumer electronics
- Drone’s structural components
- Industrial machine components
- Custom washers and spacers
- Mounts for cameras and sensors
Laser Cutting Sheet Metals
Almost every metal and alloy is compatible with laser cut sheet metal, except those that produce fumes during cutting. The most common are steel, aluminum, copper, and titanium. In fact, metals are relatively easy laser cutting materials. Additionally, both CO2 and fiber lasers can handle metal workpieces.
Now let’s discuss three major metals used in the Laser Cutting Sheet Metal project;
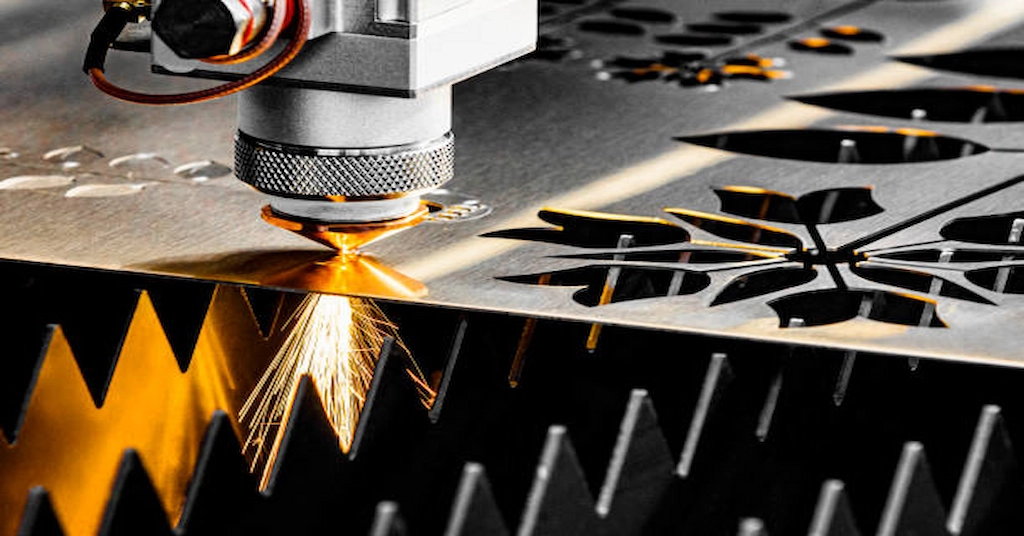
4. Steel Laser Cutting
Steel laser cutting
A laser machine can cut steel to 10 mm or thicker sheets. The precise and smooth cuts of Steel Laser Cutting are beneficial in automotive, shipbuilding, and other industrial applications. Moreover, the laser preserves steel properties, such as strength and flexibility.
One main challenge in laser cutting steel is the reflectivity of certain types of steel. Additionally, high carbon content can be hardened near the laster striking position.
- Automotive body parts
- Shipbuilding steel panels
- HVAC components
- Machining tools and dies
- Signage and lettering
- Intricate decoratives
5. Aluminum Laser Cutting
Aluminum laser cut parts
Another popular laser cutting material is aluminum, a low-weight, high-strength metal with excellent corrosion resistance and moderate ductility. The softness of aluminum allows laser machines to cut quickly ( 20 to 35 mm/s). Nevertheless, it can leave a minor volume of burrs on the cutting surface. Concerning the reflectivity of aluminum surfaces, CO2 laser cutting is relatively more suitable.
