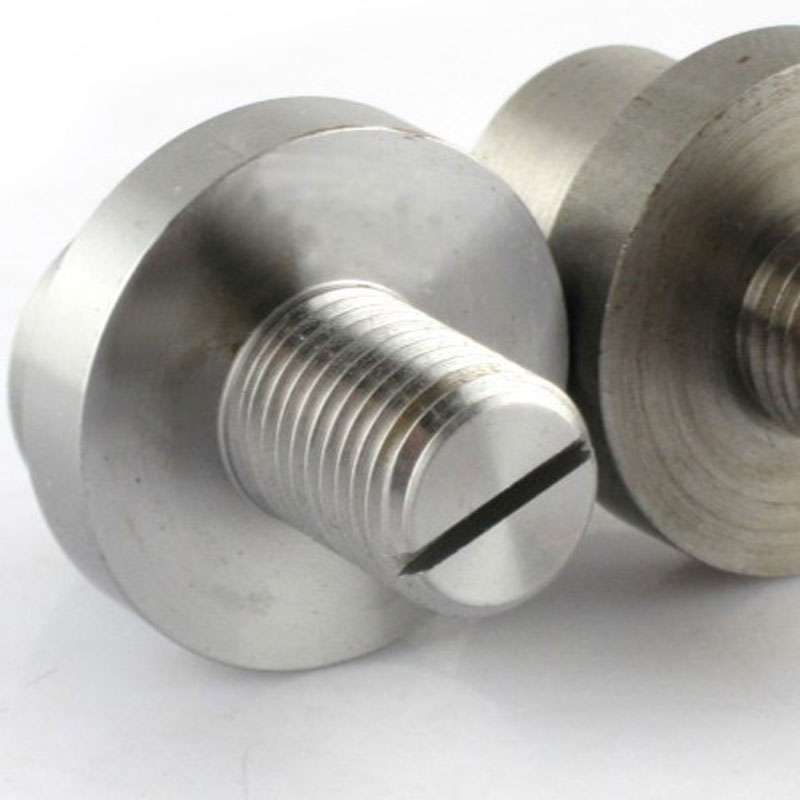
CAPABILITIES
Custom CNC Machining Service
Get precise and complex machined parts from ProleanTech. Our Custom CNC Machining Service offers quick prototypes to full-scale production tailored to your needs.
We have the capability of CNC Milling, Turning, Drilling, and many other processes.
- Tolerances down to ±0.0002″ (0.005mm)
- Parts as Fast as one day
- 50+ Material Options
ISO 9001:2015, ISO 13485, IATF 16949:2016 Certified






All uploads are secure and confidential.

CNC Milling
Our CNC milling services have 3, 4, and 5-axis milling machines. They can cut the workpiece along multiple axes.

CNC Turning
With our latest CNC lathes and turning centers, even the most complex turned parts are possible

Turning-Milling
Allow multiple operations on a single machine, perfect for high precision parts with complex geometries

Electrical Discharge
Highly accurate machining service of cutting metal to precise shapes using electricity

Wire Cut
Our wire cut services can provide high precision tolerances, as tight as ±0.0002″ for an array of industries and applications.
Prolean’s CNC Machining Capabilities
Why Choose Our CNC Machining Service
Are you looking for precise metal and plastic parts for your project? Here is why you should choose CNC machining services.
- Reliable Production
Reliable Production: CNC machining’s automatic control and minimal human intervention in operations make it a highly reliable manufacturing method. Additionally, there is significantly lower downtime with CNC.
- Volume Flexibility
It is adaptable for all volumes, from small batches to large-scale manufacturing without compromising the quality. So, businesses get scalability options at a low cost.
- Automation and Speed
High levels of CNC automation lead to faster production cycles. Meanwhile, automated tool changes and programmed instructions allow rapid production of complex parts.
- Complex Features and Profiles
The diverse tooling options and multi-axes capability of CNC machines can craft intricate geometries and profiles like undercuts, threads, pockets, curves, patterned holes, grooves, and irregular profiles.
- Cost-effective
Cost-effective: Once tooling is set, you can run multiple cycles for identical items. This makes it cost-effective for medium to large volumes, whereas the rapid tooling approach reduces the cost of prototyping and small volumes.
Try Prolean Now!
How to Order Parts?
Get a free quote from a real engineer; once we receive your design, our engineer will review it and send you a quote as fast as one hour.
Get A Quote Immediately
Upload your design or email our engineer directly and get your quotes as fast as one hour.
Start Production
Your parts will be made once your orders are confirmed. Besides, you will get real-time order updates of the production status from our order tracking system.
Receive Your Part
After all parts pass QC inspection, they will be well packed from transportation accidents. Then, your custom parts are delivered straight to your doorstep.
The Principle of CNC Machining
The main principle behind CNC machining is that computer-controlled machining tools bring the highest precision and repeatability. It starts with creating and converting a CAD drawing into CNC machine-readable instructions (G-code). Then. CNC machine controls their movements and operations with these digital instructions.
The CNC machine operates on multiple axes, from 3-axis (X, Y, and Z) to more advanced 5-axis machines. They can perform a variety of operations, including milling, drilling, turning, and grinding, depending on the machine’s capabilities.

