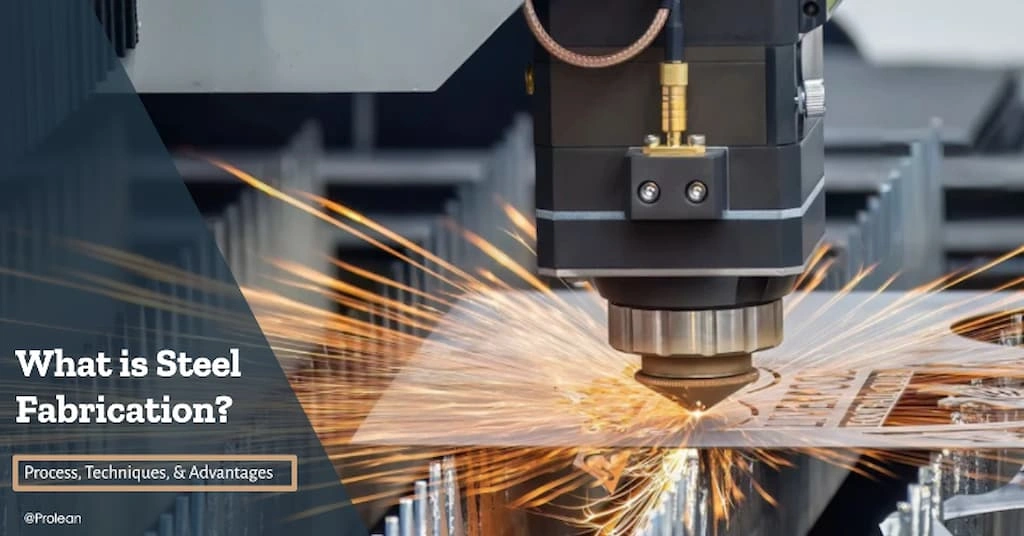

Steel fabrication
Among the several methods of producing finished steel parts, sheet metal fabrication is recognized for its versatility, customization, and precision. You can use steel fabrication to shape the desired parts from blank steel sheets.
Individual parts are first made with suitable metal forming methods and assembled together with welding, rivets, or fasteners. Some notable examples include structural beams, pressure vessels, ducts and piping, and electrical enclosures. However, it is a complex manufacturing method and requires a deep understanding of different aspects.
This article will discuss the steel grades, fabrication process, benefits, and applications.
What is Steel Fabrication?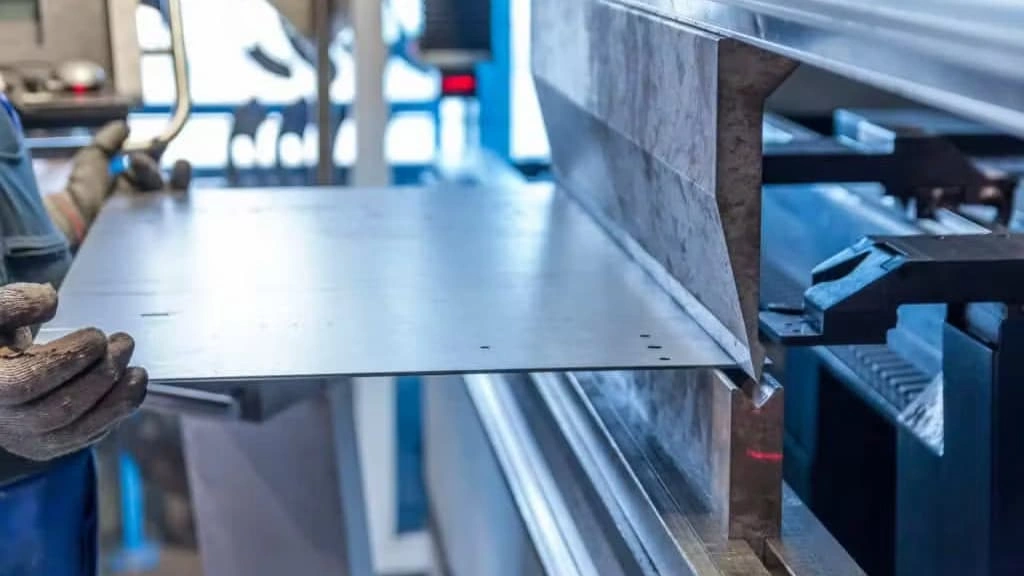 
Steel sheet forming
Steel fabrication refers to a manufacturing process in which raw steel sheets, tubes, bars, or other forms are transformed into finished parts and products. It involves a series of metalworking methods, such as cutting, bending, punching, welding, assembly, and post-processing operations.
