
Industries globally produce countless products to cater to varied consumer needs. They use different manufacturing methods, some modern and others conventional. Machining and casting metalworking are popular in plastic and metal manufacture.
None of these technologies is inferior to the other; each has its areas of application so it gives excellent results when used relevantly. As an enterprise, you want to consider analyzing the pros and cons of each before using it for a particular manufacturing requirement. For instance, machining metal is faster than casting for low-volume production, but it may not match the repeatability of casting.
This article compares and contrasts these manufacturing methods in detail.
Exploring Machining
Machining is a manufacturing technology that entails the removal of excess material from a block or workpiece to create a desired part. Machinists use machine tools to perform machining in a controlled and predictable manner.
Advanced machining is performed by specialists using CNC machines and special cutting tools. Prolean Tech uses specialists and advanced cutting tools to help clients achieve market success with CNC machining.
CNC stands for computer numerical control. It implies that the machining metal process is computer-controlled. In the previous century, the machining process was manual. The machinist personally controlled the machine using knobs and levers.
A special software based on the G-code language is at the center of this control. In simple terms, CNC machining allows the user to pre-determine the position and speed and run them repeatedly and predictably.
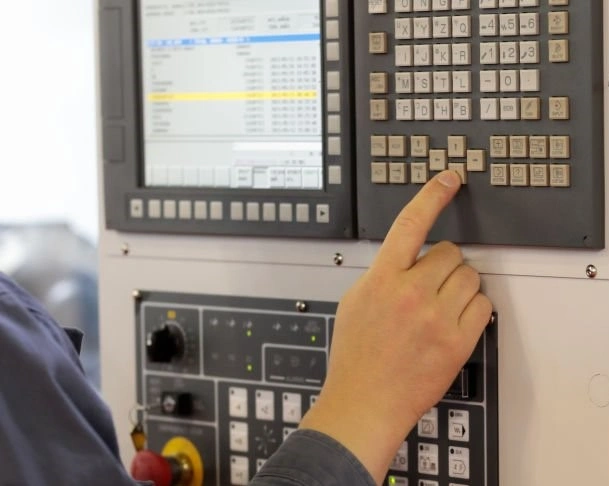

