CAPABILITIES
CNC Turning Milling Service
Allow multiple operations on a single machine, perfect for high precision parts with complex geometries
- Tight Tolerance of ±0.0004″ (0.01mm)
- Parts as Fast as 1 days
- Aluminium, Steel, Copper, Polymers & More






All uploads are secure and confidential.
Our CNC Turning Milling Service

We offer Turning and milling services for prototype development to large-scale manufacturing. Simultaneous milling and turning operations can produce complex cones, cylinders, disks, and polygons.
By combining different steps such as drilling, grooving, threading, knurling, boring, and many more. From screws and bolts to high-precision aerospace or automotive parts, all can be created by collaboration with Prolean using CNC turning-milling compound machines.
No matter how complex are your 3D designs, our advanced machining centers can convert them with the combined capability of CNC turning and CNC milling in a single setup. We ensure quality and precision in every part we deliver!


Prolean’s Machining Services

CNC Milling
Our CNC milling services use 3, 4, and 5-axis machines for complex parts and fine details. Live tooling allows for versatile, detailed features like engine blocks, gear profiles, and medical implants.
Suggest Industry Application:
Multiple Industries

CNC Turning
CNC turning rotates workpieces while cutting tools remove material. It’s used for cylindrical shapes like shafts and pins, and is quick and flexible for prototypes and end-use parts.
Suggest Industry Application:
Multiple Industries

CNC Swiss Turning
CNC Swiss turning is a multi-axis lathe machining process specialized for producing small and complex parts with extremely high precision.
Suggest Industry Application:
Multiple Industries
Our Turning Milling Capabilities
| Capabilities | Description |
| As Machined Finish (Ra) | 8 μm |
| General Tolerance | ± 0.0004 in (0.0102 mm) |
| Critical or Precision Tolerances | ± 0.0001 in (0.0025 mm) |
| Maximum Outer Diameter | 1.25 in (32 mm) |
| Maximum Length-to-Dia. Ratio | 4:1 |
| Material Capability | Metal and plastics |
| Inspection and Quality Control | Laser & ultrasonic inspections, CMM machine measurements |
You Have a Great ,We are Here to Help !
Try Prolean Now!
How to Order Parts?
Get a free quote from a real engineer; once we receive your design, our engineer will review it and send you a quote as fast as one hour.

Get A Quote Immediately
Upload your design or email our engineer directly and get your quotes as fast as one hour.

Start Production
Your parts will be made once your orders are confirmed. Besides, you will get real-time order updates of the production status from our order tracking system.

Receive Your Part
After all parts pass QC inspection, they will be well packed from transportation accidents. Then, your custom parts are delivered straight to your doorstep.
How Does Turning Milling Work?
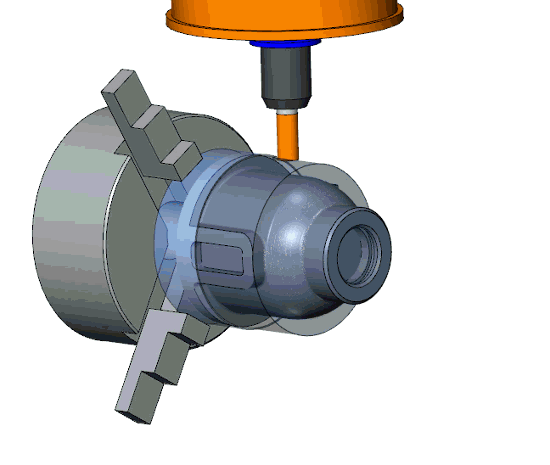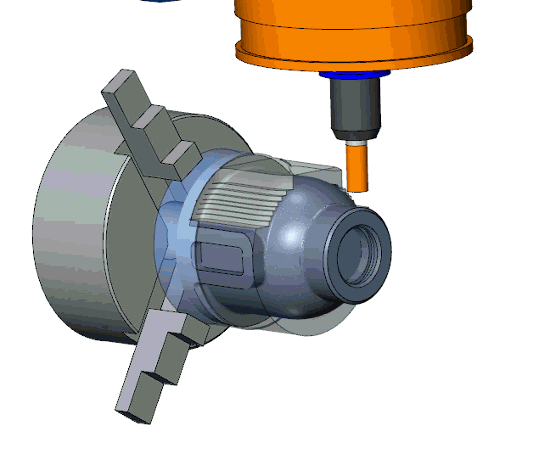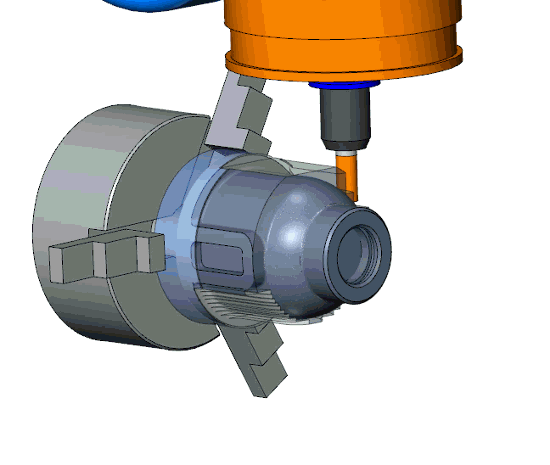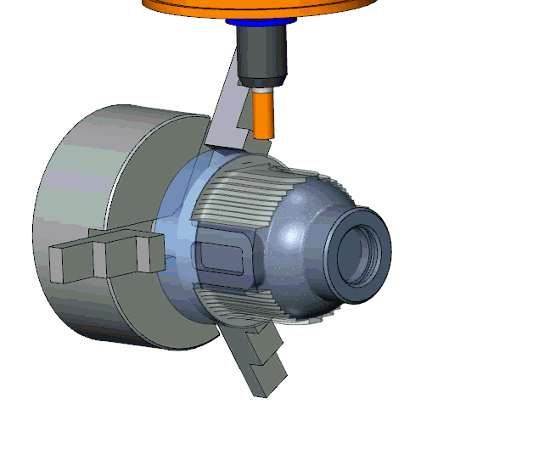