CAD Modeling
The CNC machining service with the creation of a detailed 3D model, including all geometrical features, dimensions, tolerance, annotations, labels, etc. The designer often uses tools like AutoCAD and SolidWorks. You can also directly send the design to the manufacturer if you need custom machining.

G-code Instructions
G-codes are digital instructions about feed, tool movement, coordinate position, cutting depth, and speed. They are created with CAM or other similar software. Additionally, M-codes are needed for auxiliary function control. Then, these codes are uploaded to the CNC machine’s controller, ready for execution.

Machine Setup
In machine setup, the workpiece is securely clamped or mounted onto the machining bed or in a fixture. Meanwhile, a suitable tool is set on the spindle. Here, the setup can differ on the machining method, like CNC turning, milling, and turn-milling. The tool selection depends on the equipment type and desired geometrical features. For example, end mills are ideal for complex profiles, whereas you need to use boring tools for enlarging the holes. Basically, every tool has its own capabilities.

Machining Process
On tool and workpiece and tools are set, then, the coordinates are fixed and the CNC controller executes the codes. It might process cutting, facing, drilling, and other operations to form the final shape. Moreover, it requires continuous monitoring and adjustment of variables if required.

Post Processing
CNC machining services often include post-processing and surface treatments. This step is crucial for achieving the tight dimensions and the desired set of surface properties, including aesthetics.
Try Prolean Now!
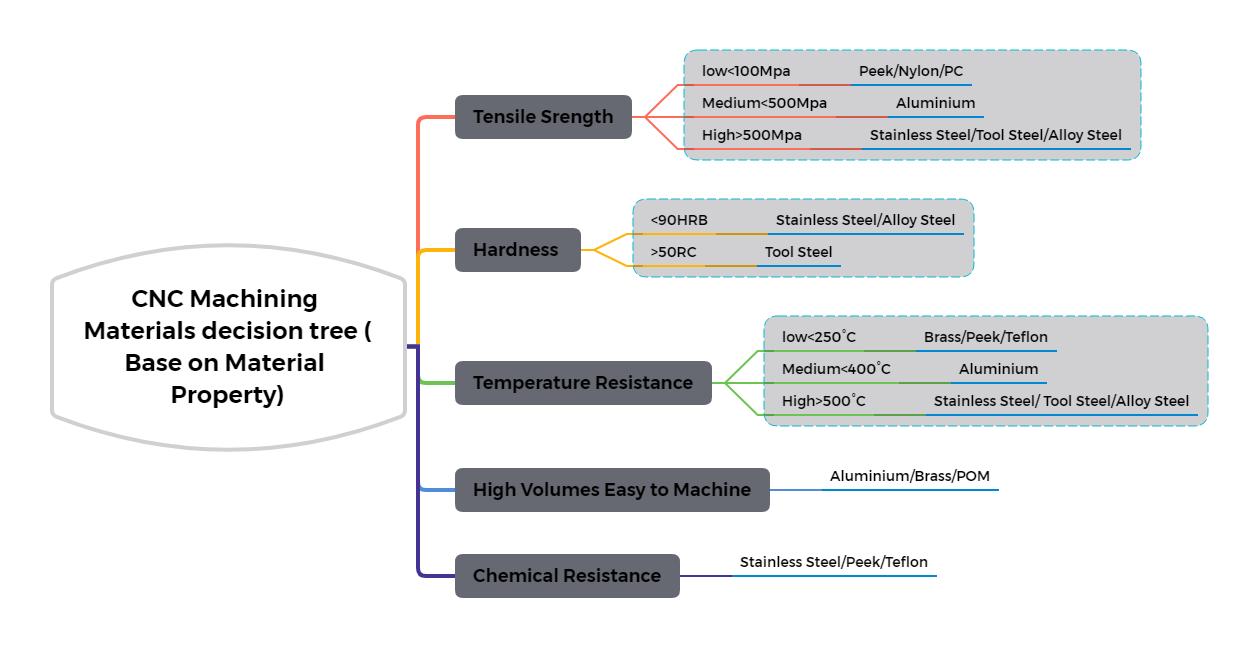
CNC Machining Materials Options
The properties of final parts or products depend on the material type. Therefore, CNC machining material selection is critical for any project. Make your choice based on requirements, metals, plastics, or composites.
You have a lot of options for CNC metals such as aluminum, stainless steel, brass, titanium, etc. Consequently, each of these metals has different alloy grades with unique composition and properties. Meanwhile, You can machine CNC plastics like ABS, Acrylic, PEEK, PC, etc.
Metal CNC Machining