Here are some applications of aluminum laser cutting;
- Aerospace parts
- Satellite components
- Bike frames
- Automotive panels
- Electronics housings
- Lighting fixtures
- Marine hardware parts
- Solar panel frames
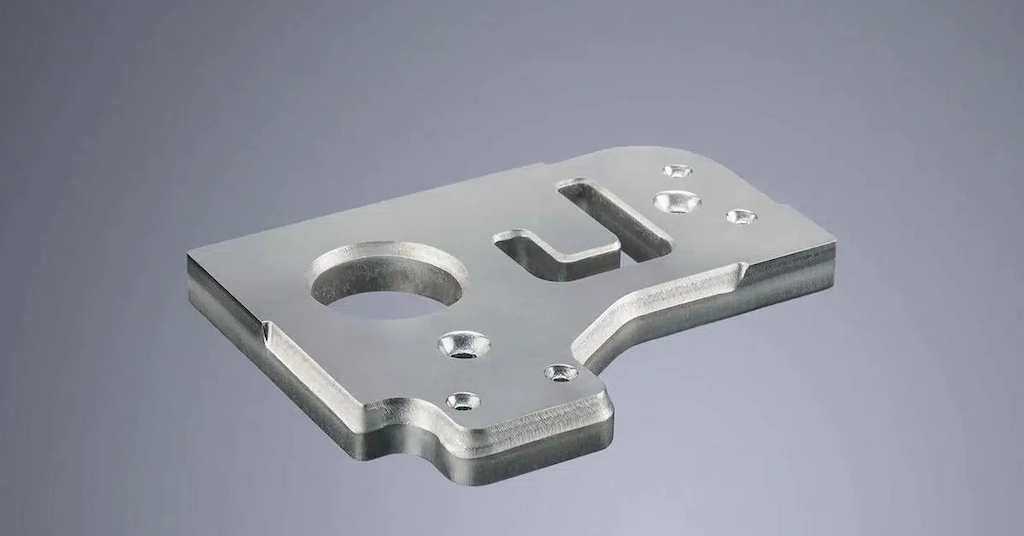
6. Titanium Laser Cutting
Laser cut titanium parts
Titanium is a hard and robust metal commonly used in high-performing applications. Its hardness also affects the laser cut process and limits the maximum cutting thickness. However, high-power lasers with assist gas can efficiently cut complex features with tight tolerances out of titanium sheets. Additionally, titanium laser cutting produces fewer heat-affected zones than other laser cut sheet metal types. The typical laser cutting speed for titanium is 5 to 20 mm/s.
Application examples of laser cutting titanium are;
- Aircraft engine and airframe components
- High-performance automotive parts
- Medical implants like hip and knee replacements
- Chemical process equipment
- Military armor and components
- Protective casings for high-pressure applications
How to Choose the Right Laser Cutting Material?
Choosing the right laser cutting materials for your project ultimately defines the final properties of the intended laser cutting application or project. It Involves Considering the laser power of available equipment, the thickness of worksheets, design complexity, and many other aspects to select the best possible material.
The following are some considerations to assist your laser cutting material selection confusion;
- Evaluate Material Properties: First, examine properties like melting point, reflectivity, thickness, and thermal conductivity to determine whether a particular material can absorb laser energy without damaging the laser system.
- Check Finish Quality: Can the material produce the cut edges and the extent of the heat-affected zone (HAZ) as per your requirements?
- Match Material with Laser Type: Align the material properties with the appropriate laser type. Use CO2 lasers for non-metal materials and fiber lasers for reflective metals.
- Consider Application Needs: Consider the end-use of the laser-cut parts, including necessary strength, durability, etc.
- Cost Factor: Evaluate the cutting speed and ease, as materials that can be cut faster may reduce overall laser cutting costs.
- Test Cutting: You can perform test runs with a few chosen candidate materials and finalize the choice according to the cutting results & your requirements.
If you are still unable to make a decision, our engineers can help you find the best match and cut the material into your designed parts or products. At ProleanTech, we provide consultation with comprehensive CNC Laser Cutting Services. Our factory has advanced CNC laser cutters to handle various metals, plastics, and composites with high precision, regardless of design complexity. Additionally, we can combine other fabrication methods like bending, punching, and welding.
Read More: Common Defects in the Laser Cutting Process
Try Prolean Now!
Conclusion
Cutting and shaping material with CNC laser cutters brings several advantages in the production of diverse industrial components and products, from automotive and electronics to defense. However, the properties of different laser cutting materials possess their respective challenges. Therefore, using the appropriate laser power based on the workpiece properties and thickness is essential to achieve precise and clean cuts.
Moreover, you need to select the appropriate material according to your application needs. It could be aluminum, steel, nylon, or any other material.
FAQs
What materials cannot be cut with CNC lasers?
Highly reflective materials, like copper, can pose difficulties for CNC lasers. Materials that emit hazardous gases when cut, such as PVC, are typically avoided to prevent damage to the laser machinery.
What materials can CO2 and fiber lasers cut?
CO2 lasers are ideal for cutting non-metal materials such as wood, acrylic, glass, paper, and some plastics. On the other hand, fiber lasers are better suited for cutting metals, including stainless steel, aluminum, and brass.
What is the lowest tolerance of the laser cutting process?
The lowest tolerance achievable in laser cutting is typically around ±0.1 mm. However, it can vary slightly based on the laser power and material type.
How durable are sheet metal laser cut parts?
They are highly durable because laser cuts without physical contact produce consistent cuts and minimize deformation.










0 Comments