At Prolean Tech, we recognize the significance of using the right material for 3D printing. As it can make or mar project outcomes. Choosing the right materials is key to 3D print visually appealing and high-fidelity prototypes. Generally, the two fundamental 3D printing materials, ABS vs PLA plastic, are used in mock-up buildup due to their distinct properties.
PLA is more effortless to print into products. It usually causes minimal warping. So, it can be used to make fast prototypes. PLA becomes brittle when UV light strikes the material overtime. On the other hand, the strength of ABS material surpasses that of different 3D Printing Plastics because it can maintain high thermal resistance and provide optimal performance for functional parts.
Prolean Tech provides its customers with advantages beyond standard PLA and ABS products. Our 3D printing process allows us to work with 50+ materials to ensure prototype and functional part quality that matches your specific project needs. Let’s sort out the distinguishing aspects of ABS vs PLA plastic materials around 3D printing.
ABS Plastic Vs PLA Comparison
ABS 3D Printed Prototypes
PLA represents an eco-friendly thermoplastic. It originates from renewable plant materials, so-called biodegradable plastic. PLA requires low operational demands because of its easy workability and minimal production requirements.
Conversely, ABS has stronger durability and better heat resistance than PLA. It outperforms standard materials in strength, impact resistance, and temperature tolerance, making it suitable for functional uses. Moreover, it works well when applied to components that require resistance against stress and harsh conditions.
Prolean Tech brings a wealth of expertise and the materials to help you achieve superior prototypes with quick development and end-use applications.
Comparison of Printing Parameters: PLA vs ABS Plastic 3D Printing
PLA 3D Printed Products
Here’s a table comparing the printing parameters for ABS and PLA:
Table 1: Comparison of Printing Parameters: ABS vs. PLA
| Printing Parameter | ABS | PLA |
| Printing Temperature | 210-250°C | 180-220°C |
| Bed Temperature | 100-110°C | 50-60°C |
| Shrinkage During Cooling | High (can cause warping) | Low (minimal shrinkage) |
| Warping Tendency | High (needs controlled environment) | Low (less prone to warping) |
| Fumes Produced | Unpleasant (requires ventilation) | Sweet, corn-like smell (non-toxic) |
| Ventilation Required | Yes | No |
Which method saves you more cost; 3D Printing vs CNC Machining? Learn both techniques.
Advantages of PLA Compared to ABS
PLA Filament For 3D Printing Parts
The advantages of PLA surpass those of ABS. Its common benefits include:
- PLA’s printing process becomes more manageable because it works well with lower printing temperatures and demonstrates better stability than other materials.
- PLA requires neither a heated bed nor an enclosed build chamber. Thus, it is more straightforward for most 3D printers.
- PLA is an eco-friendly material. It produces non-harmful by-products through industrial composting when specific conditions exist.
- PLA provides customers with an affordable price range than they would find with ABS or other thermoplastics. (Get more insights on best pla filament)
- PLA can produce detailed and refined prints. This makes it optimal for creating prototypes and detailed models.
- The printing of PLA produces almost no odor compared to the strong, unpleasant scents that emerge from ABS plastics.
Disadvantages of PLA Compared to ABS
PLA Peel-Off Issue
Besides its benefits, PLA also has several drawbacks that should be noted.
- PLA is more brittle than ABS, making it more prone to breaking under impact or stress conditions.
- PLA(Polylactic Acid) material weakens rapidly when exposed to ultraviolet radiation. Exposure to direct sunlight speeds up the breakdown process of PLA parts more than it does for ABS.
- PLA starts to soften at relatively low temperatures (around 55-60°C). This makes it less suitable for harsh environments. Although its performance can vary depending on the specific conditions.
- The strength of PLA stands below ABS. Because it becomes less durable when used for parts that experience regular wear and tear.
- The porous nature of PLA allows it to absorb moisture from the surrounding atmosphere. This impacts the quality and strength of printed objects over time.
Try Prolean Now!
ABS Overview and Comparison to PLA
Custom ABS Products
Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS) is a durable thermoplastic patented in 1948 and became commercially available in 1954. The production of ABS occurs when styrene unites with acrylonitrile during the polymerization process. ABS’s impact strength and strength exceed those of PLA because it exhibits a more flexible structure than PLA. ABS is the perfect solution for durable part requirements.
Advantages of ABS Compared to PLA
ABS 3D Printed Toys
The benefits of ABS Machining over PLA plastic include:
- The glass transition temperature of ABS plastic is higher than that of PLA. It maintains its integrity at elevated temperatures until it softens or melts. This makes it appropriate for use in hot environments.
- The mechanical properties of ABS exceed those of PLA. It demonstrates superior strength and durability. Parts needing extended endurance should utilize ABS since it handles impacts well and endures better against regular damage.
Drawbacks of ABS Compared to PLA
ABS Cracked Print Part
ABS does have some limitations. These are given below:
- The printing process of ABS usually requires elevated temperatures because it is likely to warp easily during production. Printing becomes more challenging when you lack a heated bed and a controlled setting.
