“Sheet metal gauges are the heart of sheet metal measurement in manufacturing. Since it is impossible to measure each sheet’s thickness with a conventional measurement tape, sheet metal gauges are used in this situation. In essence, a gauge represents the thickness of the sheet metal and can be expressed in millimeters or inches. Except for zinc, higher gauges represent thinner metal sheets.”
There are different Gauges for a specific material, stainless steel, galvanized steel, sheet steel, brass, aluminum, and copper. Among these Sheet metal gauges for steel are the standard ones in manufacturing, which is based on the idea that an inch of steel weighs 41.82 pounds per square foot.
The gauge system does not fall under the standard metric system. Therefore, it is an entirely independent system for typical sheet metal thickness measurements. However, with the conversion chart’s help, engineers and mechanists can convert the gauge thickness into inches or millimeters.
In this article, we will briefly overview the use of sheet metal gauges, various factors that need to be considered, the selection of gauge number, and its advantages & disadvantages.
Gauge Number and Thickness Chart
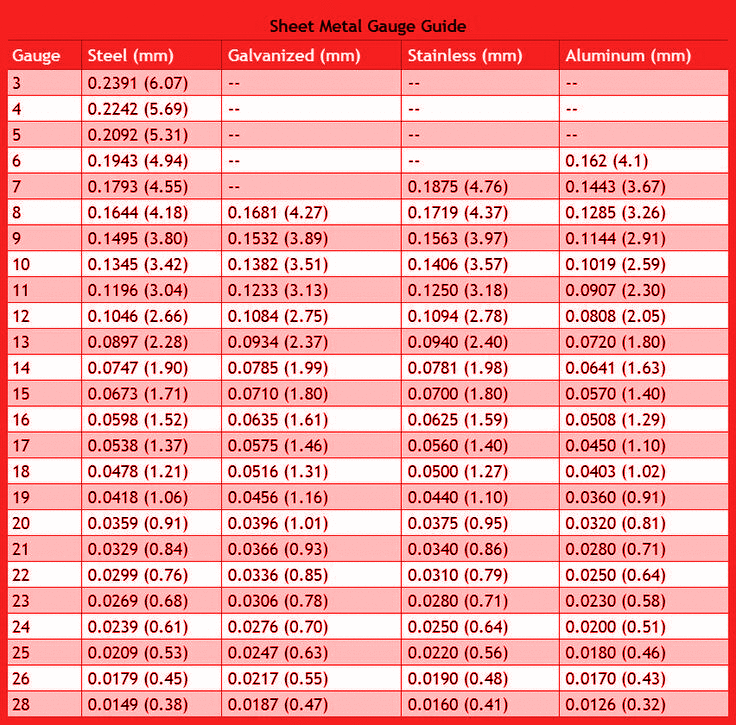
The various gauge numbers and the corresponding thickness of each type of metal are listed on a metal gauge chart. It is used in CNC machining to verify the material choice and consistency.
A portion of thickness chart
Using the gauge chart under the specific material is crucial because the same gauge number carries thickness from one material to another. For instance, 10 gauge aluminum is equivalent to 2.588 mm thickness, 10 gauge stainless steel is 3.510 mm thick, and 10 gauge galvanized steel represents 3.571 mm.
The gauge standard is based on the weight of the sheet for the specific material. Among the gauges for various materials, Manufacturers’ Standard Gage offers thicknesses for standard, galvanized, and stainless steel.
- Brown and sharp gauge: It is the American standard gauge, applicable for nonferrous material sheets such as brass, aluminum, copper, and tin.
- Birmingham Gauge: It is the United Kingdom standard gauge that is applicable for strips and tubes, and a higher number denotes a thicker sheet in terms of zinc.
Try Prolean Now!
How to Use Sheet Metal Gauges?
1. Verifying the thickness with gauge number
With the help of a millimeter hash, mark the measuring tape. According to the mark you made, note the obtained thickness. Be careful; there are two units in the measuring tape: millimeter (mm) and centimeter (cm).
Change the thickness into inches. You can multiply your noted millimeter by 0.03937 to obtain it into inches. For example, if your measuring tape gives 30 mm, it will be 30 x 0.03937 = 1.1811 inches.
