
Laser cutting demonstration
Laser cutting materials are all materials to laser cut that can be cut using focused laser beams. The process involves burning, melting, and vaporizing thin sections of the material. The most common laser cuttable materials for laser cutting are wood, but it goes beyond, including organic materials to laser cut like leather, textiles, and can produce precision cuts on materials like steel, aluminum, and composites.
Prolean Tech has advanced laser cutting technology that can produce clean, burr-free cuts and edges for sheet metal parts. We have a host of fiber, CO2, and plasma machines that can support high-volume laser-cut part production.
What Are Laser Cutting Materials?
The term laser cutting materials describes laser cuttable materials that lasers can process through precise cutting or shaping operations. The laser cut materials include laser cutting acrylic, laser cutting PEEK, and metal materials to laser cut, including stainless steel and aluminum.
The selection of laser type for cutting depends on thermal material properties because non-metal materials require CO2 lasers, while metals generally require fiber lasers. Diode lasers are rarely suitable for cutting; they are mainly used for low-power engraving on certain materials.
The cutting process creates clean edges through material vaporization or melting, which depends on laser power and speed settings. The process requires proper ventilation because certain materials release toxic fumes and chlorine gas, which can be hazardous to workers. Various materials serve different purposes in manufacturing and DIY projects because of their unique characteristics.
What Materials To Laser Cut?
Material selection for laser cutting requires evaluating thickness and composition, as well as planned usage, to achieve precise results with optimal efficiency. Different materials show unique reactions to laser types because organic materials and plastics, composites, and metals each have their own set of benefits and constraints.
Organic Materials
Organic materials from natural sources work well with laser cutting because they have low melting points and create smooth cutting edges. The solid wood species basswood makes an excellent choice for laser cutting because it maintains a uniform density, resulting in consistent results. The 3mm thickness of basswood plywood sheets makes them ideal for detailed engraving and cutting operations, as they resist warping when using low power settings. The dark appearance of walnut plywood sheets makes them suitable for design projects, but users need to adjust their speed settings to prevent edge burning.
The organic material leather responds well to laser cutting because it produces exact designs without any edge deterioration. The combination of paper and cardboard materials allows for fast prototyping because laser cutting cardboard produces complex designs at fast speeds. The cutting process of low-density foam materials remains straightforward but requires proper ventilation to control smoke production. The combination of solid wood, plywood, and textile materials, including cotton and silk, allows engraving and cutting, but you must stay alert for fire hazards. The best results for these materials are achieved when using CO2 lasers instead of diode lasers, as diode lasers do not generate sufficient power for cutting through thick materials.
Plastics and Composite Materials for Laser Cutting
The clean melting and vaporization properties of plastics and composites make them suitable for laser cutting because they create smooth edges. The laser power requirements for PMMA or plexiglass are moderate because it produces flame-polished cuts perfectly. The CO2 laser cuts thin sheets of up to 1/4 inch thickness with high precision.
The cutting process of nylon, HDPE, and polypropylene plastics works well but needs repeated passes for thick materials to stop them from distorting. The structural properties of MDF and acetal composites come from their uniform density, which enables precise engraving.
The cutting of PVC materials produces hazardous chlorine gas emissions that damage equipment and create toxic fumes, posing a risk to human health. PVC should not be cut using laser cutters. The cutting process of polystyrene foams produces styrene vapors that require proper ventilation systems.
The speed and power settings of laser cutters determine material processing, as low power protects heat-sensitive composites from melting, while high power achieves complete cuts through dense materials. The wide range of applications for plastics includes both signage production and prototype development.
Metals as Laser Cutting Materials
The high reflectivity and thermal conductivity of metals, especially in laser cutting titanium) make laser cutting materials difficult, so fiber lasers become necessary for the efficient processing of these laser-cuttable materials. The combination of nitrogen assist gas with stainless steel enables clean cuts for materials up to 1 inch in thickness at high power levels.