- Printing ABS materials produce VOCs and UFPs. These emissions can trigger eye and respiratory system problems. So, ABS’s printing process needs adequate ventilation and protective safety gear to ensure safe operation.
Which Has More Accuracy in 3D Printing: PLA or ABS?
Custom PLA Products
The determination of 3d printing accuracy depends mainly on the printer’s built-in calibration system and the complexity level of the designed model. Both filaments enable designers to create parts with precise dimensions. For instance, printed components made of PLA or ABS reach tolerances up to 0.5 mm when using a minimum wall thickness of 1-2 mm. The given range keeps the parts structurally sound.
The accuracy capabilities of PLA material exceed those of ABS material, mainly when working with complex details. PLA printing at reduced temperatures produces more stable results because it resists warping and is thus superior for fine features with sharp corners.
Try Prolean Now!
Key Differences Between PLA and ABS Properties
Infographic: Difference Between ABS vs PLA
Below is a comparison table highlighting the key properties of PLA and ABS:
Table 2: Comparison of Properties between PLA and ABS
| Characteristic | ABS | PLA |
| Suitability for Heat-Intensive Applications | Yes | No |
| Resistance to UV Light | Moderate | Low |
| Brittleness Factor | No | Yes |
| Environmental Friendliness | No | Yes |
| Emissions During Printing | Yes | No |
| Renewable Source Material | No | Yes |
| Heat Distortion Temperature @ 66 psi (°C) | 96°C | 55°C |
| Cost Efficiency | Low | Very Low |
| Tensile Strength (XZ MPa-ZX MPa) | (~32 MPa) | (~50 MPa) |
| Impact Resistance (Notched Izod, J/m) | 200 – 215 | 96.1 |
| Resistance to Wear | Yes | No |
Prolean Tech often gets regular customer inquiries regarding the distinctions between PLA and ABS. Our discussion will focus on the primary factors and the assessment of material capabilities separately. The guidelines will assist you in choosing between these options that match your requirements.
Applications
PLA is commonly used for prototyping and hobby projects. But, it also finds specific applications in biomedical fields. Industrial and consumer-grade products tend to avoid using PLA. ABS serves the manufacturing sector effectively because it delivers power and shock resistance, which meets the needs of high-demand applications.
Part Accuracy
PLA provides simple printing capabilities. It has high dimensional stability, supporting its use for precise and dependable component manufacture. Due to temperature fluctuation throughout the printing process, ABS undergoes warping, negatively affecting its precision. Our team uses advanced tools like heated beds, calibration systems, and lasers for DMLS to make ABS prints and achieve precision in complex designs.
Speed
ABS printing speed should be adjusted slightly slower than PLA speed to prevent warping and stringing defects. PLA prints are without issues when operated at elevated speeds. Because it has a lower melting temperature than ABS plastic.
Surface Finish
Prints of both PLA and ABS materials will display visible layer lines using FDM (Fused Deposition Modeling) printing. Acetone vapor enables ABS to produce glossy and uniform finishes for smoothing purposes. Comparingly, manually sanding PLA produces a smoother finish. However, this process is not suitable for PLA.
Heat Resistance
ABS material demonstrates higher heat resistance than PLA material. PLA becomes pliable at temperatures starting at 55-60°C, yet ABS maintains its structural stability until reaching temperatures of 96-105°C, which makes ABS a suitable material for heat-exposed parts.
Biodegradability
PLA is biodegradable in industrial composting facilities. But it can take up to 80 years to break down naturally. The non-biodegradable nature of ABS leads to years-long decomposition times, thus making it less environmentally advantageous than PLA.