The flexible turn-mill machines can rotate the workpiece, tool, or both, based on the required machining operations. The workpiece can be rotated against the stationery tool feed for cylindrical shapes or features on cylindrical surfaces, whereas tools can be rotated for flat and curvature surfaces. Moreover, both rotate in opposite directions for complex machining tasks.

Workpiece Rotation
Similar to standard turning, the cylindrical workpiece is mounted and rotated on the spindle.

Tool Engagement
A milling tool (rotating on its axis) is brought into contact with the rotating workpiece.

Simultaneous Machining
The tool removes materials and makes complex features like flats, grooves, or slots on the cylindrical surface.
Turning Milling Material Options
Metal
Aluminum Alloys
Aluminum Alloys
Aluminum alloys are known for being lightweight, having corrosion resistance, excellent thermal conductivity, and strengths (vary on alloying elements). They are highly machinable and offer high production speed.
- Grades: 2007, 2017A, 5083, 6060, 6061, 6082, 7075, etc.
- Applications: Aerospace components, automotive parts, sheet metal products, structural parts.
Stainless Steel Grades
Stainless Steel Grades
Stainless steel is one of the most common metals used in machining. Steel alloys provide corrosion resistance, high mechanical strength, ductility, and excellent machinability.
- Grades: 303, 304, 316L, 316Ti, 304L, etc.
- Applications: High-strength and durable parts for automotive, food processing, medical equipment, etc.
Steel Grades
Steel Grades
Steel grades provide high tensile strength, good plasticity, and varying hardness & ductility. The machinability also varies on particular alloy grades. Steel CNC machining produces durable, wear-resistant, high-strength, and heat-treatable parts.
- Grades: S235JR, C45, C40, S355J2G3, 90MnCrV8, 16MnCr5, 25CrMo4, 42CrMo4, etc.
- Applications: Automotive parts, machinery components, structural applications, tool and die manufacturing.
Brass Grades
Brass Grades
Brass is a copper alloy that offers good conductivity, formability, strength, and corrosion resistance. Brass grades are also easy to machine and the machined parts can be solder and braze. easily.
- Grades: Ms58 / CuZn39Pb3
- Applications: Electrical and thermal components, decorative items, etc.
Titanium Grades
Titanium Grades
Titanium grades are renowned for exceptional strength-to-weight ratio, corrosion protection, and biocompatibility. The machining of titanium is used for lightweight and durable parts that can withstand harsh environments.
- Grades: Grade 2 / Grade 5 (Ti-6Al-4V)
- Applications: Aircraft structural parts, medical implants, oils and gas structures, and high-stress components.
Plastic
ABS
ABS
ABS is popular in machining due to its high tensile strength and toughness. It can create parts with excellent impact-resistant, wear-resistant, flame retardantdency, and also leaves good as a machined finish. It is often used as a metal replacement in some automotive and marine applications.
Acrylic (PMMA)
Acrylic (PMMA)
Acrylic or PMMA is a transparent and tough thermoplastic with excellent surface hardness, weather resistance, wear and abrasion resistance, and chemical inertness. The machining of acrylic surfaces can weaken the transparency, but further surface polishing can achieve that. Acrylic is ideal for applications requiring optical transparency or as a cost-effective alternative to polycarbonate.
Polycarbonate (PC)
Polycarbonate (PC)
Polycarbonate is also a transparent plastic but is more durable and shatterproof, than acrylic. It is a UV-stabilized and flame-retardant material. While machining, the PC is prone to stress cracking and requires slow feed rates and sharp tools The use of Polycarbonate machining is widespread, in food and beverage, packaging, medical devices, eyewear, electronics, etc.
PEEK
PEEK
It is high-performance CNC plastic with excellent mechanical strength, fatigue resistance, chemical resistance, and thermal stability. But it can be more expensive than other plastic materials. Some application examples include tubes, bearings, seals, valves, and medical implants.
Polypropylene (PP)
Polypropylene (PP)
Polypropylene is a CNC plastic material used in applications requiring high elongation and low flexural modulus. It has a transparent black-and-white appearance. Machining PP is mainly used for prototypes and large-size products like storage items.
More Material Options
Turning Milling Part Finishing Options
The custom CNC turn-milling parts can be finished using different techniques to achieve specific surface properties and appearance. At ProleanTech, we have various surface finishing options for metal and plastic machining parts, tailored to your needs.