Laser cutting aluminum requires focused beams because of its lightweight nature and conductive properties to prevent dross formation. The reflectivity of brass and copper requires specialized cutting parameters that use fiber lasers for precise operations. The cutting process of carbon steel becomes faster when using oxygen as an assist gas.
Thin metal sheets can sometimes be cut with lower-power fiber or diode lasers in hobby settings, but industrial applications almost always require fiber lasers. The process requires the safe management of heated debris and the proper installation of exhaust systems to handle any generated fumes.
What Are Laser Cutter Materials and Which Laser To Use?
|
Material Category |
Examples |
Recommended Laser Type |
Notes |
|
Organics |
Wood, plywood, leather, paper, cardboard, foam |
CO2 lasers |
The material efficiently absorbs 10.6 μm wavelengths when used with low-power engraving, preventing burning, and works well with thin sheets up to 1/2 inch in thickness. |
|
Plastics and Composites |
Acrylic, MDF, acetal, polystyrene, laser cutting nylon |
CO2 lasers |
The material melts well, but PVC should be avoided because it produces toxic fumes during processing and requires multiple passes for thick materials and diode lasers for low-power operations. |
|
Metals |
Stainless steel laser cutting, aluminum laser cutting, laser cutting brass, copper laser cutting |
Fiber lasers |
The material reflects light intensely, so nitrogen-assist gas must be used, and high power settings are required for penetration; however, CO2 has limited penetration capabilities. |
|
Textiles and Fabrics |
Cotton, silk, polyester |
CO2 lasers |
The process requires edge sealing to stop fraying and low power settings for melt control when creating intricate designs. |
|
Other |
Glass |
CO2 lasers |
The tool functions best for engraving operations but requires low power settings to create surface frosts without breaking the material, while it does not perform well for through-cuts. |
List of Top 10 Laser-Cuttable Materials
1. Acrylic (PMMA)
Acrylic sheet cutting
Acrylic material known as PMMA achieves perfect laser cutting results that produce transparent edges that need no additional processing. The cutting process of acrylic material using CO2 lasers operates at a speed of 4-8 mm/s with high power output for efficient cutting and utilizes a low-power (40W diode) for detailed engraving of designs up to 15mm in thickness. The material reaches its melting point at 160°C, which enables smooth cuts through sheets measuring up to 1 inch in thickness when using cast acrylic instead of extruded acrylic to prevent cracking.
The different Plexiglass variants provide designers with multiple options for creating signs and models and making jewelry. The process of cutting thick materials requires multiple passes at 75-100% power while maintaining focus and air assist to stop bubble formation. The material requires ventilation for fume control, yielding ideal results for projects that require precise optical clarity.
2. Plywood
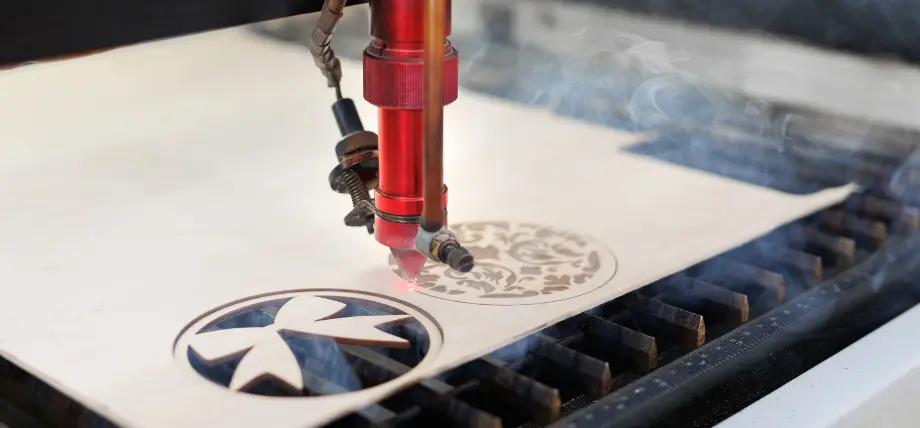

Laser engraving wood
The laser cutting process depends on plywood as its main material because basswood plywood sheets create smooth surfaces for detailed operations. The CO2 laser cuts walnut plywood sheets effectively at 10W diode power with 75% intensity and two passes for a 3mm thickness. The cutting speed of low-density plywood materials increases, but they tend to burn during operation; therefore, soaking in water at room temperature helps minimize this effect.