Cost
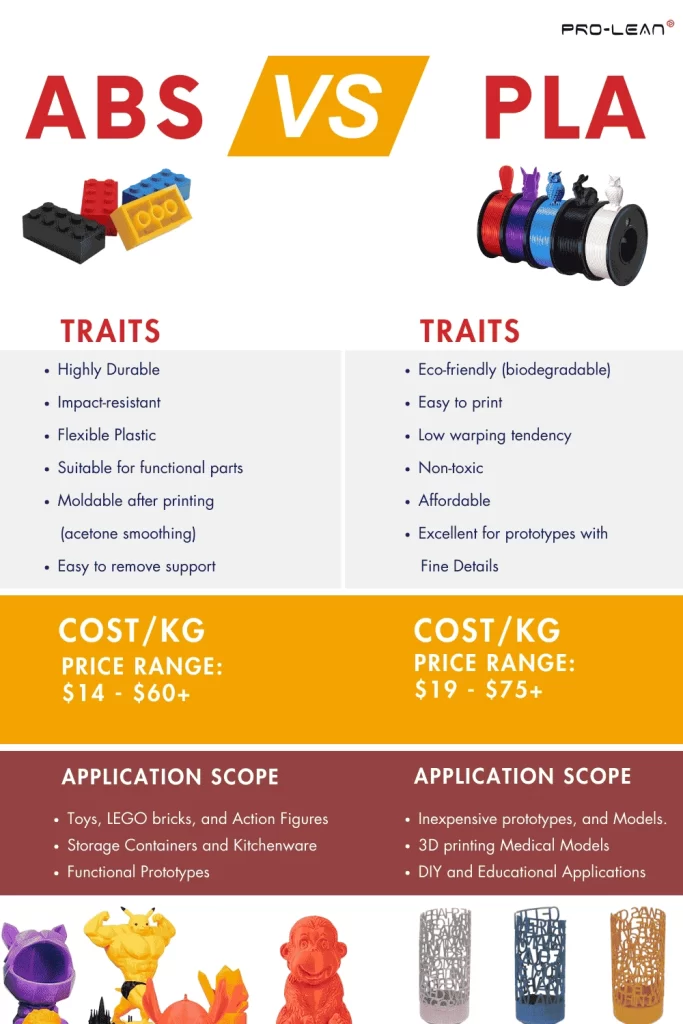
The prices of PLA and ABS 3D printing materials hobbyists use remain between $20 per kilogram. ABS costs slightly higher than PLA, although the difference in pricing between these materials remains minimal. You can utilize the Prolean Tech Instant Quoting option to check costs between materials.
Table 03: Summarizing the cost considerations for ABS and PLA
| Cost Factor | ABS | PLA |
| Price Range (per kg) | $14 – $60 (€11.90 – €51) | $19 – $75 (€16.15 – €63.75) |
| Material Source | Petroleum-based | Renewable resources |
| Price vs. Quality | Lower cost but quality varies | Generally higher cost but eco-friendly |
| Cost-Effective Option | Purchase from suppliers | Purchase from suppliers or make your filament |
| Filament Production Option | Can be made using Filament Extruders | Can be made using Filament Extruders |
Surface Finish Comparison: PLA vs. ABS
Matte Finished ABS
- Both PLA and ABS prints usually show visible layers on the finished part.
- PLA typically gives a glossy finish. Thus, it’s a good choice for aesthetic prototypes.
- ABS-printed parts typically have a matte finish. It may be less visually appealing than PLA.
- With ABS, you can use acetone during post-finishing to achieve a smooth, glossy finish.
- You can use sanding or machining for a smoother finish on PLA prints, but these processes must be done carefully.
Alternatives to PLA Vs. ABS Plastics
PETG Filament
While PLA vs ABS are commonly used materials, PETG (Polyethylene Terephthalate Glycol) is another notable option. It exhibits combined features between PLA and ABS. It prints quickly like PLA but has the strength and durability similar to ABS. Unlike ABS, PETG doesn’t warp as much and doesn’t produce harmful fumes during printing. It’s an excellent choice for projects that require good mechanical properties without the challenges.
Concluding Notes
Choosing between ABS vs PLA plastic depends on your needs. ABS is strong and flexible, making it a good option for durable parts. While PLA is eco-friendly and perfect for true-to-detail prototypes and decorative goods. Consider testing both materials and using a Filament Maker to save costs and customize your projects.
Prolean offers best-in-class custom 3D printing services. Whether you need prototyping or full-scale production, we deliver parts with SLA, FDM, SLS, and DMLS printing capabilities with precise tolerances of ±0.025 mm. Our ISO 9001:2015 certification dictates top quality, and we can precisely handle complex shapes and geometries. We offer quick turnaround times, with lead times as short as one day. Reach out to us if you have any queries.
FAQ’s
Q1. What are the main differences between ABS and PLA plastic?
ABS is more potent and can handle higher temperatures, while PLA is biodegradable and easier to print. PLA has a glossy finish, while ABS has a matte finish. ABS is better for functional parts, and PLA is better for prototypes and visual models.
Q2. Which plastic is better for 3D printing beginners: PLA or ABS?
PLA is easier to print and works well for beginners. It doesn’t require a heated bed and prints at lower temperatures. ABS can be tricky to print and needs more control, like a heated bed.
Q3. Can ABS and PLA be used interchangeably in plastic machining?
No, ABS and PLA aren’t used the same way in machining. ABS is more rigid and works better for functional parts. PLA is more brittle and isn’t ideal for parts that need strength.
Q4. Is PLA or ABS better for the environment?
PLA is biodegradable and made from plants. ABS is made from petroleum and isn’t biodegradable. PLA is a more eco-friendly option.
Q5. Which plastic is better for high-temperature applications?
ABS is better for high-temperature applications because it can handle higher heat. PLA can start to soften at lower temperatures and isn’t suitable for heat-sensitive parts. ABS stays strong in heat.
Q6. Does ABS or PLA have a lower production cost in manufacturing?
PLA is generally cheaper to produce because it’s made from renewable materials. ABS is slightly more expensive as it’s made from petroleum. The cost difference is usually slight.
















0 Comments