You can make large steel structures, spare parts, and custom industrial components with sheet metal fabrication services. The application preferences are automotive panels, construction elements, energy structures, and machinery components.
Steel fabrication differs from machining, where a single machine can produce a final part from a material block. Instead, it utilizes a range of equipment and techniques, such as laser cutters, CNC bending machines, punching presses, and welding machines.
The Process of Steel Fabrication
Fabrication process for steel components follows a specific set of steps, from raw material selection to final inspection and packaging.
Let’s look at the individual steps of steel fabrication: part designing, marking & cutting, forming, assembly, and post-processing.
Part Designing
Steel fabrication design
The process of steel or any other types of sheet metal fabrication starts with creating the engineering design of the final part you want to fabricate. The only difference is that considerations of steel properties and raw steel forms, such as sheet, plate, bars, etc.
Designing is also about achieving the desired strength, manufacturability, and cost reduction. It involves focus on mimizing sharp corners, stress concentration sections, uneven transitions, weld strength, and structural reinforcement.
Moreover, the design must define the dimensions and geometrical features, as well as the assembly directions. You can refer to this metal design guide while designing the steel fabrication parts.
Steel Marking & Cutting

Steel sheet cutting
Based on the design, the steel sheet is marked and cut into smaller sizes to form (or shape) individual components. Fabricators typically employ techniques such as shear cutting, laser cutting, or plasma cutting.
Forming and Machining
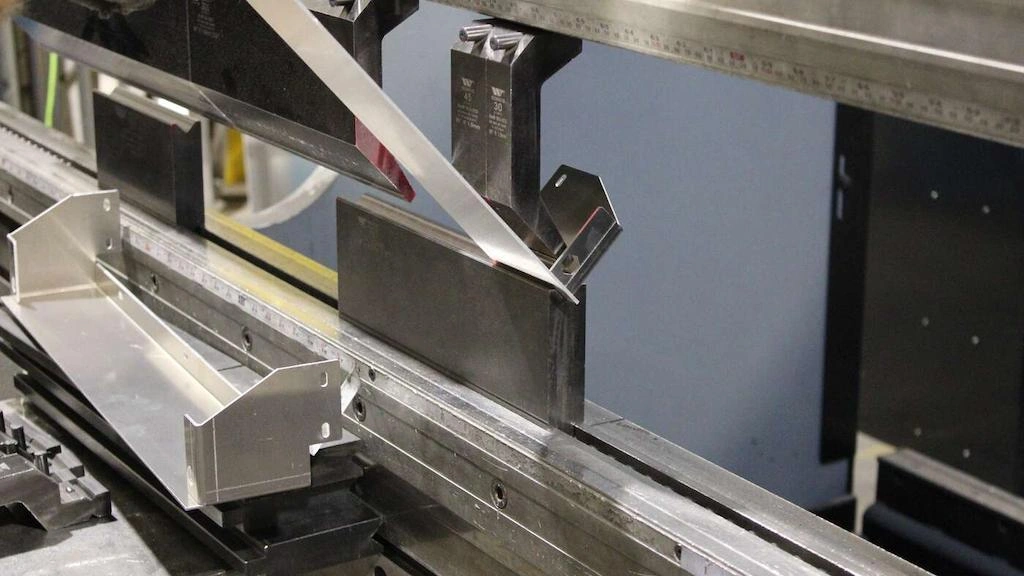

steel forming process
Steel sheets are cut into specific sizes and then shaped using suitable metal forming techniques. Often, machining processes are also combined with forming to shape the steel sheets. We will later discuss the types of forming techniques in detail.