The material works well for furniture prototypes and architectural models because engraving at 1000 mm/s speed creates textured effects. The material needs clamping to stop warping while maintaining proper focus alignment for achieving uniform depth up to 1/4 inch. The material selection should avoid high-resin plywood because it produces excessive smoke while offering flexibility for building complex DIY structures.
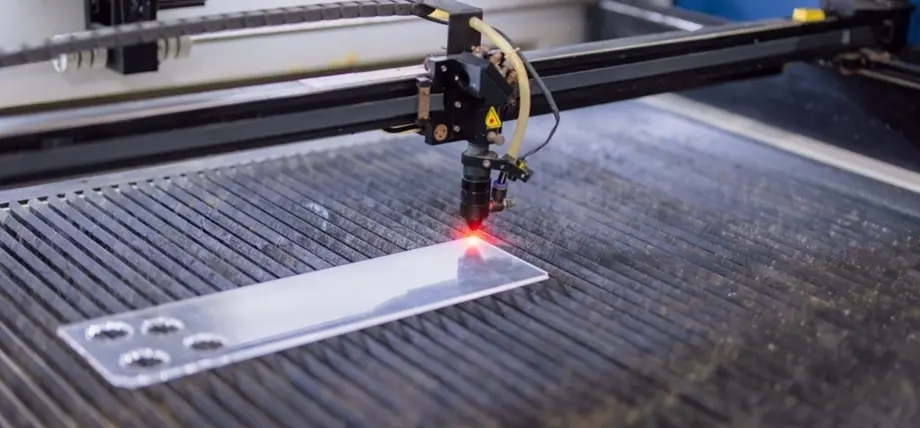
3. MDF (Medium-Density Fiberboard)
Laser cutter in action
MDF provides excellent conditions for laser engraving because its uniform density produces uniform tones without any interference from wood grain patterns. The CO2 laser system requires at least 40W of power to cut MDF materials with a thickness of 3-6mm in a single operation. However, the resin content in the material generates smoke that requires exhaust systems and acrylic grid tables.
The best choice for MDF materials should be premium or double-refined to prevent toxic substance exposure during use. The diode laser produces high-contrast engravings but needs multiple passes to cut thin sheet materials. The material requires fast processing speeds (two passes at moderate power) to stop charring during model and signage production. The machine needs proper ventilation to handle formaldehyde fumes, while users should perform regular cleaning operations after each use.
4. Stainless Steel
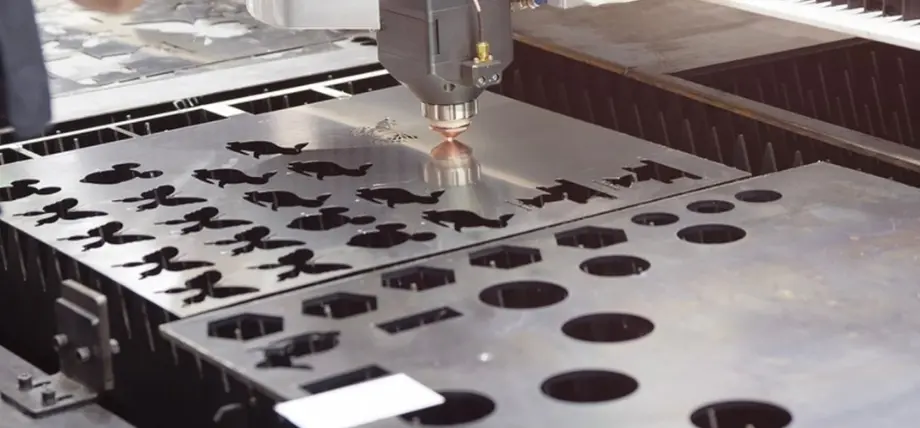

Fiber laser cutting metal
The process of cutting stainless steel requires fiber lasers because they provide accurate cuts and maintain corrosion resistance after finishing operations. The p1 kW or more ofss requires 1kW+ power to cut 4mm gauges of material with nitrogen assistance, which prevents dross and stops oxidation. The engraving process for serial number addition requires speed adjustments to minimize heat-affected zones (HAZ), which stay non-hardened in 304 grades.
