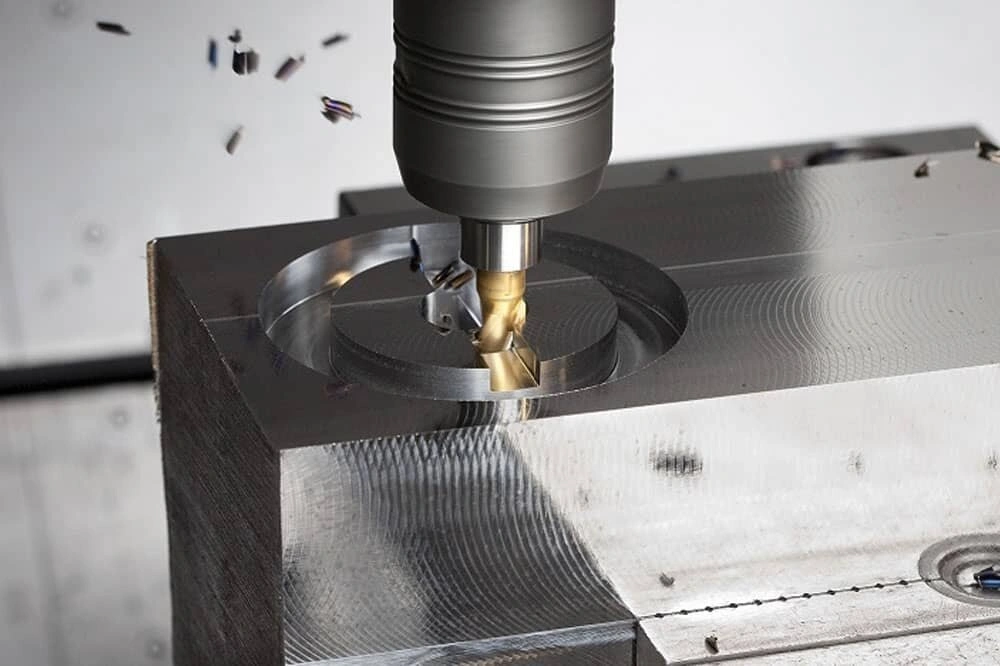
Stainless steel is a widely used material in CNC milling projects, from simple kitchenware to high-performance industrial parts. One of the key features affecting the final quality of those parts is milling stainless steel speeds and feeds. Feed defines how fast the cutting tool is rotating (RPM), whereas feed refers to millimetres of workpiece material the tool covers in one minute.
The use of optimal speed and feed is essential to achieve the desired machining specifications and durability of the coating tool. Additionally, the size and shape of the cutting tool also affect these variables.
Continue reading. This article will cover all about speeds and feeds for milling stainless steel, including a table and the factors you need to consider for optimal values.
Feed Rate and Speed in CNC Milling Defined
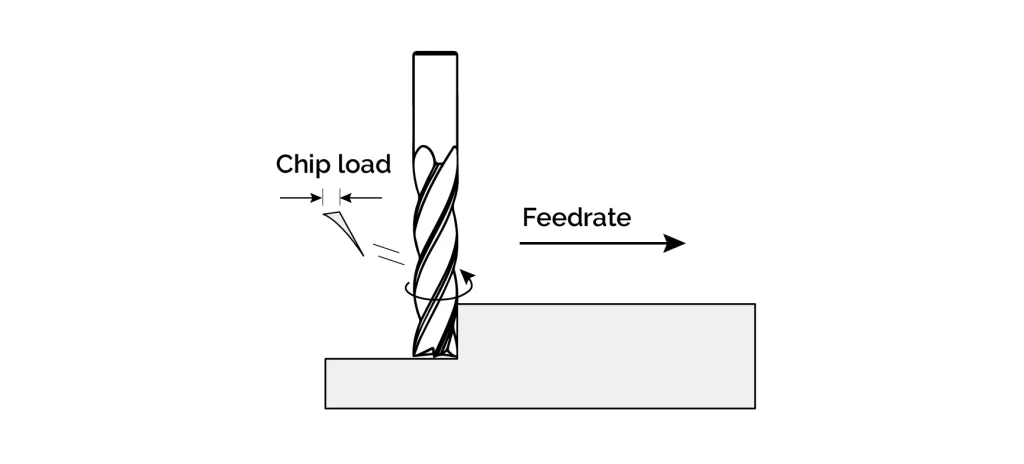
Feed rate concept
The feed rate in CNC characterises how fast the tool is removing the material. It is typically expressed in millimetres per minute or inches per minute. So, it’s about the length of material that the milling tool passes through in a minute, with constant cutting depth. Consequently, feeds are also known as “Feed Per Tooth”, how much work length a tooth covers during milling operations. It is a critical parameter in CNC machining that directly impacts tool life, surface finish, and removal rate.