Assembly
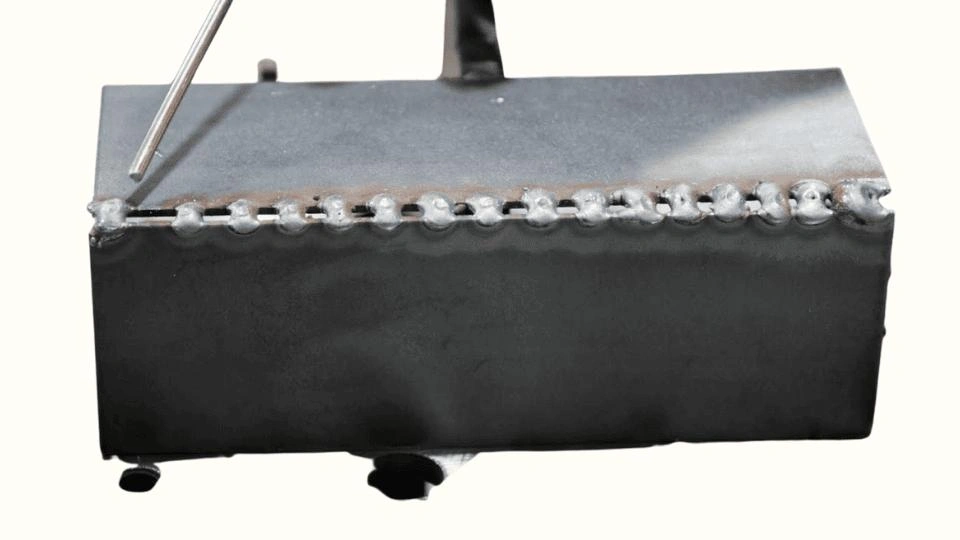

Steel welding
This step involves joining the multiple steel parts into a single item. Techniques such as welding, riveting, and bolting are the most common assembly methods in the steel fabrication industry.
Post-processing & Finishing
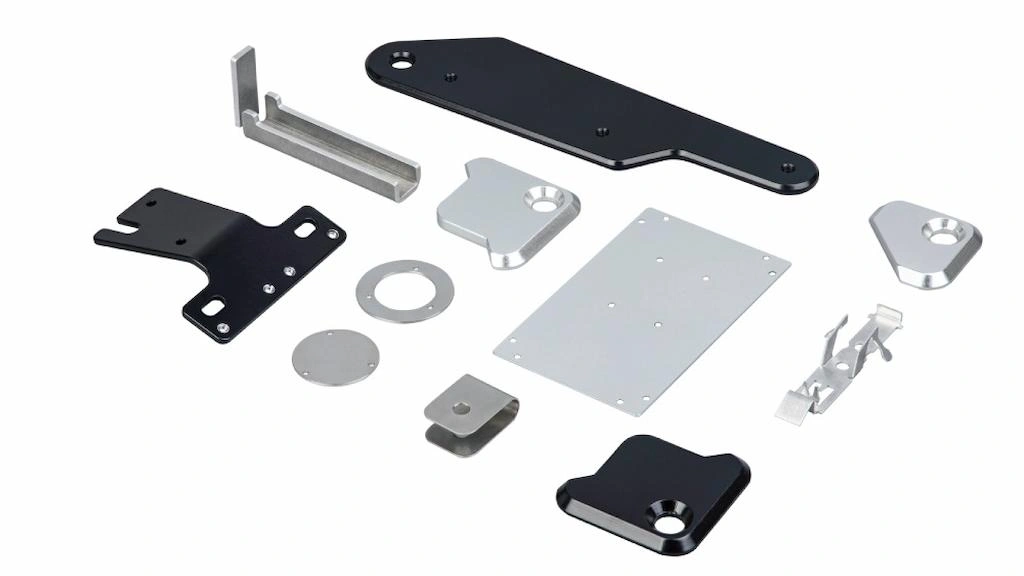

Finished steel fabrication parts
Post-processing involves trimming the edges, deburring, and even minor machining to correct the designed specifications. Finally, the fabricated steel parts are finished with coating, plating, or other methods to achieve the desired aesthetic.
