Whether it is the construction of bridges, heavy machinery, or simple multi-part components, they require custom bolts for assembly and mechanical joints. A bolt is a mechanical component that has a thread on the external surface with a head at the top, which can be tightened in crossposting holes through torquing of matching nuts. Compared to welding & riveting, these fasteners can be disassembled easily by losing the nuts.
Among different methods for manufacturing the bolts, CNC machining is known for precision and complexity. The computer-controlled tool movement allows manufacturers to produce CNC fasteners with tight tolerances consistently.
Continue reading, we will discuss the type of custom-made bolts, material options, machining techniques, and bolt terminologies.
What is Meant by a Mechanical Bolt?
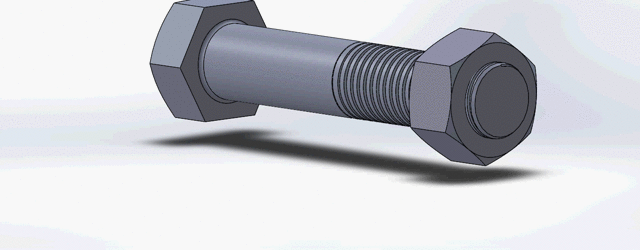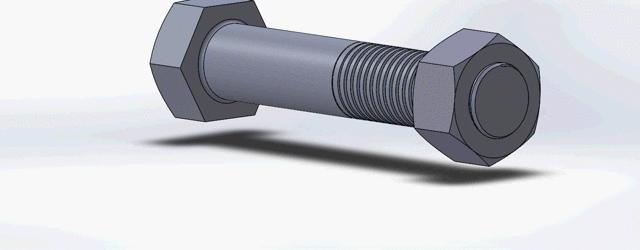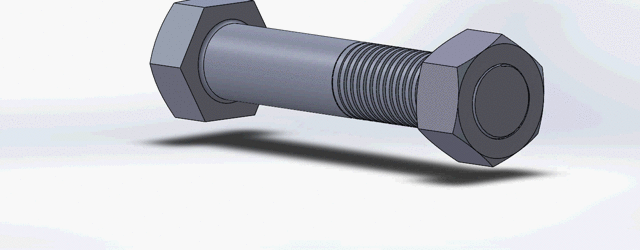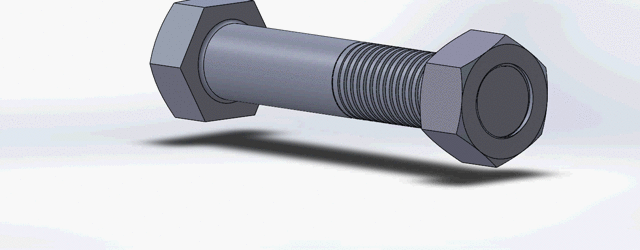
Nut and bolt concept
A mechanical bolt is a type of fastener that joins two or more individual components by inserting holes and tightening the helical threads with corresponding nuts. You might be confused with custom screws and bolts. Although both serve the same purpose of fastening, the bolt contains an un-threads portion (plain surface, called shank) near the head and the screws have threads fully up to the head.
The schematic diagram below shows a typical structure of a bolt;
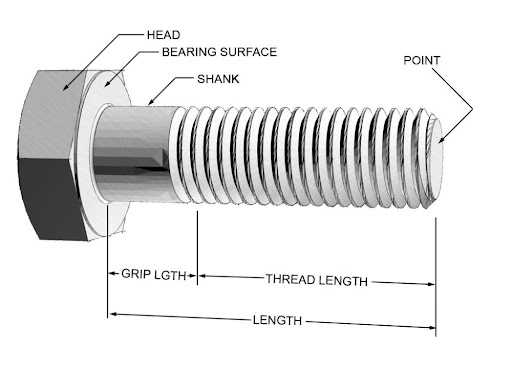
Typical structure of mechanical bolt
Hexa bolt geometry
The bolt shown in the above diagram is a Hexa Bolt(defined by the head geometry), which is the most typical form across industrial uses. In the market, you can get standard forms of fasteners with specific nominal diameters, pitch, and thread lengths. For example, M3 x 1.5 x 30 is the common size of bolt available in the market. It means a bolt with a nominal diameter of 3 mm, a pitch of 1.5mm, and a length of 30 mm.
In different applications, industries need custom bolts that serve unique requirements. Custom automotive fasteners for wheel assemblies and engine heads are one such example.
Try Prolean Now!
Bolt Terminologies
Now, let’s see what each terminology describes about the bolt;
| Bolt Terms | Description |
| Head | The top part of the bolt (apply torque) |
| Bearing Surface | It sits against the material being fastened (load distribution) |
| Shank | Unthreaded part of the bolt (Short or absent in screws) |
| Thread Length | Threaded portion(engage with or tapped hole) |
| Point | Flat or chamfered shape at the end |
| Length | The total length of the bolt from the head to the point. |
| Major Diameter | The diameter is measured from the outer edges. |
| Minor Diameter | The diameter was measured from the roots (innermost points). |
| Pitch | Distance of two adjacent threads (Threads per inch) |
| Drive Type | Bolt head that determines the tool required (e.g., hex, Phillips, Torx). |
| Root | Threaded portion that engages with or tapped hole) |
Types of Custom Bolts
There are different types of bolts based on their shape, application preference, torquing mechanism, etc. The following are the typical bolt types;
Anchor Bolt

