TPE vs TPR Material Comparison
If you’ve ever had to choose between Thermoplastic Elastomers (TPE) and Thermoplastic Rubbers (TPR), you know it’s not as simple as flipping a coin. Both materials are widely used across various industries, including automotive, healthcare, and consumer goods; however, they’re not interchangeable.
Selecting the wrong one can result in unnecessary costs, performance issues, or a product that fails to meet expectations. That’s why we’re here to help you make sense of it all.
With this guide, you can choose between TPE and TPR, whether you’re building a product that requires durability, flexibility, or ease of processing. We’ll break down the key similarities and differences between TPE and TPR, so you can confidently select the one that works best for your specific project.
So, if you’re ready to take the guesswork out of material selection, scroll down to see why we’re trusted by professionals just like you.
What is TPE?
Pile of White TPE Plastic Pellets
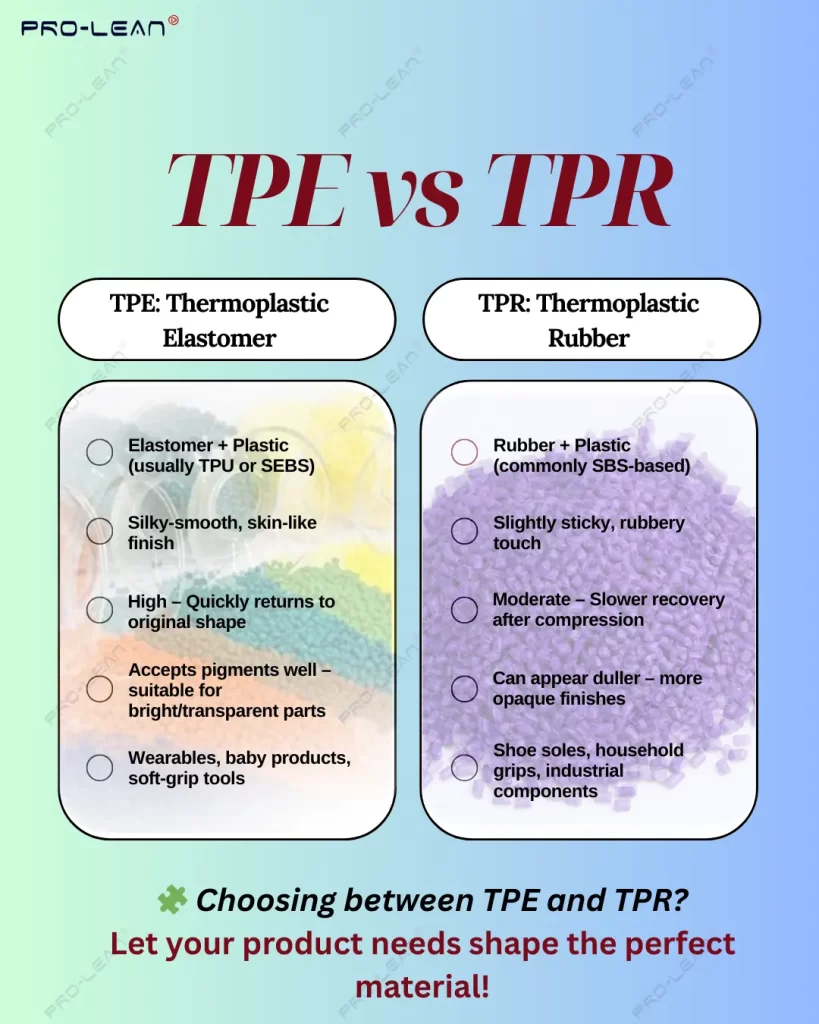
TPE stands for Thermoplastic elastomers. They show Rubber-like performance qualities, which are manufactured similarly to plastics. Block polymers and mixtures of crystalline and amorphous polymers are among them.
A comprehensive overview of injection molding reveals that the hard blocks impart TPE material polymers with properties such as resilience to temperature changes.
In addition to providing elastomeric qualities, the soft blocks are responsible for hardness, flexibility, and the degree of irreversible deformation. The key difference lies in their processing: thermoplastic elastomers can be repeatedly melted and reshaped, whereas rubber typically undergoes irreversible vulcanization.
Interesting Read: Guide to custom undercut mold parts
Despite being thermoplastic, thermoplastic elastomers exhibit the same elasticity as their cross-linked rubber counterparts. Its hardness or softness, as measured using a Shore durometer, determines this.
TPEs are soft gel materials that range in quality from 20 Shore OO to 90 Shore AA. They have characteristics of crosslinked rubber. They can be constructed to reach a hardness of up to 85 Shore D when they are introduced to the Shore D scale.
Again, in line with TPE, TPRs come in a broad range of durometers, from 20 Shore OO to 85 Shore D.
What is TPR Material?
Pile of White TPR Material Pellets
Block copolymers, such as styrene-butadiene-styrene (SBS), are used to create thermoplastic rubber with a semi-crystalline structure. TPR rubber can be produced more affordably and supports injection molding and other manufacturing processes, in contrast to vulcanised rubber, which requires a lot of time and labour to make.
Understanding the key components of injection molds simplifies the process. Complex pieces can be made by injecting molten TPR into a mould; overmolding is the process of molding it over a more rigid material, such as a tool handle.