Next, the chart below illustrates the steps we took to carry out the steel fabrication process after receiving the design from businesses or individual clients.
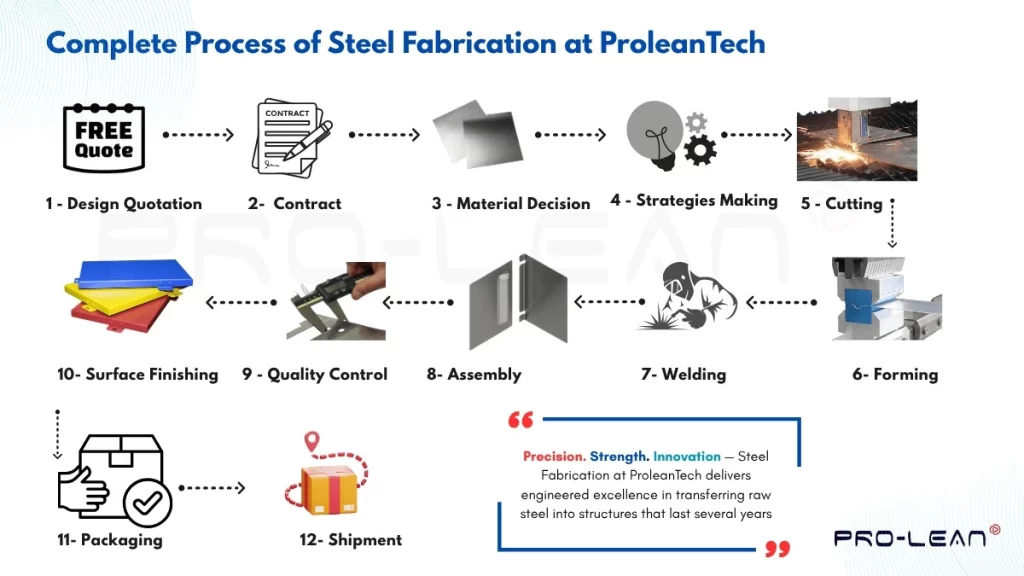
Steel fabrication process
Try Prolean Now!
What Are the Types of Fabrication Steels?
Mild, stainless, and alloy steels are the main choices for fabrication projects, whereas tool steels are typically not preferred due to their brittleness and low formability.
Let’s briefly elaborate on three types of fabrication steels.
Mild or Carbon Steels
These are the most common types of steels used in fabrication due to their high formability, weldability, and competitive pricing. The application ranges from general machinery hardware to structural frames and automotive chassis panels.
Fabrication Grades: ASTM A36 / S235, A1011, AE 1018/1045, etc.
Stainless Steels
Stainless steels are renowned for their high strength, good formability, corrosion resistance, durability, thermal stability, and hygienic properties. They can be cut, formed, and welded into the desired Parts. The fabricated stainless parts are used in various sectors, including architecture, fittings, food processing, automotive, and others.
Fabrication Grades: 301, 303, 304, 316, 420, 430, and 2205.
Alloy Steels
Besides carbon and iron, alloy steel contains elements like chromium, molybdenum, and nickel in its composition. Additional elements improve toughness, wear resistance, strength, and other properties. Alloy steels are used to fabricate gears, shafts, structural frames, and crane parts, among other applications.
Fabrication Grades: 4130, 4140, 4340, A572, etc.