Inserting code for CNC machining
Try Prolean Now!
Examples of CNC Methods
Since the merger of tools with motors in the 1940s, several CNC machining methods have emerged. The most commonly used CNC machining methods include the following:
CNC Turning
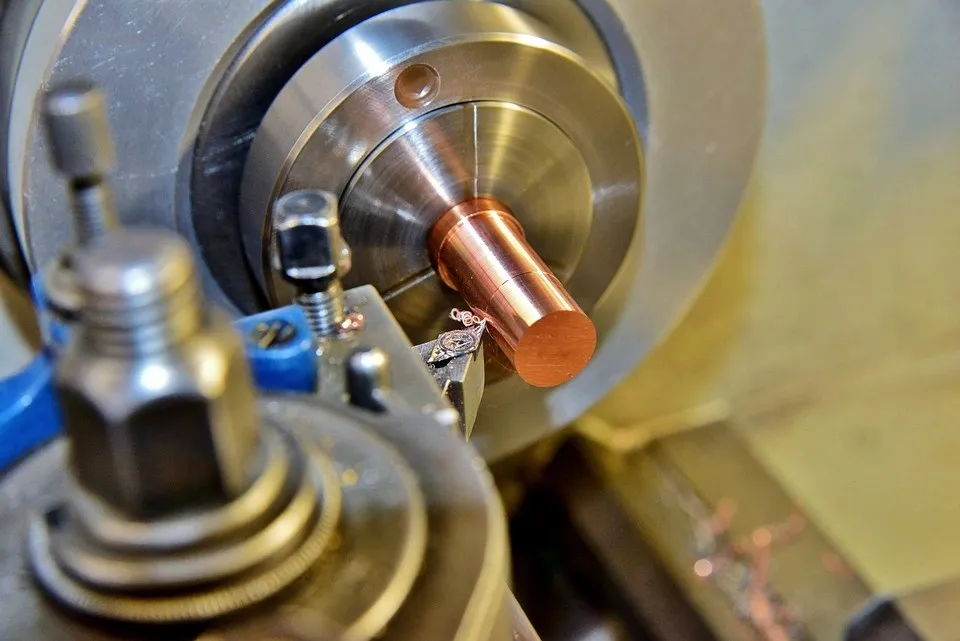
Metal turning operation on a lathe
Turning is a popular traditional machining technique, probably one of the earliest metal machining methods. This process involves holding a workpiece on a mandrel or plate. The mandrel or place rotates at a specified speed as a tool fixed on a fixture removes material from the workpiece.
The fixture connects to a movable slide, which can be at any position. The slide can move to and from the centerline, and closer or farther from the mandrel/plate.
Machinists use lathes to produce concentric shapes on workpieces. A lathe can produce features such as threads, slots, shafts, and cylinders. Contact us to learn about many other lathe products.
CNC Milling
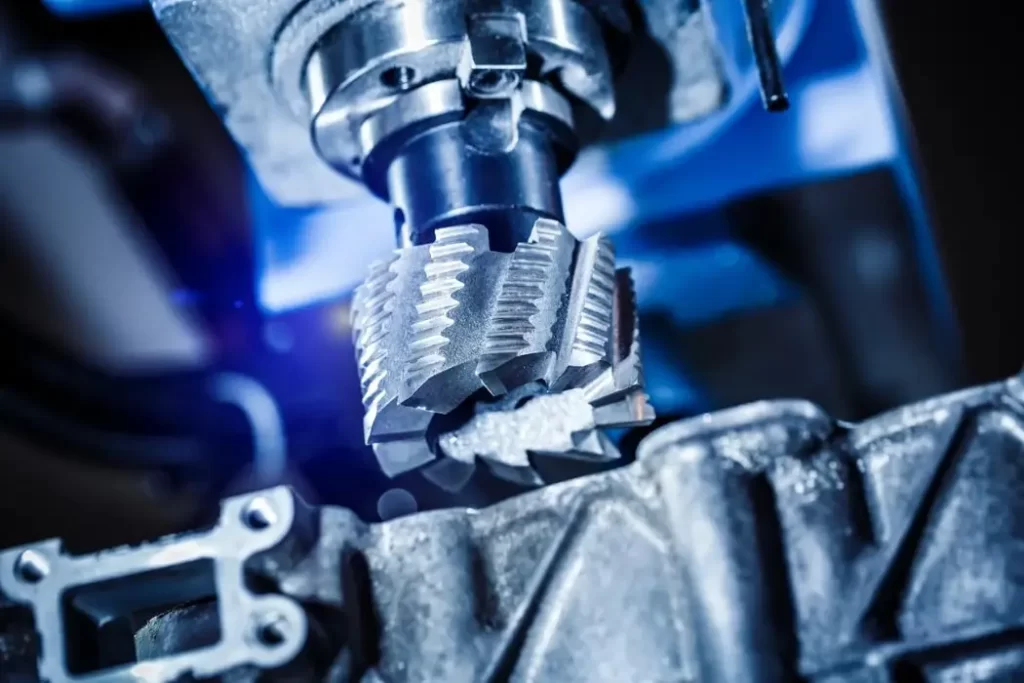