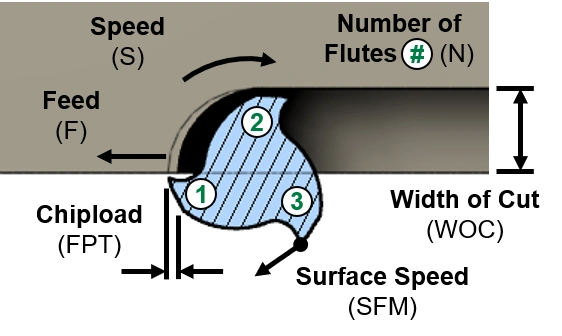
Cutting speed and other terminologies
CNC milling speed is the rate at which the spindle rotates the tool to remove material, revolution per minute(RPM). Additionally, cutting speed is also measured in surface feet per minute(SFM), the speed at which the cutting edge of the tool travels across the workpiece surface.
How to Calculate Feeds and Speeds for Milling?
Milling feed and speed formulas
For feed rate calculation in CNC milling, you can use the formula below;
F=fz×N×Z
Where:
- F = Feed rate (mm/min)
- fz= Feed per tooth (mm)
- N = Spindle speed (RPM)
- Z = Number of teeth on the cutter
Next, you can use the following expression for cutting speed is;
S= V×1000/ (π×D)
SFM= (Spindle RPM x cutter diameter x π)/12
Where:
- S = Spindle speed (RPM)
- V = Cutting speed (m/min)
- D = Diameter of the cutter (mm)
Online CNC Feeds and Speeds Calculator
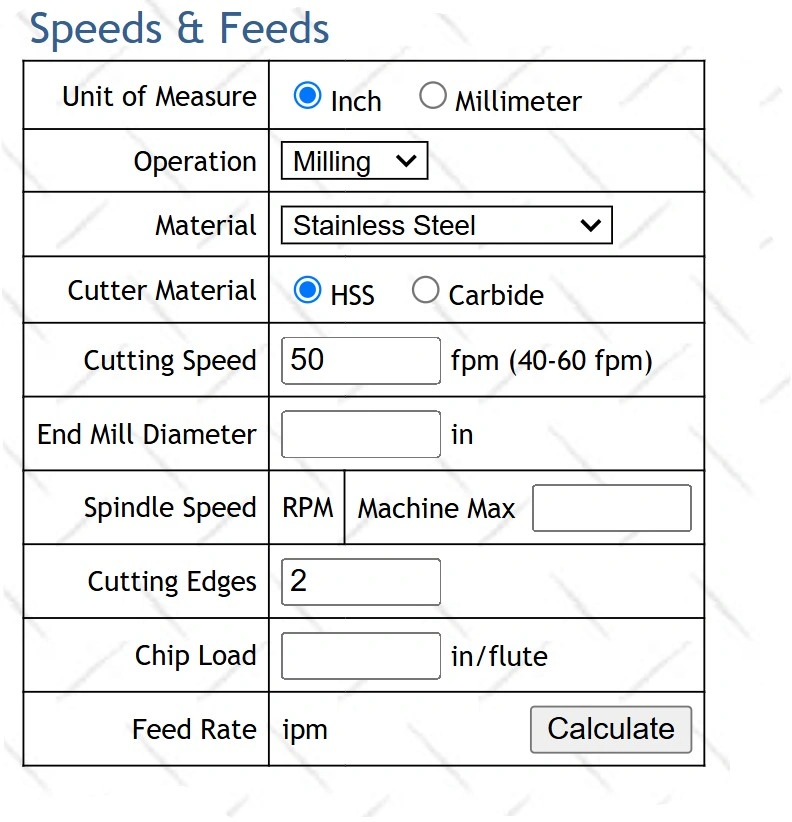
Now, let’s see how to calculate feeds and speeds for milling with online calculators. Several web tools are available on the internet, where you can input milling parameters to find out the Milling stainless steel speeds and feeds or for any other material.
Online speed and feed calculator
Step 1: Choose the right online speed and feed calculator; they provide options for different materials, including stainless steel.
Step 2: Select the material type and milling tool you are using, and fill in the values for parameters like cutting edges on the tool, tool diameter, etc.
Step 3: Click on calculate and check the values in the milling feeds and speeds table, then, choose close feed and speed from there with reference to your calculated value.
Milling Feeds and Speeds Table
Engineers and operators use the “ Milling Feeds and Speeds Table” to find out the feeds and speeds for stainless steel, and other types of workpieces. It recommends cutting speed(m/min), SFM, and feed rates(mm/min) based on the type and size of the milling tool you are using.