After getting the measuring thickness into inches, look at the gauge chart of the material and find the nearby gauge number.
2. Using the wheel gauge for thickness measurement
Wheel-gauges
Choose the appropriate gauge wheel first, depending on whether you are measuring ferrous or nonferrous metals because there are different gauge wheels for measuring ferrous and nonferrous materials. Nonferrous and ferrous metals are labeled in front of the wheel.
3. Wheel gauge
The gauge has gaps of various sizes with labels for thickness on the front. Check your sheet by inserting it into each opening and adjusting it until it is the best fit. After the sheet has the perfect fit on the gap, take note of the thickness label on the front.
Sheet metal gauge chart
Selection of Correct Gauge Number in Manufacturing
The selection of a proper gauge for sheet metal plays a vital role in manufacturing. It ensures the functionality as well as the economy of the parts to be fabricated.
The following factors should be taken into account by a designer and a mechanic when choosing the gauge number.
- Strength: Because the sheet with a lower gauge would be more rigid and strong, it is also necessary to consider the required strength, rigidity, and other mechanical properties when choosing the gauge.
- Performance & Suitability: The performance and effectiveness of the manufactured project and the sheet’s workflow are determined by the ideal thickness of the sheet. Therefore, the engineer must consider performance and suitability when choosing the appropriate gauge of sheet metal during the design phase.
- Installation site: There is a high risk of wear and tear of the sheet metal components and entire product made of sheet metal if the installation site is in an open environment, so thinner material will be required. A lower gauge would be better in these circumstances.
- Economics: Budget constraints are another consideration when choosing a gauge because thicker sheets cost more. After all, the thickness of the sheet metal will determine its weight. Therefore, the cost-effective gauge should be selected while keeping the mechanical properties and required specifications.
Try Prolean Now!
Advantages and Disadvantages of Sheet Metal Gauge
There are several advantages of sheet metal gauge in the manufacturing industry because it is a very straightforward approach to measuring and confirming the thickness. Let’s look at some of the prime advantages in brief;
- Rapid procedure: Direct measurement takes much longer than measurement with a sheet metal gauge. As a result, it cuts down on manufacturing-related inspection time.
- Low skill level: Semi-skilled laborers can also use this system to ensure thickness because the gauge is a straightforward measurement process.
- Mass production: Have you ever thought about how workers and engineers can guarantee the thickness of the product produced in large quantities? In contrast to direct measurement, using a gauge allows them to quickly and efficiently ensure the dimensional stability of a large number of products.
- Cost: Gauges are affordable on their terms, and because they can be inspected more quickly, the inspection cost will also decrease.
Disadvantages
- Wear and tear on the sheet metal gauges can lead to errors in the thickness measurement.
- In many cases, It does not provide a sheet metal’s precise thickness value.
- It requires using different sheet metal gauges for ferrous and nonferrous sheets.
Conclusion
Sheet metal gauges are a crucial component of the manufacturing process for ensuring material thickness and selection. For each type of sheet material, there is a different gauge chart from which engineers and mechanics can compare the results of their measurements and select the appropriate gauge number.
You can receive any necessary consultation regarding the sheet metal gauge system at the Prolean. We are the top-notch service provider in sheet metal manufacturing. We offer professional CNC sheet metal manufacturing services such as cutting, punching, bending, welding, etc. If you require any related services, don’t hesitate to contact us.
FAQ’s
What are the uses of sheet metals?
Sheet metal has applications in various industries, from automotive and aircraft to construction.
What is the primary purpose of sheet metal gauges?
A sheet metal gauge system is used to measure and certify the thickness and selection of material type.
Is there a different gauge for ferrous & nonferrous metal sheets?
Yes, there are separate gauges for Ferrous and nonferrous metals. In fact, according to the material (Steel, aluminum, copper, and brass), there is a different chart for gauge numbers and their corresponding thickness.
What factors should be considered while selecting metal sheet thickness (gauge)?
There are several factors, such as strength, effectiveness, cost, and installation site.
What does it mean by a lower gauge number?
The lower gauge number represents the higher thickness of the metal sheet (Except for Zinc).








0 Comments