If you are interested in the fabrication of metals other than steel, read aluminum fabrication and brass metal fabrication here.
Metal Forming Techniques in Steel Fabrication
In a complete process of steel fabrication, several forming techniques can be used, depending on the complexity of the parts. For example, fabricating a complex pressure vessel needs multiple techniques, whereas mounting clips can be made with simple cutting and bending.
Let’s look at the most frequently used forming techniques in brief, including sheet metal cutting, punching, blanking, bending, drawing, stretching, and welding.
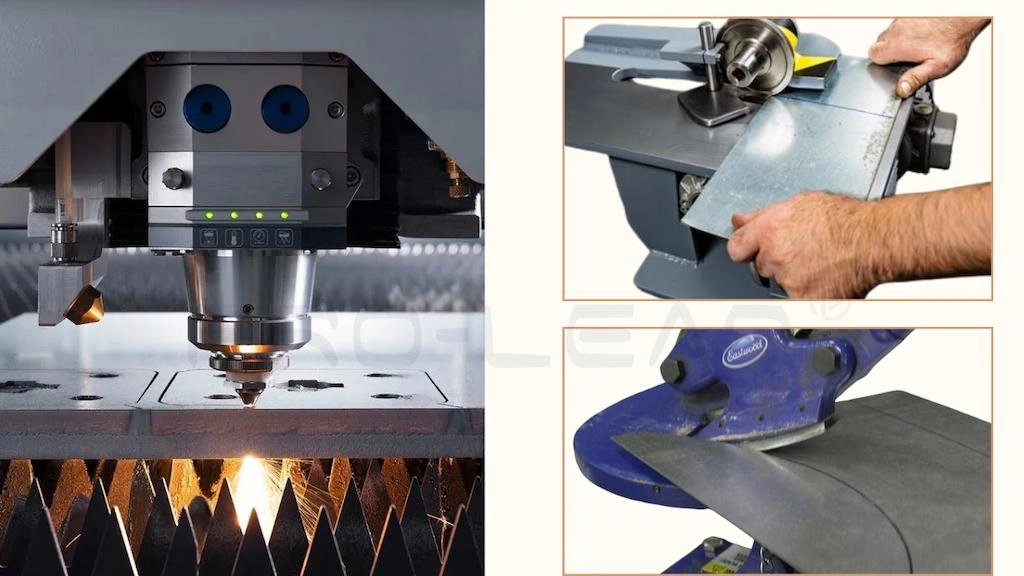
Steel Sheet Cutting
Cutting is not limited to splitting the large steel sheet into smaller pieces, but it is also about cutting to a specific shape or profile and creating holes. The common steel sheet cutting techniques are shear cutting, laser cutting, and plasma cutting.
Steel Sheet Punching
Punching uses dies and punches to create holes, pierce, notches, and other related features in steel sheets. The punch involves a profile identical to the geometry of the desired hole. When the punch strikes the sheet, its edges shear the material.
Steel Sheet Blanking
Blanking is similar to punching, except that the punch-out profile is the desired part, and the parent sheet becomes scrap after the blanking.