Even for the same work materials and the same cnc milling techniques, the feeds and speeds can be different. Characteristics of the milling tools like tool diameter, chip load, and flute number impact these values.
Below is the typical table structure of speeds and feeds for milling stainless steel with end mill tools (Data Source: 6GTools)
|
Speed (SFM) |
Feeds – Inches/tooth and mm/tooth |
|||||||||
|
Free Machining |
350 |
.0006″ .016mm |
.0011″ .028mm |
.0017″ .043mm |
.002″ .051mm |
.0025″ .064mm |
.0028″ .071mm |
.0032″ .081mm |
.0033″ .084mm |
.0041″ .104mm |
|
Ferritic |
280 |
|||||||||
|
Austenitic 304/316 |
250 |
.0004″ .010mm |
.0009″ .023mm |
.0013″ .033mm |
.0016″ .041mm |
.0019″ .048mm |
.0021″ .053mm |
.0026″ .066mm |
.0028″ .071mm |
.0028″ .071mm |
|
Martensitic |
210 |
|||||||||
|
PH 17-4 PH |
160 |
|||||||||
This table/chart can be in other formats as well, illustrating different values for speeds and feeds corresponding to tool diameter and flute numbers. Tool suppliers and manufacturers typically use their own custom charts and tables for reference. Consequently, computer simulation is another way to find out the right feed and speed, you can simulate the milling operation by adjusting the parameters.
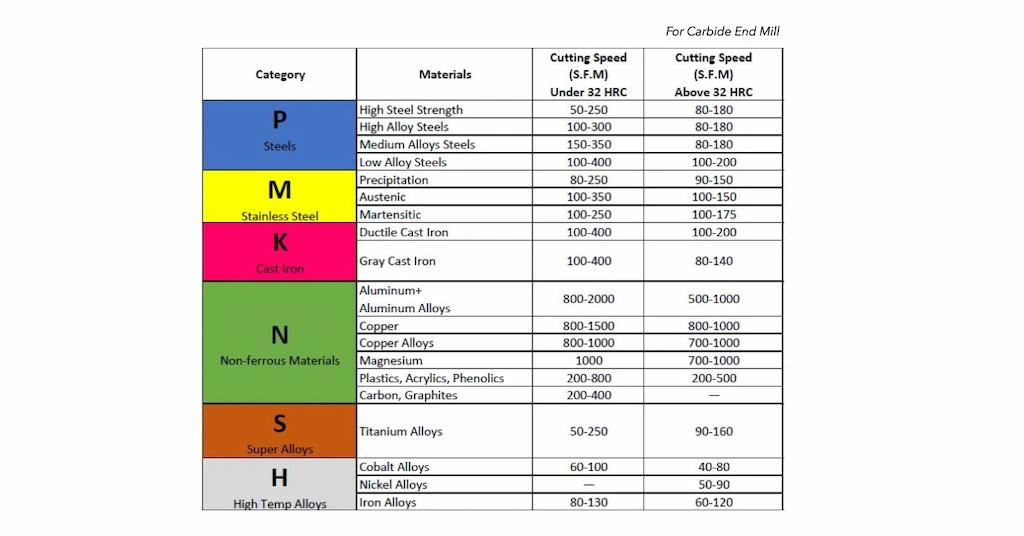
Let’s look at the other feeds and speed chart ;
Milling feed and speed chart for carbide end mill
Try Prolean Now!
Pro Tips for Milling Stainless Steel Speeds and Feeds
Stainless steel CNC milling
We have discussed the different factors above that should be considered when setting the appropriate feed rate cutting speed in a CNC milling machine.
Next, the table below outlines the suggested range along with suitable toolings for different milling operations;
|
Milling Operation |
Recommended Tooling |
Cutting Speed |
Feed Rate in/tooth |
Pro Tips |
|
General Milling |
Carbide end mills with TiAlN coating, sharp edges |
120-160 |
0.002-0.004 |
Use climb milling, apply coolant, and avoid tool dwell |
|
Slotting |
Stub-length tools, chip breaker geometry |
120-160 |
0.001-0.003 |
Ensure chip evacuation; use pre-drilled entry/exit holes |
|
Finishing |
High-flute carbide tools, positive rake angles |
200-300 |
0.001-0.002 |
Minimise tool overhang; use cutting fluid for a fine finish |
|
Roughing |
Coarse pitch carbide rougher, heat-resistant coating |
100-150 |
0.003-0.005 |
Employ dynamic milling, ensure machine rigidity |
Which Factors Affect the Feeds and Speeds in Stainless Steel Milling?
The following are the main factors that affect the optimal values for speeds and feeds in stainless steel;
Material Properties of Stainless Steel
One of the key factors affecting CNC speeds and feeds is material properties, stainless steel in this case. In particular, toughness, hardness, and work-hardening properties need to be considered. The chromium and nickel content in alloys like 304 and 316 enhances the machinability, so the feed and speed.