Aluminum Alloys
Aluminum alloys are known for being lightweight, having corrosion resistance, excellent thermal conductivity, and strengths (vary on alloying elements). They are highly machinable and offer high production speed.
- Grades: 2007, 2017A, 5083, 6060, 6061, 6082, 7075, etc.
- Applications: Aerospace components, automotive parts, sheet metal products, structural parts.
Stainless Steel Grades
Stainless steel is one of the most common metals used in CNC machining. Steel alloys provide corrosion resistance, high mechanical strength, ductility, and excellent machinability.
- Grades: 303, 304, 316L, 316Ti, 304L, etc.
- Applications: High-strength and durable parts for automotive, food processing, medical equipment, etc.
Brass Grades
Brass is a copper alloy that offers good conductivity, formability, strength, and corrosion resistance. Brass grades are also easy to machine and the machined parts can be solder and braze. easily.
- Grades: Ms58 / CuZn39Pb3
- Applications: Electrical and thermal components, decorative items, etc.
Steel grades provide high tensile strength, good plasticity, and varying hardness & ductility. The machinability also varies on particular alloy grades. Steel CNC machining produces durable, wear-resistant, high-strength, and heat-treatable parts.
- Grades: S235JR, C45, C40, S355J2G3, 90MnCrV8, 16MnCr5, 25CrMo4, 42CrMo4, etc.
- Applications: Automotive parts, machinery components, structural applications, tool and die manufacturing.

- Grades: Grade 2 / Grade 5 (Ti-6Al-4V)
- Applications: Aircraft structural parts, medical implants, oils and gas structures, and high-stress components.
Plastic CNC Machining

ABS CNC Machining
ABS is popular in CNC machining due to its high tensile strength and toughness. It can create parts with excellent impact-resistant, wear-resistant, flame retardantdency, and also leaves good as a machined finish. It is often used as a metal replacement in automotive and marine applications.
CNC Acrylic Parts
Acrylic or PMMA is a transparent and tough thermoplastic with excellent surface hardness, weather resistance, wear and abrasion resistance, and chemical inertness. The machining of acrylic surfaces can weaken the transparency, but further surface polishing can achieve that. Acrylic is ideal for applications requiring optical transparency or as a cost-effective alternative to polycarbonate.
CNC Machining PC (Polycarbonate) Part
Polycarbonate is also a transparent plastic but is more durable and shatterproof than acrylic. It is also UV-stabilized and flame-retardant. While machining, the PC is prone to stress cracking and requires slow feed rates and sharp tools. Polycarbonate machining is widespread in food and beverage, packaging, medical devices, eyewear, electronics, etc.
Machined PEEK Parts
It is high-performance CNC plastic with excellent mechanical strength, fatigue resistance, chemical resistance, and thermal stability. But it can be more expensive than other plastic materials. Some application examples include tubes, bearings, seals, valves, and medical implants.
Polypropylene (PP) Parts
Polypropylene is a CNC plastic material used in applications requiring high elongation and low flexural modulus. It has a transparent black-and-white appearance. Machining PP is mainly used for prototypes and large-size products like storage items.
Try Prolean Now!
CNC Machining Material Guide
CNC Machining Service Finishing Options