CNC milling
While the workpiece for turning operations rotates, it is stationary for CNC milling operations. Instead, a rotating spindle holding the milling tool rotates. In the most common setup, a table that can move in the X and Y directions holds the workpiece firmly via a vice.
The spindle of a CNC milling machine can move in the X, Y, and Z directions. It can also accommodate different types of milling tools. Unlike the CNC turning machine, the CNC miller can remove material from unconventionally shaped workpieces. Some features you can achieve with CNC milling are keyways, profiles, and chamfers.
CNC Laser Cutting
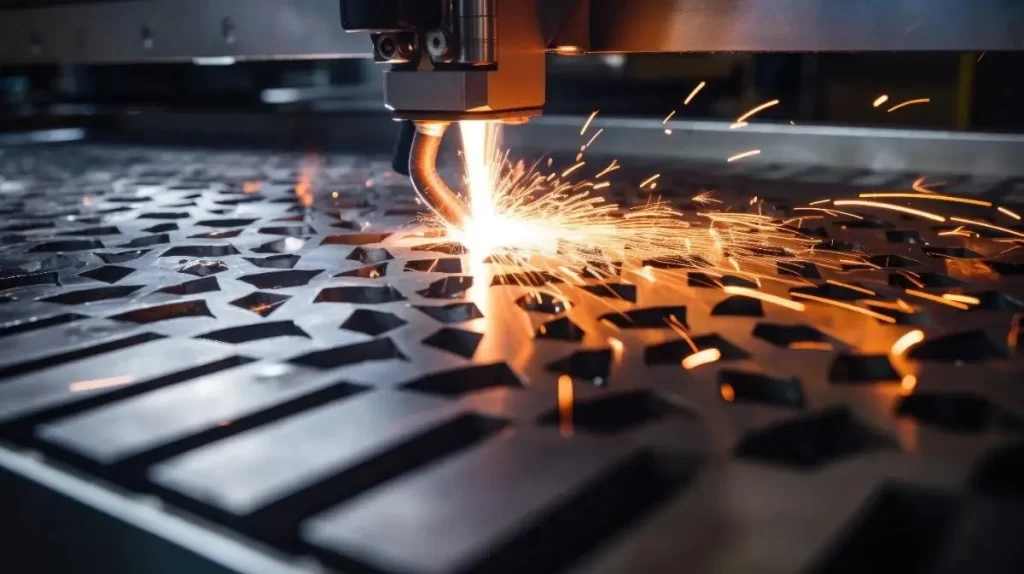

CNC laser cutting in progress
This machining method cuts and engraves material using a computer-controlled powerful laser beam. It is an incredibly accurate technique that produces intricate shapes that are difficult to achieve by hand. Medical, automotive, and electronics are among the leading users of CNC laser cutting.
The CNC laser cutting process starts with a design of the desired shape. The computer-aided design (CAD) software design is then converted to machine language and fed into the CNC machine.
Once the CNC laser cutting machine is set up, the laser beam is focused on the material to follow the programmed path. The beam removes material along the path through vaporization or melting. If required by the application, this cutting may be followed by post-processing steps such as surface treatment and deburring.
CNC Plasma Cutting
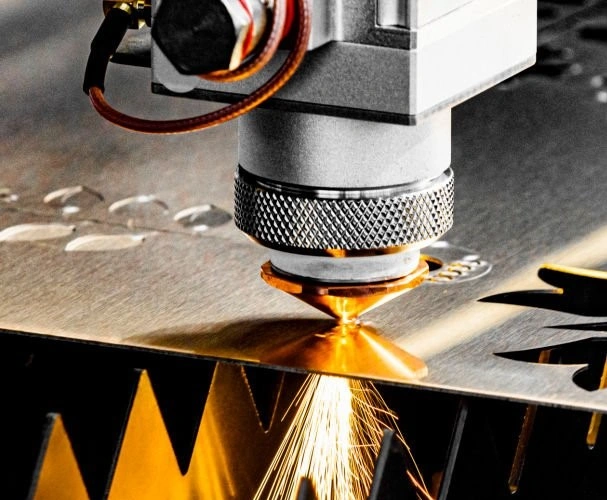