Milling Tool and Coating
CNC end mill cutters
Next, the choice of cutting tool significantly affects feeds and speeds. Carbide cutters or TiAIN-coated tools can handle higher feed rates and speed due to their heat-resistant and hardness properties.
Tool Geometry
The sharpness of cutting edges and optimal rake angles determines the chip flow, so which type of tool you are using affects the feeds and speeds. Therefore, also consider flute design while setting speeds and feeds in CNC milling.
Cutting Depth
Large cutting depths increase the load on the cutting tool and generate more heat, so speed and feed need to be adjusted in the lower range. Small cutting depths are suitable for stainless steel to enhance machining efficiency and tool life.
Operator Skill
Experienced operators can fine-tune feeds and speeds based on real-time observations of tool wear, chip formation, and machining noise.
Why Right Cutting Speed and Feed Rate is Important?
There are two main importance of using optimal cutting speed and feed: Tool Life and Machining Performance. Incorrect speeds can result in excessive heat generation, leading to premature tool wear and poor surface finishes. On the other hand, optimal values facilitate seamless material removal and keep the cutting tool stable for a CNC milling metal, including stainless steel.
Too High Feed Rates → Overloads the tool and can cause machining chatter, risk of tool breakage.
Too Low Feed Rates → Rough surface and machining inefficiency
Furthermore, the right combination of feed rate and speed is also critical. It means they are interrelated with each other. If you set the right feed rate values but the speed is inconsistent, it also causes machining defects.
CNC milling tool failure
Aggressive feeds increase the risk of tool breakage, whereas slower cause rubbing of the tool with a wok, and heat. Both of these phenomena accelerate tool wear. So, the use of the right feed and speed combination is also important for tool integrity and durability.
Try Prolean Now!
Do you Need Assistance in CNC Milling Projects?
Are you struggling to find the optimal speeds and feeds for milling stainless steel, our engineers and industry professionals can help you to achieve this. We have been working in the CNC machining industry for more than a decade, handling complex multi-milling axis projects, from complex aircraft items to custom prototypes for medical research.
Our CNC milling service includes 3, 4, and 5-axis milling machines and custom tooling strategies to craft intricate designs with high precision down to ±0.0002″.
So, if you need any assistance in CNC milling, upload your design and leave the queries!
Summing Up
Choosing the right values for milling stainless steel speeds and feeds is essential to achieve dimensional accuracy, smooth finish, and enhance the tool life. Additionally, the hardness of the stainless alloy, cutting depth, tool geometry & size, and complexity of design impact these machining variables.
The CNC feeds and speeds calculator or value chart can be helpful in finding the optimal values for any milling operation.
FAQs
What speed do you cut stainless steel?
The recommended cutting speed for stainless steel workpieces in CNC milling operations is 150 to 250 150 to 250 surface feet per minute (SFM), especially if you are using standard end mills.
What is the feed rate and cutting speed for 316 stainless steel?
The suitable feed rate and cutting speed for SS 316 alloy is 150 to 250 SFM and the feed rate highly depends on the tool size. For instance, the best feed rate for a 0.750 to 1.00” inch end mill is 0.0018 to 0.0024 inches/tooth.
What is the best spindle RPM for milling stainless steel?
For any CNC milling process, the best RPM depends on cutting speed and cutter diameter, which can be calculated using the given formula.
- RPM = (Cutting Speed × 12) / (π × Cutter Diameter)
Which factors affect the milling of stainless steel speeds and feeds?
Many factors influence the selection of speeds and feeds for stainless steel works;
- Material Hardness: Speed decreases as the hardness of stainless alloys increases.
- Tool Coating: Hard tool coatings like tungsten carbide allow high speeds.
- Machine Rigidity: Roubst machines can handle higher speeds and feeds.
- Depth & Width of Cut: Deeper or wider cuts may require lowering of speeds and feeds.


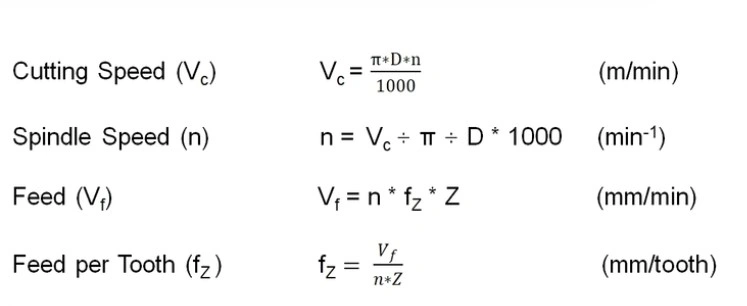







0 Comments