As the machined or deburring
The machined or deburring finish is the standard finish where unwanted attach chips are removed with deburring tools, and sharp edges are chamfered to smooth the surface (3.2 μm).
Bead Blasted
Bead blasting produces a matte texture, removing all the marks of machining tools. It applies to ABS, Aluminum, Brass, Stainless Steel, and Steel parts.

Anodizing
Anodizing involves adding an aluminum oxide coating to aluminum and its alloys. The layers, which come in various colors, increase strength and shield the surface from corrosion.

Powder coating
Powder coating is the electrostatically applying of dry powder to the surface. It produces a thin layer providing excellent resistance to wear, corrosion, and abrasion.

Polishing
Physical rubbing of a metal surface to create a shiny surface is called a polishing surface finish. It increases the reflectivity and does not affect the dimensional stability of parts.
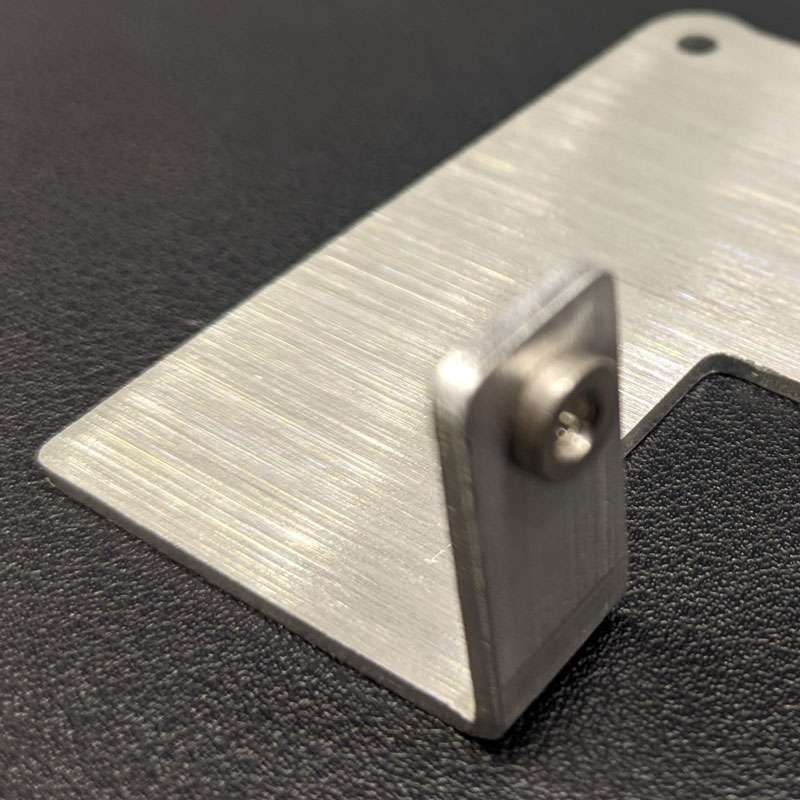