The material selection for industrial parts requires argon gas for edge quality, but CO2 lasers show limited performance. The process requires setting the focus length for 80% penetration, followed by breaking the remaining material.
5. Aluminum
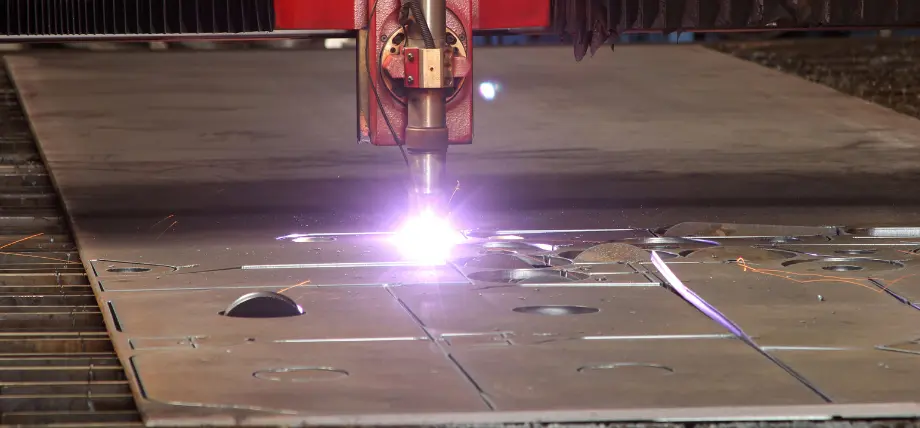
Laser Cutting Aluminum
The processing speed of fiber lasers reaches 1/4 inch thickness because aluminum has a low melting point. The engraving process on anodized materials becomes more visible when using high-pressure and gas-assist systems with nitrogen or oxygen to remove molten material and prevent dross formation. The material selection for aerospace parts requires power and speed adjustments based on material thickness, starting with a focus on 80% cut, then breaking. The short wavelength helps reduce reflectivity, while maintaining an inert gas environment protects against oxidation.
Try Prolean Now!
6. Leather
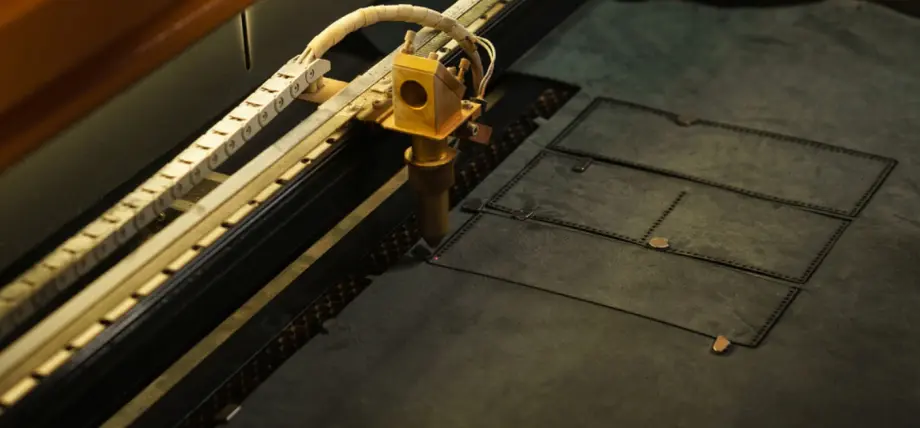
Laser cutting leather
CO2 lasers above 40W cutting process of natural veg-tan leather (2mm thick) requires 75% power at power levels, cut leather materials without fraying while producing detailed engravings in a single operation pass. The85% depth, while diode lasers can cut up to 1/4 inch, but produce edge charring.