Explore aerospace-grade injection molding to know more about the applications of TPR material.
Try Prolean Now!
TPE vs TPR: One-on-one Comparison
| TPE | TPR |
| High-flexural fatigue resistance | High-flexural fatigue resistance |
| Resistant to tears and abrasions | Resistant to tears and abrasions |
| High-impact strength | High-impact strength |
| Good dielectric properties | Good dielectric properties |
| Excellent weather and chemical resistance | Excellent weather and chemical resistance |
| Recyclable | Recyclable |
| Temperature range: -22°F to 284°F (30°C to 140°C) | Temperature range: -22°F to 284°F (-30°C to 140°C) |
TPE vs TPR
What are the Advantages and Disadvantages of TPE?
Advantages and Disadvantages of TPE
For a thorough understanding of the process, you should refer to ‘Metal Injection Moulding (MIM): A Complete Guide’.
Benefits
Thermoplastic elastomers offer the following benefits:
- Excellent pliability for uses requiring compression and stretching without breaking
- Processing simplicity with conventional thermoplastic techniques, such as injection molding
- Durability for usage in tough locations and demanding situations
- Cost-effectiveness, particularly in production runs with large volumes
- TPES is a fantastic option for medical tubing due to the ease of sterilisation.
- Don’t need stabilisers, curing resins, or reinforcing agents.
- Created with a variety of characteristics, including rigidity against flexibility and softness versus hardness.
Drawbacks
- Use in high-temperature applications is restricted by a lower melting point.
- Limited ability to withstand chemicals
- When exposed to UV light, TPEs deteriorate or discolour, which restricts their use in outdoor settings.
- They include specific types of additives that make them difficult to recycle.
- More costly than rubber-based materials
What are the Advantages and Disadvantages of TPR Material?
Advantages and Disadvantages of TPR Material
Here are some of the advantages and disadvantages of TPR material:
Benefits
Thermoplastic rubber materials offer the following benefits:
- Durability and flexibility for applications requiring compression, bending, or twisting
- Processing simplicity for large-scale production, such as Injection Molding.
- Using chemicals like lubricants and solvents in hostile conditions requires chemical resistance.
- less expensive than specific specialty polymers and natural or synthetic rubber
- TPR’s qualities and usage are versatile, with applications ranging from footwear to medical devices.
Drawbacks
Despite their numerous benefits, TPR materials have certain drawbacks.
- Loss of flexibility or brittleness when exposed to temperatures outside of their service range
- Not as resilient or able to bounce back as natural or synthetic rubber
- The possibility of creep, or gradual deformation under continuous load that may lead to dimensional changes, is minimal.
Learn about Different Injection Mold Types: Analyzing Classifications and Characteristics.
Try Prolean Now!
Which is better, TPE or TPR?
TPE or TPR: Which Material is Better?
Choosing between TPE and TPR often sparks debate, but neither is universally better. TPE is an umbrella term that encompasses a diverse family of flexible, rubbery plastics. TPR is a specific, popular member of this family, known for its classic rubbery feel and cost-effectiveness.
TPR, primarily based on styrenic block copolymers, excels in applications that demand a familiar flexible grip, such as shoe soles and tool handles. It offers an outstanding balance of performance and type material price.
However, the broader TPE family boasts members with unique strengths. Do you require extreme temperature resistance or specific chemical resistance? Specialized TPEs often outshine TPR. Looking for gel-like softness or rigid flexibility? Again, the broader TPE spectrum provides more options.
So, depending on the application, you can find both as the better option from time to time. For everyday rubbery needs, TPR is often the ideal choice. However, for specialised demands, exploring the diverse TPE family is crucial to finding the perfect material match.
If you’re wondering about where to buy TPE and TPR material, ProleanTech-Your custom parts manufacturing partner is the best choice.
Wrap Up
When choosing between TPE and TPR, consider your specific application requirements. TPR offers cost-effective flexibility for everyday applications, while specialized TPEs provide unique properties for demanding environments.
Understanding these materials helps you make informed decisions that impact product performance and manufacturing costs. For optimal results in your Injection Molding projects, consult with ProleanTech’s materials experts.
Ready to start your next project? Contact us now for guidance on material selection and receive an instant quote for your custom manufacturing needs.
FAQs
Q1. What does TPE stand for?
TPE stands for thermoplastic elastomer. It’s generally modified from SEBS and has applications in medical devices and grips.
Q2. Is TPE plastic or rubber?
Thermoplastic elastomers (TPEs) are a type of plastic that has been refined to create a soft, rubbery feel. They have a springy texture but are made of plastic.
Q3. Does TPE contain BPA?
TPAs are considered safe and non-toxic as they do not contain BPA.
Q4. Is TPE FDA approved?
TPE helps keep food preserved and as fresh as possible. Star TPE is an excellent choice for use in consumer and industrial food and beverage applications.
Q5. Is TPR the same as silicone?
TPR material is a kind of thermoplastic rubber, while silicone is a highly active adsorbent material, which is an amorphous substance.
Q6. Is TPR plastic safe?
Yes, TPR does not contain any harmful chemicals, and it’s BPA-free. Therefore, it has applications in the food and medical industry.











0 Comments