Brushing
Brushing is achieved by applying an abrasive brush to the metal surface, which produces a unidirectional satin finish. And it is not recommended for highly corrosive materials.
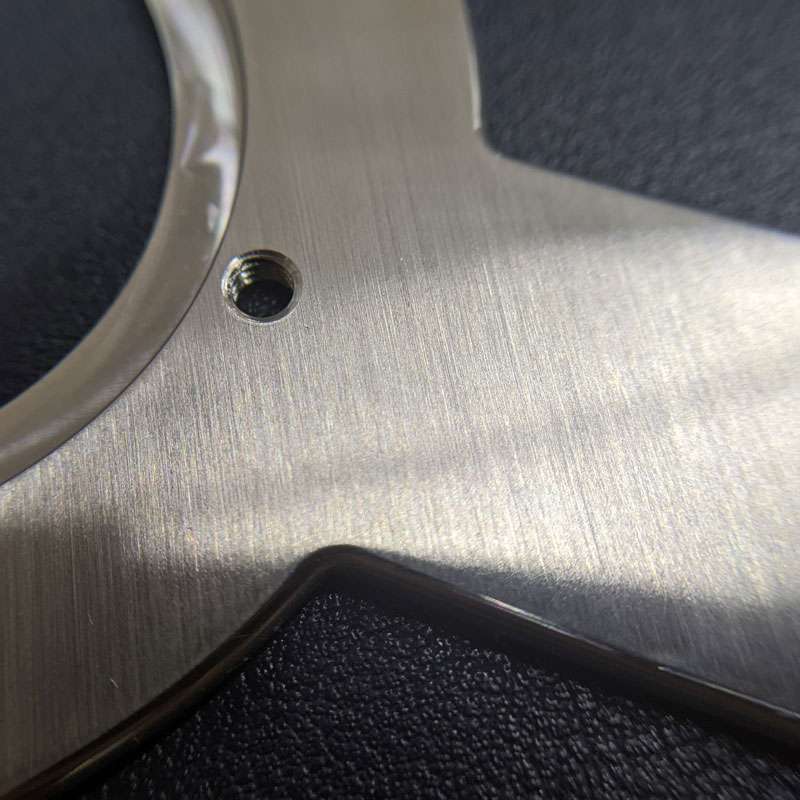

Smooth machining
Smooth machining is done by controlling the machining process, such as feed rate & cutting speed. It minimizes the tool marks and risk of corrosion.
Black-Oxide
Black oxide finish reduces surface reflectivity and offers mild corrosion protection. It involves adding a thin layer of magnetite to the surface.

Electro-less Nickel Plating
A thin layer of Nickel is created on the surface from a nickel-containing solution without electrolysis. Electro-less nickel plating provides a shiny appearance, excellent hardness, abrasive, wear, and corrosion-resistance to the substrate material.

Alodine
Provides excellent corrosion resistance property to the aluminum parts with greenish-gold color. It is the low-cost and quick surface finishing approach.

Electroplating
Electroplating increases the hardness of the steel &aluminum parts. It offers excellent corrosion, wears, and abrasion resistance.

Nickel plating
Make the parts super resistive to corrosion. It enhances mechanical strength, hardness, wear resistance, lubricity, and ductility. Nickel plating is applicable in different materials, including Steel, aluminum, copper, and brass.
Passivation
Enhance the appearance and functionality of the parts. After Passivation, parts of Steel and its alloys become super resistive from corrosion.
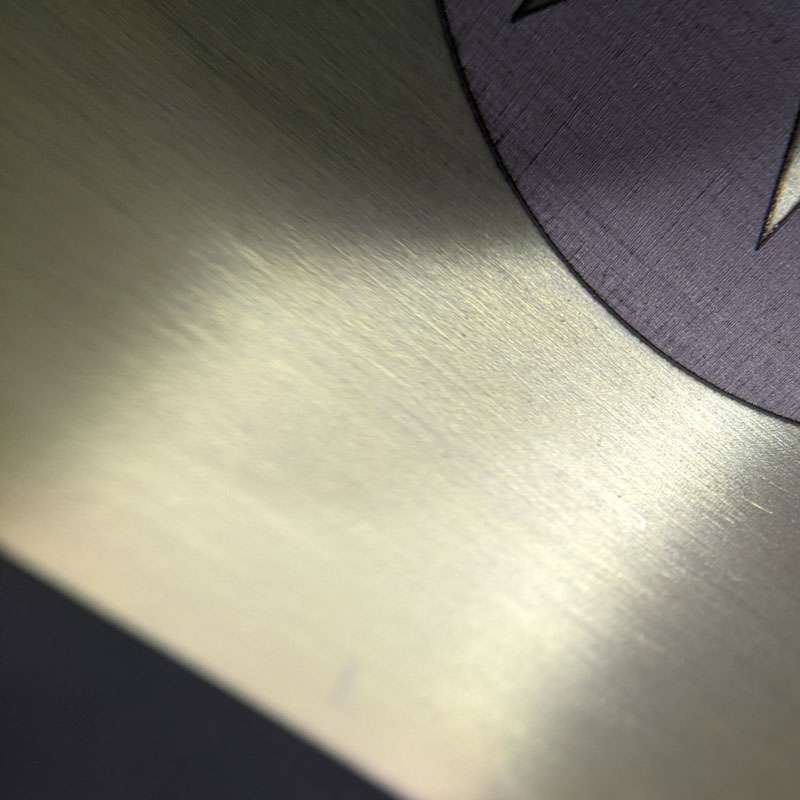