CNC plasma cutting
For this CNC machining method, there is a combination of three elements of plasma: Speed, energy, and temperature. Plasma is a highly ionized gas, usually called the fourth state of matter. It instantly heats most metals above their melting points, hence it is a very effective machining force.
The process of this cutting technique starts with the provision of inert gases and oxygen to the cutting head. Arc ignition follows, instantly creating free electrons and ions, which comprise plasma. Since plasma is extremely powerful and thousands of degrees centigrade hot, it can easily cut through metal.
CNC plasma cutting is highly precise and efficient, and that’s why it is present in many industries. It is widely used in automotive, construction, and manufacturing, among many other industries that use machined metal.
CNC Drilling
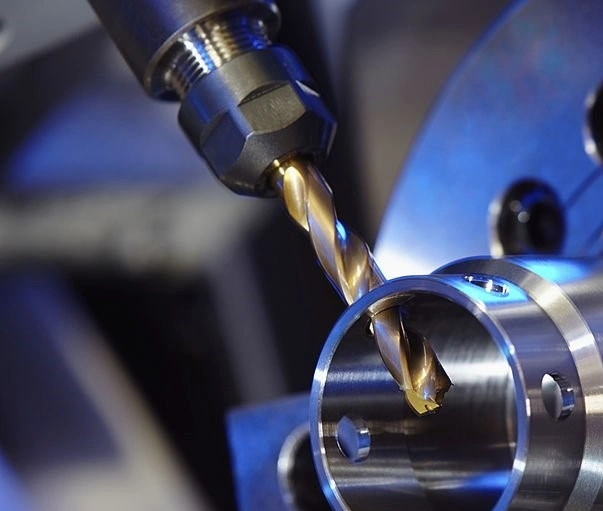

CNC Drilling
CNC drilling is another popular CNC machining metal process that follows almost the same steps as other operations. Machinists use it to create round holes in a workpiece for bolts and screws in assembly projects.
First, a digital design is created using CAD software. This is followed by the conversion of this design to drilling machine instructions. The CAM software is popular for the generation of the required codes for the machine.
When these codes are fed to the CNC machine, they dictate how the drilling process proceeds. The operator ensures the machine has the right tooling and then executes the machining operation.
CNC Waterjet Cutting
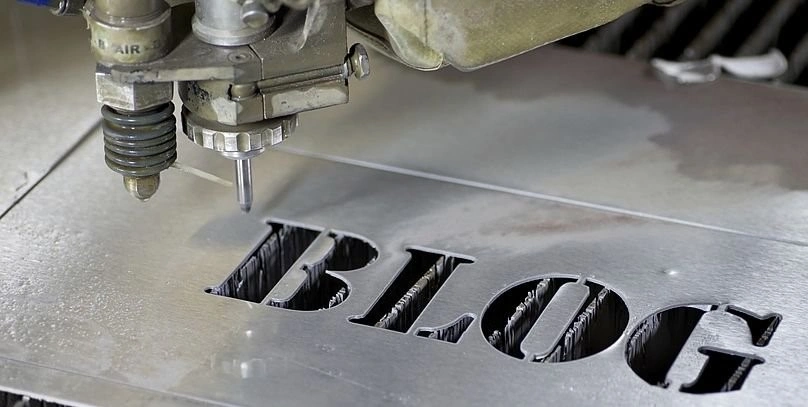

Waterjet cutting method
The CNC waterjet cutting technology comprises a high-pressure water stream plus abrasives directed on the workpiece. Accurate and versatile, this machining technique is used for many materials and industries.
The water pressure can reach 90,000 psi, thanks to the powerful intensifier pumps embedded within the machine. Other main components of the CNC waterjet cutting machine are the jet nozzle, abrasives system, cutting table, and control software.
The Pros and Cons of Machining
| Pros of Machining | Cons of Machining |
| Tight tolerances and high-precision | Machining complex shapes can be costly and time-consuming. |
| Versatile – can work on a wide range of metals and non-metals | Production time is higher for parts that need high material removal. |
| With the right expertise, minimal material wastage | Replacements needed for tools, |
| Capable of producing superior surface finish | High expertise needed for CNC programming and setting up the machine |
| Repeatability through the reuse of saved CNC programs | The worktable limits the size of machined metal. |
What is a Casting?
Casting metalworking is an ancient metal manufacturing method of creating the desired product by pouring molten metal into a specially shaped mold. After the molten metal has been poured into the mold, it solidifies after some time.
The most popular application of the casting method in the olden days was in the production of soldiers’ armor and swords. Over time, metal casting has advanced to the modern version which is more intricate and versatile. It can be compared competitively in the machining vs casting debate.

