Trimming is a critical process in sheet metal manufacturing, ensuring precision, efficiency, and smoothness in the final product. It involves removing excess material from a workpiece, bringing it to its desired size and shape. However, there are various trimming operations, each with its unique characteristics and applications. Understanding these different operations can help in choosing the most appropriate one for a particular project or application.
In this article, we’ll delve into six major types of trimming operations in sheet metal manufacturing.
1. Blanking
The blanking process involves cutting out desired shapes from a larger sheet of metal. The cut-out piece is known as a “blank” and is used as the primary product, while the remaining sheet material is discarded. Blanking is widely used due to its ability to produce parts quickly and in large volumes.
Key Components of a Blanking Process
- Design and Blueprint: The process starts with creating a design and blueprint for the blank that is to be cut out.
- Die Creation: The blueprint is used to create a die that will be used to cut the metal sheet.
- Blanking: The die is applied to the sheet metal under high pressure, cutting out the desired shape.
- Inspection: The cut-out blanks are inspected for any deformities or imperfections.
Benefits of Blanking
Here is a list that outlines some of the benefits of blanking:
- Speed: Blanking is a fast process, especially when compared to manual cutting.
- Precision: The use of dies ensures that the cut parts are identical and precise.
- Volume: Blanking is ideal for large production volumes.
Common Applications of Blanking
Here are the common applications of blanking across industries;
- Automotive: Blanking is used to create various parts of a vehicle, such as gear parts, gaskets, and body panels.
- Electronics: Many electronic components are made using the blanking process.
- Construction: Many construction materials are produced through blanking.
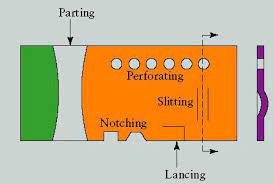
2. Parting
Parting is a sheet metal trimming operation that involves cutting a workpiece into two or more sections. Unlike blanking, parting uses the entire sheet, and all parts are utilized further.
Steps Involved in the Parting Process
- Planning: This involves deciding the parting line and considering the implications on the final product.
- Cutting: The sheet metal is cut along the parting line.
- Deburring: The cut edges are smoothened and cleaned for further processing.
Benefits of Parting
Some of the advantages of parting include:
- Efficiency: Parting is an efficient process as it utilizes the entire sheet, leaving minimal waste.
- Versatility: It can be used on a wide range of materials.
- Adaptability: The process can be adapted to various sizes and shapes.
Common Applications of Parting
Parting finds its uses in several applications, such as:
- Manufacturing of pipes and tubes.
- Creation of metal plates and bars.
3. Notching
Notching is a type of trimming operation in sheet metal manufacturing that involves removing material from the edge of a workpiece. This operation is used when the workpiece needs to have specific shapes or patterns on its edge.
Notching Process in Detail
- Design: The design or pattern to be notched is finalized.
- Setting Up: The workpiece is placed and secured in the notching machine.
- Notching: The machine cuts the workpiece according to the design.
- Inspection: The notched piece is inspected to ensure it meets the required specifications.
Benefits of Notching
Notching has several advantages, including:
- Precision: Notching can create precise patterns and designs on the edge of a workpiece.
- Versatility: It can be used on a variety of materials and thicknesses.
Common Applications of Notching
Notching is commonly used in:
- Creation of ventilation systems.
- Production of decorative metalwork.
Try Prolean Now!
4. Nibbling
Nibbling is a trimming operation used in sheet metal manufacturing that involves making a series of small cuts to create complex shapes and contours that are not possible with other techniques. This process is especially useful for detailed or intricate work.
The Nibbling Process in Detail
- Design: A detailed design is created, outlining the shape and contour that needs to be achieved.
- Setup: The workpiece is secured into the nibbling machine.
- Nibbling: The machine then makes a series of small cuts to create the desired shape.
- Inspection: The final product is inspected to ensure accuracy and quality.
Benefits of Nibbling
The advantages of nibbling include:
- Precision: Nibbling allows for high-precision work and is capable of creating complex shapes and contours.