The accessory material requires low power settings (3000 mm/s at 90%) to prevent burning, while ventilation systems handle oil and odor dispersal. The material must be kept flat and secured because any movement will ruin the cut. The material works best for creating custom bracelets.
7. Cardboard
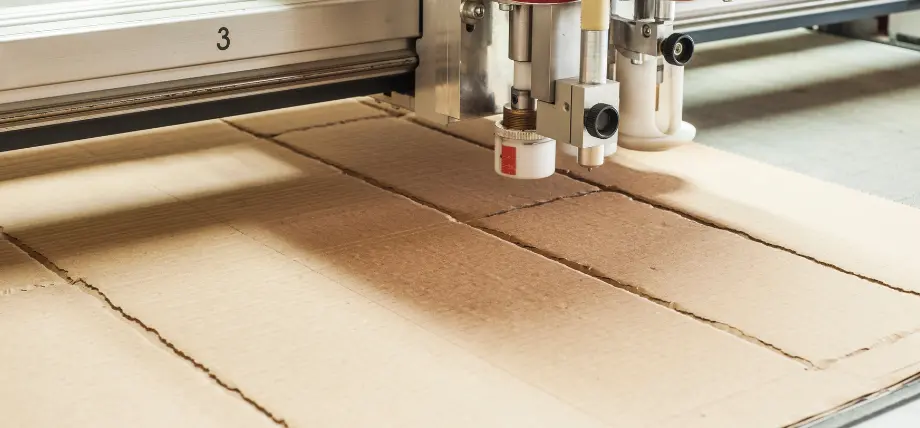

Laser cutting cardboard
CO2 laser systems can easily cut cardboard materials for creating prototypes up to 3mm in thickness. The process requires low power settings and active air assist to minimize fire risk. Cardboard should never be cut indoors without a proper exhaust and fire-suppression system. The material works well for packaging needs, and STL to SVG conversion enables sculpture creation while multiple layers help construct complex structures. The cutting process with diode lasers takes longer than that with CO2 lasers, and smoke exhaust systems remain necessary for operation.
8. Textiles

Laser cutting fabric
CO2 lasers cut through cotton, polyester, and silk materials with precision while sealing the edges to stop them from unravelling. The engraving process creates motifs, while speed settings determine the extent of melting, which requires testing scrap materials before use and disabling air assist for specific fabric types. The material works well for fashion applications when secured with weights after proper cleaning and pressing of the material.
9. Acetal
The precise cutting of Acetal (POM) by CO2 lasers occurs because this material maintains its shape and has low friction properties. The extruded types of this material tend to warp during processing, but work well for creating mechanical parts with smooth edges. The tensile strength of this material ranges between 60 and 90 MPa, and it can be recycled and requires a thermoplastic form. The engraving process needs specific marking settings to work with this material, which makes it suitable for creating enclosures.