Traditional sword
ProleanTech is home to advanced casting processes, specifically vacuum casting. The company produces high-quality prototypes and low-volume parts. It uses 3D printing and CNC machining to create accurate patterns.
Consider These Methods of Casting
There are many casting methods based on the product’s size and shape, among other considerations. Below are some of the most common metal casting methods for machining vs casting.
Sand Casting
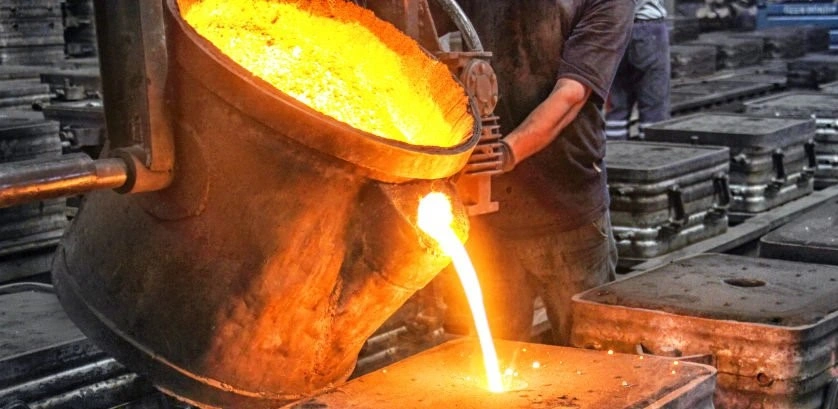

Sand casting process
This is another traditional casting metalworking method, which involves charging molten metal into cavities formed in bonded sand. As the molten metal solidifies, it forms the shape of the cavity. In the most basic form, two boxes, each with a shape of a section of the intended part.
Sand casting is versatile, being capable of producing small and large parts. Most metals can be used in this technique. The process starts with the formation of the pattern, then followed by mold creation. When the mold assembly is ready, the molten metal is introduced into the mold cavity.
The process is given time to cool before the metal casting is extracted from the mold.
Die Casting
Die casting is a complex manufacturing procedure that is popular in automotive industries among other areas. It entails feeding molten metal to a mold cavity to generate the envisaged product. Aluminum, zinc, and other non-ferrous metals are the most applicable for die casting services.
The general steps of die casting are die preparation, metal preparation, metal injection, cooling, ejection, and finally, trimming.
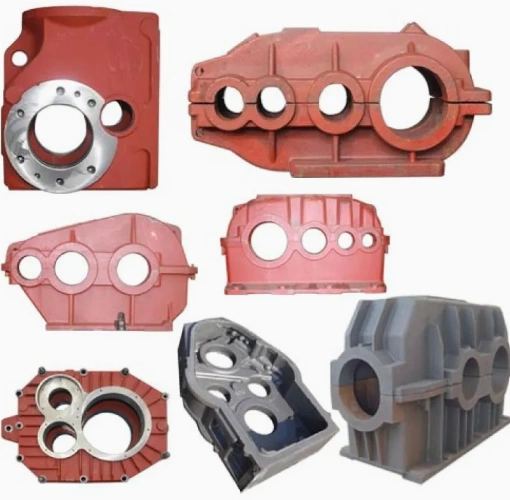