- Versatility: It can be used on a wide range of materials and thicknesses.
Common Applications of Nibbling
Nibbling finds application in:
- Electronics manufacturing: For making complex shapes in circuit boards.
- Aircraft manufacturing: For creating detailed components.
5. Shearing
Shearing is a trimming operation that involves cutting a sheet of metal along a straight line. It’s a relatively simple and fast process that results in clean, straight edges.
The Shearing Process Detailed
- Measurement and Marking: The sheet metal is measured, and the cut lines are marked.
- Setup: The metal sheet is placed into the shearing machine.
- Shearing: The machine cuts the sheet along the marked lines.
- Inspection: The sheared pieces are inspected for accuracy and quality.
Benefits of Shearing
Shearing has several benefits, including:
- Efficiency: Shearing is a quick and efficient method for cutting sheet metal.
- Precision: It provides straight, clean cuts.
6. Lancing
Lancing is a unique trimming operation in sheet metal manufacturing where the sheet metal is cut and formed without removing any material. This operation creates a feature that is integral to the sheet itself.
Detailed Lancing Process
- Design: The lancing design is finalized, considering the function and application of the lance.
- Setup: The sheet metal is placed into the machine.
- Lancing: The machine cuts and forms the lance without removing any material.
- Inspection: The final product is inspected for quality and functionality.
Benefits of Lancing
The benefits of lancing include:
- Material efficiency: Since no material is removed during the process, there’s no waste.
- Flexibility: It allows for the creation of complex, integral features on the sheet metal.
Common Applications of Lancing
Lancing is used in applications such as:
- Automotive: For creating vents and louvers in auto parts.
- HVAC: For creating vents in the ductwork.
Summing Up
Understanding the different trimming operations in sheet metal manufacturing can aid in selecting the best technique for a specific project. Factors like the material type, shape and size of the workpiece, production volume, and desired finish can all influence this decision. Remember, the ultimate goal is to achieve a balance between cost-effectiveness and quality in the final product.
At Prolean, we provide expert sheet metal manufacturing services, including all the trimming operations discussed above. With a commitment to quality, precision, and customer satisfaction, we’re equipped to handle a wide variety of sheet metal projects. Contact us today for your sheet metal manufacturing needs!
FAQs
What is the primary purpose of trimming operations in sheet metal manufacturing?
The primary purpose of trimming operations is to remove excess material from a workpiece to bring it to its desired size and shape.
How is shearing different from other trimming operations?
Shearing is different because it involves cutting the workpiece along a line without the formation of chips or the use of burning or melting.
Can I use any trimming operation for any sheet metal manufacturing project?
Not necessarily. The choice of trimming operation depends on factors like the material type, shape and size of the workpiece, production volume, and desired finish.
How can Prolean’s services help me with my sheet metal manufacturing project?
At Prolean, we provide a range of sheet metal manufacturing services, including various trimming operations. Our team of experts can guide you in choosing the right trimming operation for your specific project needs.











I have experienced that achieving the precision in trimming of corner notches is very challenging. Do you have any specific suggestion.
Achieving precision in trimming corner notches can indeed be challenging, but using 2D laser cutting technology can help due to its high precision and accuracy. One specific suggestion is to use a laser cutter with a fine nozzle diameter and optimize the cutting speed and power settings for the specific material you’re working with. Additionally, using computer-aided design (CAD) software to precisely control the laser path can ensure that the notches are trimmed to the exact specifications needed.
Last year i outsource gear parts for my research from Prolean and now i got this article! So professional written about Sheet metal trimming.
Thanks for this blog. 1 thing I would choose to say is that nibbling is the best way for trimming the metal parts. Especially, you need to trim the sharp corners.
That’s correct !
Thank you for your insight! I agree, nibbling does seem like an efficient method for trimming metal parts, especially when dealing with sharp corners. It’s precise and helps in maintaining the integrity of the material. Do you have any specific tools or techniques you prefer for nibbling?