Steel Sheet Bending
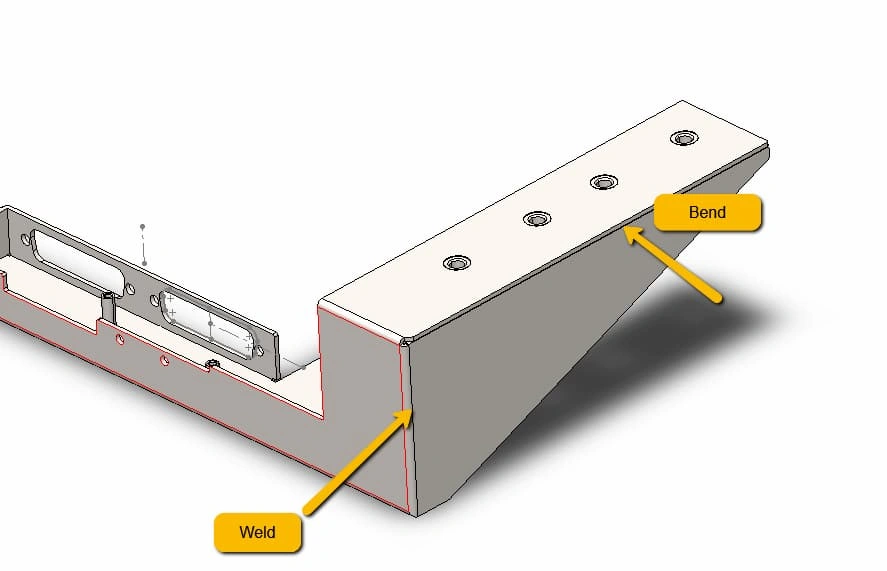
It is the most versatile forming technique in fabrication that bends the steel sheets into the desired angle, curvature, or profile. Consequently, complex shapes can be formed through multiple bends on the worksheet. You can use press-die bending, rotatory bending, roll bending, or any suitable metal bending technique.
Steel Sheet Drawing
Drawing or deep-drawing technique involves pulling the steel sheet into the die cavity, allowing the material to flow inward and form deep & complex parts. It is mainly used for tanks, containers, and other similar shapes.
Steel Stretching
It refers to stretching the steel sheet over a die to form the desired shape. Metal stretching decreases the thickness and lengthens the parts via tensile force.
Steel Sheet Nibbling
Nibbling is a metal forming technique that cuts tiny notches in a repetitive pattern along a pre-determined path. Moreover, sheet metal nibbling is useful to cut custom-shaped curves, internal cutouts, and patterns on steel sheets.
Steel Sheet Hemming
Hemming refers to the bending (or folding) of sheet edges towards itself in closed, open, rolled, teardrop, or any other form. Sheet metal hemming is used in steel fabrication for finish and structural reinforcement.
Steel Welding
Welding permanently joins multiple steel components into a single component, product, or structure. Based on the type of steel and parts thickness, TIG, MIG, or stick welding is used. Therefore, it is critical in the sheet metal fabrication assembly of individual steel parts.
Steel Extrusion
Although steel extrusion is not as common as aluminum, it is used to form a wide range of shapes and profiles. In the process, the hot steel is forced through a die cavity, and then it flows and takes the cavity’s shape.
Try Prolean Now!
Our Steel Fabrication Approach and Custom Solutions for Industries
At ProleanTech, we focus on fabricating steel components and products tailored to meet the specific application requirements. Every time we receive a design from the client, our goal is to deliver high-quality results that meet industry standards.
We follow niche-based fabrication strategies, whether they are spring, wire, tank, structural elements, spare parts, machinery hardware, or any custom items. Additionally, we combine machining, post-processing, and various surface finishing techniques along with the forming.
Our custom steel fabrication services cover the following industries.
- Industrial Machinery
- Oil and Gas
- Renewable Energy
- Medical Equipment
- Automotive
- Architecture
- Transportation
- Furniture and Interior, etc.
Read More: Aerospace Sheet Metal
Advantages of Steel Fabrication
Versatility is one of the main benefits of steel fabrication in manufacturing. It covers numerous metal forming & shaping techniques, which enable the production of components with varying complexity.
Other advantages of steel fabrication are listed below:
- Strength-to-Weight Ratio: Steel fabrication items offer high strength without being excessively heavy, which makes them suitable for load-bearing applications.
- Longer Lifespan: The raw steel properties and strong buildup make the part/products durable, even in high-stress and some harsh environments.
- Customization: With a wide range of metalworking techniques available to shape the steel, fabrication offers a high degree of customization leverage.
- Precision: The use of modern CNC equipment and robotics systems in fabrication allows for tight tolerances and repeatability.