Die cast parts
The two major categories of this metal manufacturing method are hot-chamber and cold-chamber die casting. Aluminum and other alloys with high melting points apply for cold chamber die casting, while hot chamber die casting works best with low-melting-point metals such as magnesium.
Follow this guide on Top Casting Metals for Manufacturing: Choices & Applications for more about the materials.
Investment Casting
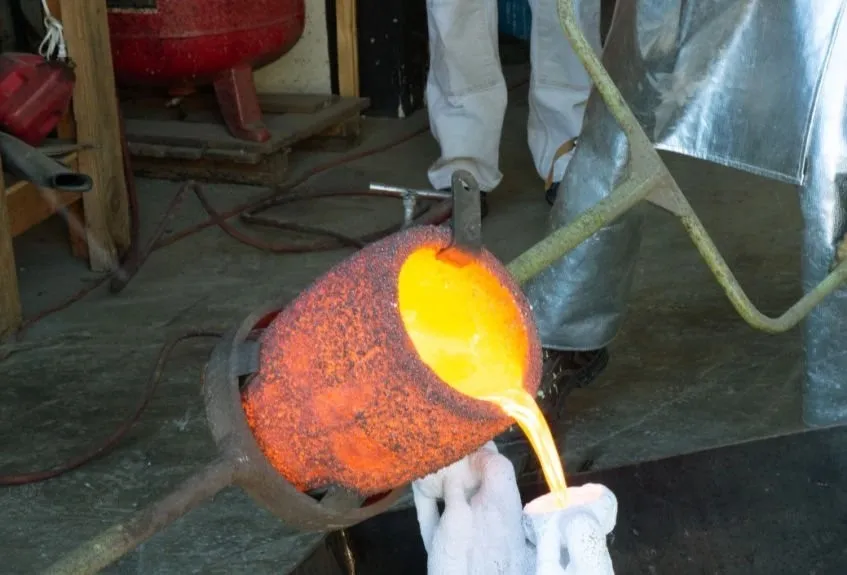

Lost-wax casting
This centuries-old metal processing method is also called lost-wax casting. Manufacturers of precise parts prefer this casting technique, particularly for repeatable productions.
The first step in investment methods of casting is the formation of a wax pattern representing the desired part shape. A ceramic shell is then applied to the pattern and allowed to solidify to create a mold.
When the wax is melted, it leaves behind a cavity within the ceramic shell mold. Molten metal is then poured into the mold cavity, allowed to solidify, and retrieved by breaking the mold. Investment casting is an ideal technique for complex shaped and smooth-surfaced parts.
Vacuum Casting
Akin to the name, vacuum casting is a metal casting method that utilizes vacuum pressure to expel bubbles and gases from the molten metal and mold cavity respectively. This happens in a vacuum chamber with pressure of up to 100 bar.
Automobile part manufacturers are renowned for using vacuum casting, although the method is also present in the aerospace and electronic industries.
Try Prolean Now!
The Pros and Cons of Methods of Casting
| Pros of Casting | Cons of Casting |
| Complex shapes | Not effective for too-large parts |
| Cost-effective | Defects and porosity in parts |
| Many sizes of products | Not suitable for materials that cannot be melted and solidified |
| Versatile | Time consuming |
| Minimal waste | Challenging to deliver extremely tight tolerances |
What is the Difference between Casting and Machining? Points to Remember When Choosing
Consider the following points when choosing between machining vs casting:
Design Complexity
For the manufacture of complex parts, metal casting manufacturing is better than CNC machining services. This technique is effective in producing sharp corners and edges, which machining would struggle to produce. Since the metal is first melted and then poured into the mold, virtually no shape is not produced.
This argument doesn’t entirely rule out the capability of machining to produce intricate part geometries. CNC machining is used to produce screws, bolts, and other parts with specific features.
Dimensional Accuracy
Casting tends to have less dimensional accuracy than machining because of warping and shrinking caused by the inability to completely control the cooling process. With advanced cutting tools and CNC machines, there is an advantage to machining metal parts with higher dimensional accuracy.
Cost of Manufacturing
Cost is a fundamental consideration for most manufacturers comparing machining vs casting. One may be tempted to conclude that machining is the obvious costlier process because of all the advanced technologies involved. However, it is important to consider all the different factors and scenarios that may be at play.
The specific material and production volume can sway the cost to either side. For low volumes, CNC machining may have an edge. Casting manufacturing is more economical in high production volumes.
Material Suitability
The type of material used to manufacture the product is another significant factor. Any metal that can be melted and poured using the crucible can be cast. A long list of ferrous and non-ferrous metals apply in this case. Casting accommodates non-metals as well, including concrete and epoxy.
About versatility, there is an advantage in machining a broad range of metals and non-metals.
It is important to note that casting works best for specific metals that are well-suited for the method.
Production Volume
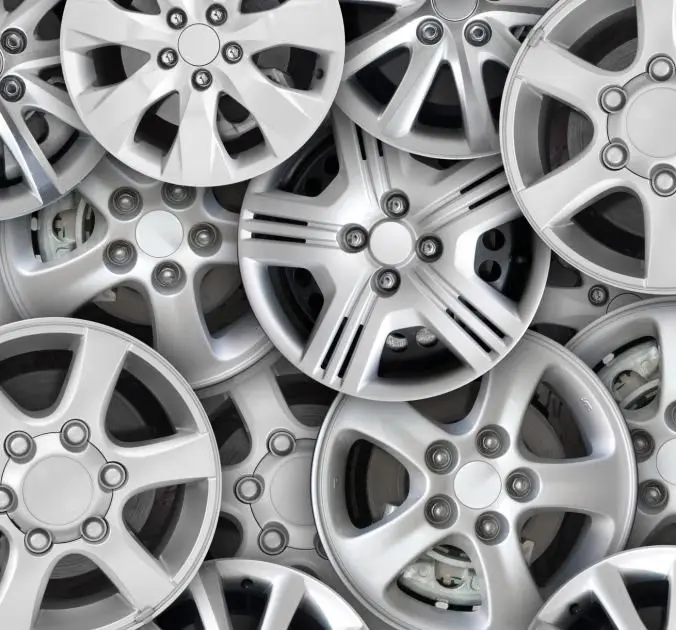