Types of anchor bolts
Anchor bolts are used for the external attachment of parts like a hanger on the wall. It contains a long threaded end that is inserted into parts and bolted after the externally attached parts. Additionally, they are widely popular for securing external items to the concrete wall.
Arbor Bolt

Arbor bolt
Arbor bolts have a washer attached between the head and the end of the threaded length. They are mainly used for powder components like machining blades and hand saws.
Carriage Bolt
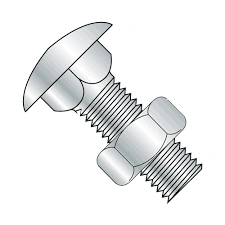
Carriage bolt
A carriage bolt contains a rounded head and a square shank. It can work on both wood and metal workpieces. Custom carriage bolts can be made with a designed square shank below the head that holds the bolt securely in assembly.
Custom U Bolts
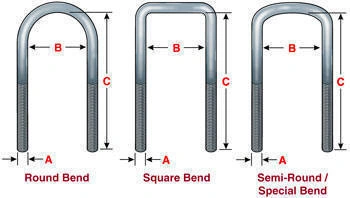
Custom U bolts
As the name suggested, U bolts have a letter shape “U” with threaded length at both ends. These types of fastening are used for stable joints. For example, beam & pipe supports, roof anchors, and engine shafts. Typically, the U bolts require customization for accurate thread positions, length, and U-curve bending.
Hex Bolt

Hex bolt
Hex bolts are characterized by the hexagonal geometry of the bolt head, they are among the top choices for industrial uses, heavy machinery, structural elements, metal construction, etc. Next, the Hex bolt does not involve a washer unlike most of the bolts.
Eye Bolt
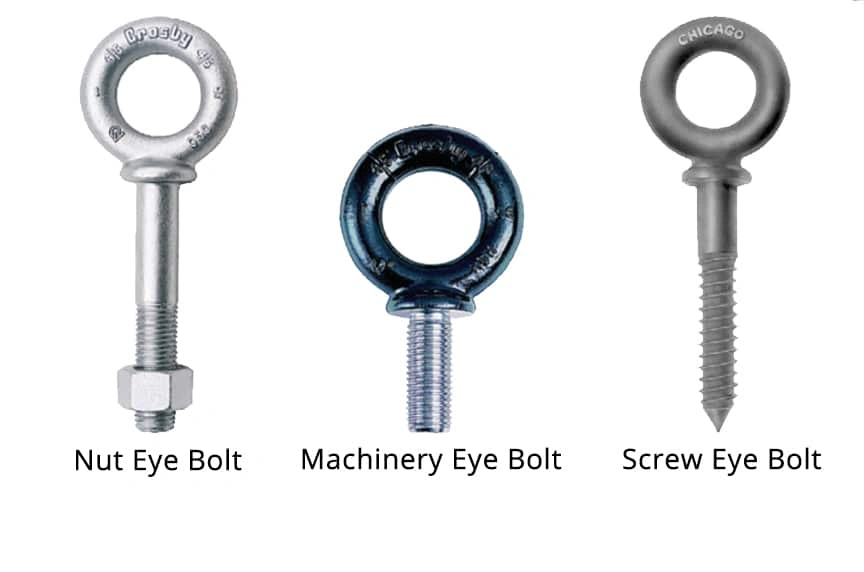