Steel Structure Fabrication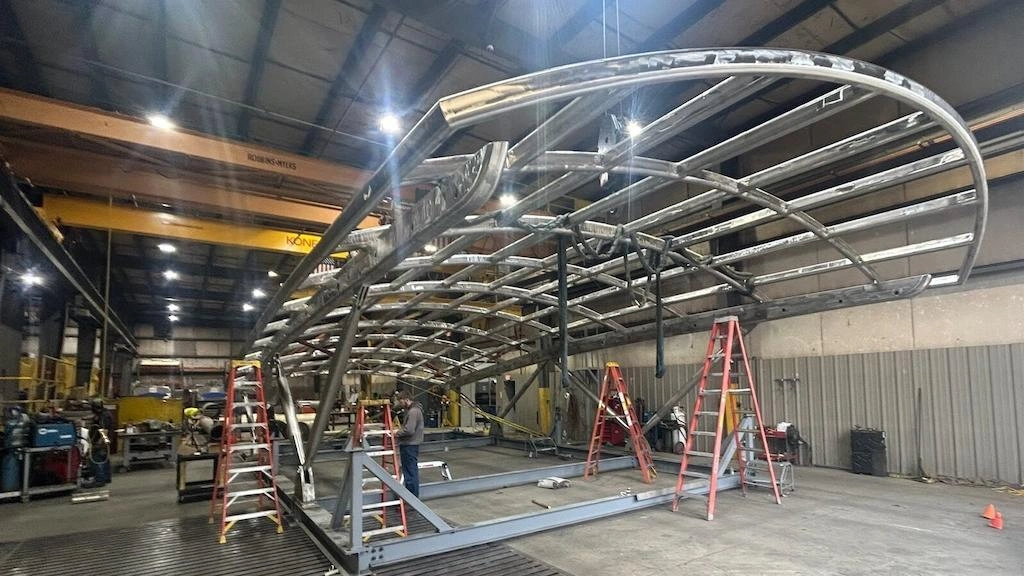 
Steel structure fabrication
It is a specialized steel fabrication process that primarily focuses on the production of structural components, like beams, joints, columns, and trusses. Raw steel plates, sheets, tubes, or bars are cut, bent, shaped, and joined together to form the diverse structural components.
Structural fabrication also emphasizes the use of specific grades of steel that are tough, durable, and meet safety requirements—for example, ASTM A36, A572, and S355.
Some notable applications of structural and heavy steel fabrication are as follows:
- Load-bearing elements in construction.
- Steel columns and beams.
- Components of Trusses
- Heavy-machinery Parts
- Renewable energy structures
How much does Steel Fabrication Cost?
It is hard to tell a number how much steel fabrication costs. A variety of factors influence the cost of your fabrication project. However, fabrication is considered a cost-effective method in manufacturing, which provides value through the performance and durability of manufactured items.
The cost influencing factors in steel fabrication are as follows:
- Type of Steel
- Material thickness and size
- Design complexity
- Forming method needed for fabrication
- Require precision
- Assembly requirements
- Surface finishing
- Project timeline
Furthermore, to determine the cost of your steel fabrication project, please upload the design file and request a quote. We will provide an estimation with a clear breakdown.
Conclusion
Steel fabrication is a broad manufacturing process that encompasses a range of metal forming, shaping, and joining techniques, from metal cutting to parts joining. Thereby, it has diverse applications across the industries.
Moreover, fabricating a steel part requires understanding the design and using metal shaping strategies accordingly, such as determining which techniques to use in what sequence to achieve the desired results.
FAQs
What does a steel fabricator do?
A steel fabricator handles everything in the manufacturing stage, from assistance in design optimization and design and interpretation to assembly and surface finish.
What are the 4 types of steel?
Carbon, stainless, tool, and alloy steels are the 4 types of steels. Among them, tool steel is less common for metal fabrication.
What is the difference between steel fabrication and steel manufacturing?
Steel manufacturing is the process of producing raw steel material in standard forms, such as sheets and plates, available in markets. On the other hand, fabrication refers to taking those and shaping them into application-specific components




0 Comments