10. Glass
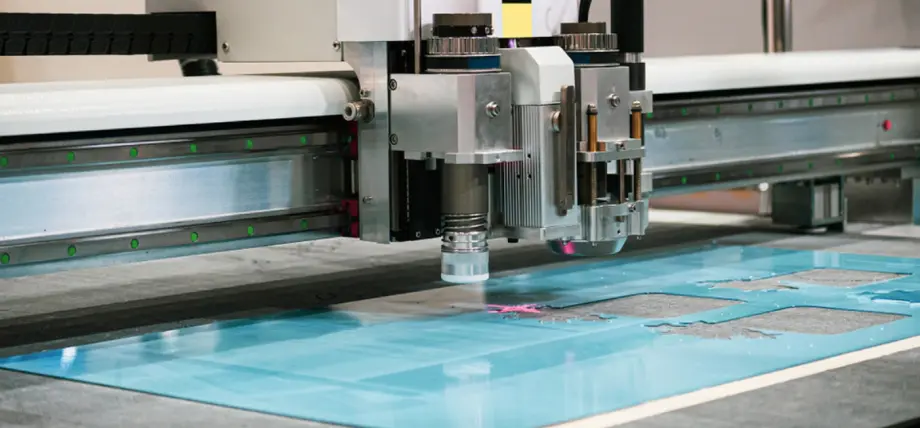

CNC router cutting glass
Glass engraving with CO2 lasers is typically performed using low power and a wet paper or masking layer, often with the image set to 70–100% black in the design file. The cutting process has restrictions, but paint application enables diode etching followed by settings between 30-100W to create frosted surfaces without breaking, while achieving grayscale matrix effects at cleaning with a solution. The use of rotary tools becomes necessary for curved objects, while safety glasses protect users from broken glass fragments.
Try Prolean Now!
Laser Cutter Maintenance Tips For Different Materials
- The maintenance process for wood and plywood requires weekly cleaning with isopropyl alcohol to eliminate resin while vacuuming the bed after use, and monthly rail lubrication and biweekly air filter inspections for char buildup.
- The exhaust filters need inspection following each session to handle vapors while avoiding PVC materials because they cause corrosion, and the cooling systems require distilled water flushing every few weeks, and mirrors need monthly alignment.
- The maintenance of stainless steel and aluminum metal components requires nozzle cleaning after cutting for spatter removal and deionized water usage in chillers, and regular checks of gas systems for nitrogen/oxygen purity and scheduled focus and power output calibration.
- The maintenance of leather and textile equipment requires vacuum cleaning of bed lint and frequent air filter cleaning because of oil buildup, operator training, and exact bed level adjustment.
- The work environment requires proper ventilation to handle smoke and toxic substances, and users should replace filters monthly, maintain a clean work area, and avoid operating indoors without exhaust systems.
- Daily inspections of electrical parts should be done along with gas system maintenance and deionized water checks in chillers and material-specific training for operators to minimize equipment breakdowns.
Laser Cutting Services
Proleantech provides laser engraving and laser cutting services for metals, composites and high performance plastics.
Key advantages of working with Proleantech:
- Shorter lead times
- Online laser cutting quotes 24/7
- Optional DFM support
- Prototype to high volume production support
Request a free quote today!
Conclusion
The selection of appropriate laser cutting materials combined with proper laser settings enables engineers to achieve optimal results when working with what materials can be laser cut. The selection of appropriate laser types and settings with knowledge of material compatibility leads to superior results in engineering and design applications. The use of safety protocols helps protect users from toxic gas exposure during laser cutting operations.
FAQ
What Materials Can A Laser Cut?
Lasers perform cutting operations on wood and acrylic materials, as well as metals, leather, paper, foam, and textiles, based on the specific laser type and power output.
What Materials Can A Laser Cutter Cut?
The laser cutting process works with solid wood and plywood as well as acrylic plastics and MDF composites, and specific metal materials when using suitable lasers.
What Materials Can Be Laser Cut?
The materials that work well with laser cutting include acrylic for achieving smooth edges, plywood for building structural elements, leather for making flexible designs, and stainless steel for creating long-lasting parts.
What Materials Does A Laser Cutter Cut?
The laser cutter operates on basswood plywood sheets and plywood and PVC-free plastics and metals with fiber lasers and fabric materials with sealed edges.
What Materials Are Used For Laser Cutting?
The standard materials used for laser cutting consist of walnut plywood sheets for visual appeal, cardboard for testing, glass for engraving, and aluminum for lightweight operations.




0 Comments