Yellow Chromate conversion coating
A shiny appearance with goldish color provides excellent corrosion resistance. It is applied on the surface of aluminum, magnesium, and their alloys. A layer of chromate also enhances the conductivity of parts

PTFE (Teflon) Coating
The Teflon layer on the parts offers excellent corrosion resistance, water resistance, and non-stickiness with a non-reactive surface.

Fine machining
The higher-precision machines produce delicate machining surfaces by utilizing sharper tools and regulating feed rate and cutting speed. Surface roughness up to Ra 0.8 μm can be maintained with smooth machining.

Laser Cladding
Provides excellent corrosion, wear, and abrasion resistance. Laser Cladding is also effective for treating minor surface imperfections such as cavities, tiny cracks, and rust damage.
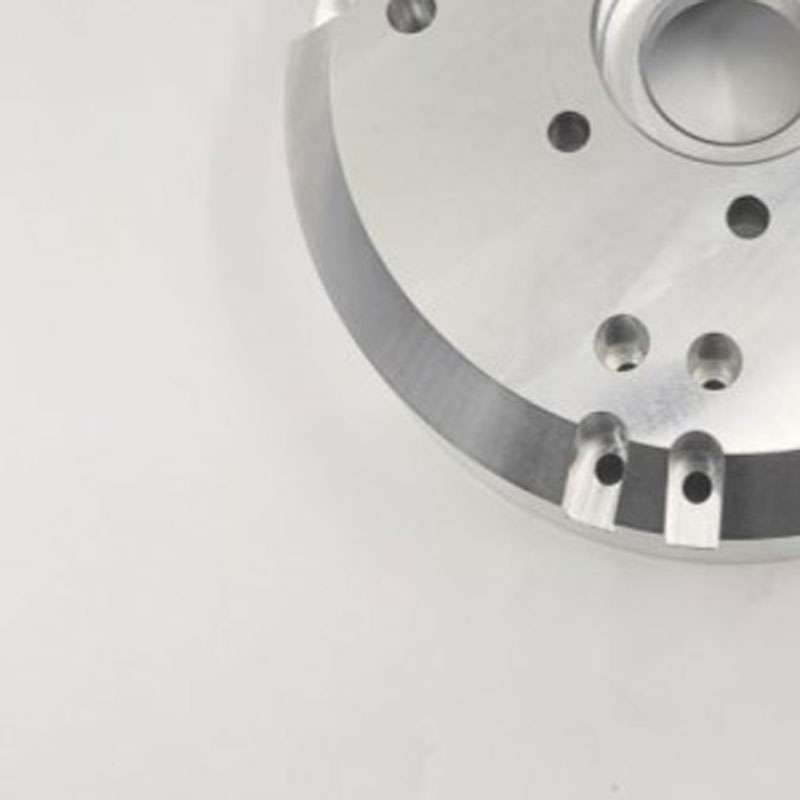

Sanding
Provides a random, non-linear texture with a shiny, high gloss finish. However, it might be unable to create sharp corners and pockets
More Finishing Options
Please click this block for more fishing options
Precision Machining Tolerances
CNC Machining Service
Type | Tolerance | No Drawing |
| Linear dimension | +/- 0.025 mm +/- 0.001 inch | ISO 2768 Medium |
| Hole diameters (not reamed) | +/- 0.025 mm +/- 0.001 inch | ISO 2768 Medium |
| Shaft diameters | +/- 0.025 mm +/- 0.001 inch | ISO 2768 Medium |
| Part size limit | 2000 mm x 1500 mm x 300 mm | ISO 2768 Medium |
3 Ways to Ensure Perfection
Standards
Metals: ISO-2768 fH (fine)
Plastics: ISO-2768 mK (medium)
Metric threads tolerances: ISO 965-1 standard UN Threads Tolerances: ASME B1.1-2003 standard
Knurling: ISO13444:2012 standard.
Our factory is ISO 9001:2015 certificated
Inspection and Protection
Constant visual inspection conditions
Quantification of cosmetic surface quality
Process requirements
Part cleaning and Protection
Quality Inspection Report
Inspection Confirmation
Dimensional confirmation
Appearance confirmation
Quality documentation
Comparison with Other Manufacture Processes