Eye bolts
Eyebolts are defined by their ring structure in the head position. Often, it does not contain any shank or is very small. The ring structure makes the bolt stable without the shank.
Read more: Types of washers
How to Make Custom Bolts?

Bolt machining
Depending on the type, size, and material, you can use forging, CNC machining, cold forming, or hot forming methods to make your custom bolts or fasteners.
| Method | Process Overview | Best Suited For | Typical Applications |
| Forging | Shaping of hot material under pressure | Large bolts, high-strength fasteners | Heavy-duty applications (e.g., automotive, aerospace) |
| CNC Machining | Material is precisely cut to shape with CNC turning, swiss custom screw machining, etc. | Custom or precision bolts | Specialty bolts for electronics, aerospace, medical devices |
| Cold Forming | Shaping the material by deformation at room temperature | Small to medium-sized bolts, high-volume | Standard fasteners (e.g., automotive, construction) |
| Hot Forming | Material shaped at elevated temperatures | Large or complex-shaped bolts | Structural bolts, high-load applications |
Try Prolean Now!
Bolt or Fastener Materials
The material of the bolt is directly associated with the application, functionality, performance, cost, and durability. Typically, metals with high-strength and formability metals or alloys are used for this. However, plastics and composites can be CNC machined to make the bolts.
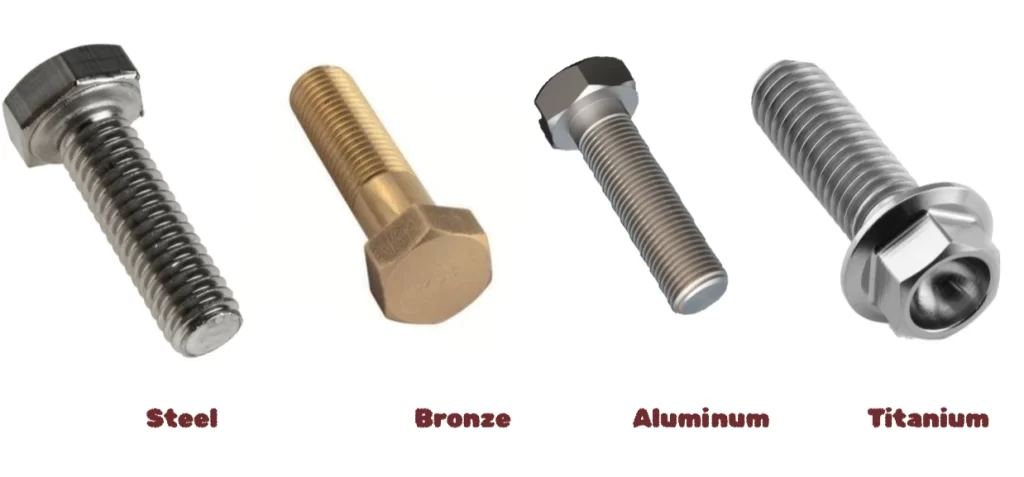