Car Rims
Metal casting is faster than metal machining in high-volume part manufacture. As long as the mold is ready, the solidification time is shorter and the processing time is shorter too.
If your project seeks to produce many parts quickly, you would rather use a metal casting method. Machining beats casting metal on speed if the parts needed are only a handful. This is because there are no molds to prepare in CNC metal machining.
Prototyping
If you are at the prototyping stage of manufacturing, then choosing CNC machining over metal casting would be better in machining vs casting comparison. Molds can be extremely expensive for this exercise, probably in the thousands of dollars per design. Plus, you need to create a different mold every time a design is rejected.
CNC machining is more flexible when it comes to changing a design. All that’s required is to modify the model and program.
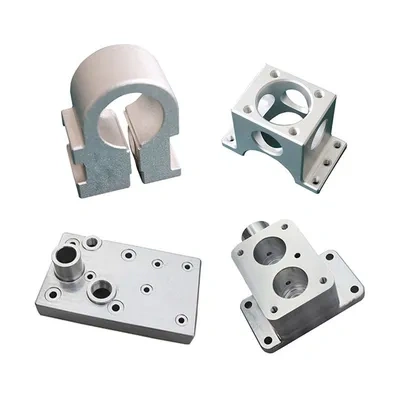

Metal prototypes
Try Prolean Now!
Conclusion
Both machining and casting are relevant in today’s manufacturing environment. However, their pros and cons may differ, so their preferences and suitability in different projects are varied. For someone looking for the best surface finish, machining would be the better method. Casting is ideal for complex products and mass production.
Contact Prolean Tech to learn the intricacies of machining vs casting manufacturing methods. However, if you are certain which technique suits your requirements, request to get your quote now.
FAQs
Is cast stronger than machined?
No, cast is generally weaker than machined metal. The internal defects (porosity) that form during casting render cast metal weaker. The inconsistencies in microstructure cause cast metals to be weaker than machined metals.
Is CNC better than casting?
It depends on the specific application and user preferences. There are instances when CNC is better and others when casting is better. For instance, casting is more effective when the required production volume is high.
Are screws cast or machined?
Screws are machined, not cast. The tight tolerances needed for effective threads are easy to achieve with machining, but not with casting. Casting can introduce weakness through porosity and other defects, which can compromise the usability of screws.




0 Comments