CNC Machining Vs Conventional Machining
Unlike CNC, conventional machining involves controlling cutting tools manually with levers and handles. It is not accurate as CNC machining as it can not maintain precise cutting speed, feed rate, and cutting depth. Conventional machining is easy to adjust and cost-effective for simple parts.

CNC Machining Vs 3D Printing
3D printing is additive manufacturing that builds by adding successive material layers based on the provided CAD design. It is fast and simple in terms of tool setup and process handling, but the parts compromise the structural strength. 3D printing is ideal for the initial stages of testing prototypes.
| Feature | CNC Machining | Conventional Machining |
| Precision & Complexity | Complex geometries with high precision, (±0.127 mm) | Precision and complexity are limited by operator skill |
| Automation | High automation; It can change tools and settings automatically | It requires manual adjustments and tool changes |
| Repeatability | Highly repeatable; identical parts across batches | Variability in quality based on operator proficiency |
| Material Type | A wide range, including hard and brittle materials | Limited to softer materials |
| Flexibility | Programmable; efficient design changes and modifications | Adaptable for small production runs or prototypes |
| Setup Time | Initial setup and programming are time-consuming | Simple and fast setup |
| Production Volume | Prototyping to large-scale runs | Better for low-volume production |
| Feature | CNC Machining | 3D Printing |
| Precision & Complexity | Complex geometries with high precision, (±0.127 mm) | Moderate, ideal for complex designs |
| Automation | High automation; It can change tools and settings automatically | Fully automated, minimal intervention |
| Repeatability | Highly repeatable; identical parts across batches | Repeatable, great for prototyping |
| Material Type | A wide range, including hard and brittle materials | Limited to specific materials |
| Flexibility | Programmable; efficient design changes and modifications | Highly flexible, easy design switching |
| Setup Time | Initial setup and programming are time-consuming | Minimal, mainly digital preparation |
| Production Volume | Prototyping to large-scale runs | Ideal for prototyping, small-scale runs |
Technology Overview
What is CNC machining?
CNC refers to Computer Numerical control. CNC machines are electro-mechanical devices that can manipulate tools around varying axes with high precision as per instructions from the computer. As a result, the CNC machine can create complex geometrical parts with high precision in less time. In addition, because all machining controls, such as feed rate, tool positioning, and speed, are automated, tight machining tolerance is achievable compared to labor-intensive machining approaches.
Principle of CNC machining
The operation working principle of a CNC machine consists of four primary steps:
• Uploading a CAD file
• Digital instructions
• Adjusting the workpiece position
• Running the machine with programming
The CAD file of the parts to be machined is first uploaded, and instructions are sent via digital command before the tool begins to form the shape with the attached workpiece.
Workpieces can be machined in multiple axes depending on machine capacity (3-axis, 4-axis, 5-axis, & 6-axis). An electric motor controls each axis’ movement.
The cutting tool moves following the digital command, and operations such as tool speed, feed, depth of cut, and others are controlled by coding (CNC programming). A warning system also alerts the operator to any operational errors or safety precautions throughout the machining process.
Different types of CNC Machining
Numerous (10+) types of CNC machines are designed for specific machining operations. For example, CNC milling creates complex geometries that allow up to six-axis machining. Milling rotates the workpiece and removes the tool following the uploaded drawing and command. CNC routers are functionally similar to CNC milling machines. Still, they are used for softer materials such as aluminum, wood, and plastics—the CNC routing machine routes the spindle and tool path.
CNC Turning is primarily used for cylindrical workpieces, and it renovates the material from the outer surface of the rotating workpiece for facing, chamfering, and other operations. Its caliber is generally measured by rotating speed. CNC plasma cutters use electronically ionized gas (plasma) to cut the workpiece precisely. The plasma beam strikes the metal and cuts it, even though the plasma temperature can reach 10,000 degrees Celsius.
The process of CNC machining