Bolt materials
The following are the materials for custom fasteners;
Carbon Steel
It is high high-strength and cost-effective material that can be machined or formed in different bolts, cars, construction sites, manufacturing machinery, furniture, etc. Although it is less corrosion-resistant, the protective coating can be applied.
Furthermore, it is more cost-effective than stainless steel bolts and can serve high-preference requirements.
Stainless Steel
You can find various stainless steel bolts popular in many uses, hex, carriage, shoulder, U-shaped, and other bolt types. The high corrosion resistance, strength, and performance under stress makes stainless an effective material choice for bolts.
Brass and Bronze
Both of them are alloys of copper material, brass( Cu +Zn), and bronze(Cu +Sn). These are preferred in saltwater and where conductivity matters. Additionally, bass and bronze bolts are used in piping & other related hardware due to their corrosion resistance properties.
Aluminum
Although custom fasteners made with aluminum have lower strength than steel, it has low weight and good corrosion protection behavior. It forms an aluminum oxide layer after exposure to air or a humid environment, which further protects the bolt fasteners. One of the popular examples is the aluminum 6060-T6 fastener. Subsequently, aluminum bolts can be finished with anodizing or metal plating to enhance the wear & abrasion resistance.
Titanium
Titanium is one of the popular choices for bolts, screws, and washers, especially for high-performance applications. The superior corrosion resistance, strength-to-weight ratio, thermal stability, and other various useful properties make perfect for this. Titanium bolts show higher inertness toward salt water and chloride solvents. Grade 2 and Grade 5 Titanium alloys are most preferred for the bolt making.
Non-Metallic Bolts or Fasteners
Besides the metal and alloys, plastic and composite bolting is also a viable alternative in certain applications. The high strength-to-weight ratio, superior corrosion & chemical resistance, thermal insulation, and low cost have made them popular in electrical, electronics, aerospace, oil & gas, and many other industrial applications.
- Nylon
- Polyethylene Terephthalate (PET)
- Polycarbonate(PC)
- Polyether Ether Ketone (PEEK)
- Fiberglass-reinforced plastic (FRP)
- Glass-Filled Nylon
- Carbon Fiber-Reinforced Polymer (CFRP)
Moreover, the choice of material for custom bolts depends on strength & load requirements, application environment, weight constraints, etc.
Do You Need Custom Bolts? Contact ProleanTech
Making the custom bolts can be challenging, especially with the tool selection and machining of custom thread geometries. ProleanTech is a leading company in Custom CNC machining & Fabrication services. We can provide any type of fastener manufacturing services tailored to your application needs.
Our factory is equipped with cold-forming machinery, multi-axis CNC machines, and advanced forging equipment for bolt manufacturing. So, send us your requirements. Our engineers will guide you toward optimal solutions.
Try Prolean Now!
Summing Up
There are different types of bolts available in the market with various shapes, sizes, and materials. For some specific applications and performance requirements, you might need custom bolts that you can make with forging, CNC machining, metal forming, and other suitable processes. Next, the choice of bolt type and material depends on particular design & application preferences.
FAQs
How to make a custom bolt?
The bolt customization requires careful considerations from the beginning, design & material selection. Then you need to choose which method is best for you, machining, forging, hot forming, or cold forming.
What are the common types of bolts?
The common types of bolts are hex, arbor, anchor, carriage, eye, U-bolt, etc. They have unique geometry, support capability, and preference over their uses.
Why stainless steel is common for Bolts?
Stainless steel has high resistance to rust formation, even in some harsh & humid conditions. Subsequently, they provide the perfect balance of performance and cost. So, stainless steels are common for bolts, like ASI 304 and ASI 316 Ti.
What material is the construction bolt made with?
Carbon Steel grade 2, grade 5, and grade 8 are the common choices for construction bolts due to their high mechanical strength. They are either galvanized or coated with corrosion-protective layers like powder coating, chrome plating, etc.




0 Comments