CNC machining is a type of manufacturing in which computer software dictates the movement of tools and machinery. CNC machining can control various complex machinery, including grinders, lathes, mills, and routers. Three or more dimensional cutting tasks can be completed using a single set of prompts with CNC machining.
Under CNC Machining, Machine tools function through numerical control. A computer program is customized for a workpiece. The machines are programmed with a CNC machining language called G-code that essentially controls all features like feed rate, coordinate, location, and speeds. In addition, the computer controls the exact positioning and velocity of the operation.
See why customers dig us
We were working on some stainless steel turning projects and contacted Polean to outsource a couple of parts. We sent our design and they made the parts. Those were exactly to needed specifications. Our factory will come back for other projects.
-Paul Campbell, TechFab Innovations
The ordered milling gears were as per our drawing. The surface treatment also looks nice. Once we get feedback from our vendors, I will contact you for subsequent batches. We might need to modify the teeth size and other parameters.
-Jennifer Baker, Senior R&D Engineer
ProleanTech's Mill Turn services have consistently delivered exceptional results for our custom heat sinks. We appreciate their professionalism and commitment to timely delivery.
-Jason Adams, Director of Operations at CastMaster Technologies
Their services of machining justify the name “ProLean” . Engineers and operators are pro at technology and seems like they have mastered the lean manufacturing principles.
-Hannah Murphy, Head of Tooling Engineering at PrecisionMold Works
Thank you. The engineers really go the extra step to set up the custom tooling for our Mechanical coupling components. We will also order some other CNC-turned parts for our new project.
-Richard Green, MachiningPro Labs
Proleantech CNC turning services exceeded my expectations. They send me to inspect my small steel parts before the full-scale run. The precision and exact specifications of the final pieces were flawless. I'll recommend and return.
-Victoria Harris, Product Development Engineer
FAQs
Technical FAQ’s
What kind of CNC Machine Does ProleanTech Have?
We have various equipment and machines at our CNC factory, including 3 to 5-axis CNC mills, CNC lathes, CNC turning centers, laser cutters, and CNC grinders. Diverse tooling options are also available on these machines.
What are the Standard CNC Machining Tolerances Available from Prolean?
Our CNC machines can limit tolerance to ±0.0002 “ (0.005 mm). However, if you have a critical product, we can further tighten the tolerances.
What is the Maximum Achievable Part Size at Your Factory?
Our maximum CNC machining build is 2000 mm x 1500 mm x 300 mm, which is large enough for furniture and architectural components. Overall, we are happy to serve the prototyping and production of large machined parts made of plastic or metal.
How do You Control the Quality of CNC Machined Parts?
We have an In-house quality control facility with advanced equipment like digital gauges, CMM machines, calipers, micrometers, X-ray analyzers, and hardness testers. We can also provide you with a first-article inspection report for your parts.
General FAQ’s
What is the Difference between CNC milling and lathe machining?
CNC milling involves rotating cutting tools and stationery workpieces, whereas lathe machining or turning involves rotating workpieces. Milling is preferred for flat and complex profiles and turning excels in cylindrical parts manufacturing
Why Choose CNC over Conventional Machining?
Choosing CNC machining over conventional machining has many advantages. You can achieve a high degree of accuracy, complex geometries can be created, and it significantly reduces production time.
What are the industries where CNC machining is applicable?
Automotive, aerospace, medical, energy, Defense, transportation, ship, and many more industries use parts created from CNC machining.
What are the common types of CNC machining Operations?
The common types of CNC machining operations are milling, turning, turn-milling, drilling, tapping, threading, boring, laser cutting, plasma cutting, etc.
Related Blog
A Guide On Machining Polyurethane and Essential Considerations
Machining polyurethane for durable custom plastic parts
Alumina Ceramic Machining: A Detailed Explanation
Alumina ceramic machining challenges and solutions explained
Six Chemical Resistant Plastics for CNC Machining
Common chemical resistant plastics used in CNC machining
Get Your Parts Made Today
All uploads are secure and confidential.


