Standard (As-Machined)
This finish refers to parts just after the machining process, sometimes followed by minor grinding. It contains tool marks, small burrs & chips, but provides tight tolerances. The roughness can be as low as 3.2 μm. This finish is suitable when aesthetics is not a requirement.

Bead Blasting
Bead blasting strikes the tiny glass, ceramic, or other beads on the machined surface at high pressure to remove tool marks, burrs, chips, and other surface irregularities. It produces a light and smoothie texture with an attractive appearance.

Anodized (Type II Or Type III)
The CNC-machined aluminum or non-ferrous parts can be anodized, which refers to adding and protective oxide layer on their surface. Type II is clear and color anodizing, whereas type III (MIL-A-8625/MIL-PRF-8625) refers to hard coating. Anodized surfaces resist harsh environments and save the parts from corrosion, wear, and surface degradation.

Powder coating
It is the electrostatic deposition of a thin powder layer(powder of epoxy, polyester, etc) and curing at high temperature, up to 400. Powder coat surfaces are highly corrosion-resistant and can be achieved in any color. It is applicable to all material-type machine parts with complex geometries.

Polishing
Polishing can be applied through electrochemical and mechanical methods. It produces a smooth and fine, mirror-like finish with Ra as low as 0.3 μm. This surface finish is preferred for machined parts if low-surface friction is essential for performance or aesthetics is important.

Black-Oxide
Black oxide is a surface treatment for ferrous materials that creates a sleek black appearance and offers mild corrosion resistance. It chemically converts the metal surface into an oxide layer, preserving tight tolerances. This finish is ideal for precision components where a low-reflective, durable surface is desired.
Try Prolean Now!
Comparison with Turning and Milling

The turn milling process does not need separate machines and changing of workpieces from one setup to another if the works need both cylindrical and curvature shapes. It allows for multiple complex machine operations within a single setup, reducing the production cycle time and risk of dimension deviations.
Comparation Table
| Feature | CNC Turn-Milling | CNC Turning | CNC Milling |
| Typical Use | Complex parts that require both turning and milling | Cylindrical or symmetrical parts | Parts with flat or sculpted surfaces |
| Machining Capability | It performs both milling and turning operations together | Best for radial symmetry, cylindrical shapes | Best for flat, boxy, or sculpted shapes |
| Efficiency | Fast cycles and minimal error | High efficiency for cylindrical parts | High efficiency for boxy and flat parts |
| Tolerance | As low as ±0.0004″ (0.01mm) | ±0.0002″ (0.005mm) | ±0.0004″ (0.01mm) |
The turn milling process does not need separate machines and changing of workpieces from one setup to another if the works need both cylindrical and curvature shapes. It allows for multiple complex machine operations within a single setup, reducing the production cycle time and risk of dimension deviations.
Industry Applications of Turning Milling

Automotive
CNC turn milling is ideal for producing automotive components that require both rotational symmetry and complex milled features, such as grooves or holes. Examples: Brake discs, camshafts, crankshafts, and wheel hubs.

Medical
Medical parts require a high level of precision and complex shapes. CNC turn milling allows for the efficient production of these components with smooth surfaces and intricate details. Examples: Prosthetic joints, surgical instruments, and orthopedic implants.

Electronics
CNC turn milling is used to produce electronic parts with precise dimensions and complex geometries, ensuring proper fit and function in devices. Examples: Housings for electronic devices, connector bodies, and heat sinks.

Robotics
Robotics components often need both turning and milling operations to create complex shapes and features, which CNC turn milling can efficiently handle in a single setup. Examples: Robot arm components, precision gears, and custom brackets.

Oil and Gas
Components for the oil and gas industry often need to withstand high pressures and harsh environments, requiring robust materials and precise machining, which CNC turn milling can deliver. Examples: Valve bodies, pump components, and pipe fittings.
CNC Mill Turn Parts Gallery
3 Ways to Ensure Perfection
Standards
GENERAL TOLERANCE
For metals, the standard is ISO-2768 fH (fine)
For plastics, the standard is ISO-2768 mK (medium)
Metric threads tolerances:ISO 965-1 standard UN Threads Tolerances: ASME B1.1-2003 standard
knurling: ISO13444:2012 standard Our factory is ISO 9001:2015 certificated
Visual inspection and Protection
Constant visual inspection conditions
Quantification of cosmetic surface quality
Process requirements
Part cleaning and Protection
Quality Inspection Report
Inspection Confirmation
Dimensional confirmation
Appearance confirmation
Quality documentation
Try Prolean Now!
Technology Overview
What is CNC Turning-Milling?
While turning machining only rotates the workpiece and milling machining rotates the cutting tools, turning-milling machining combines both approaches in which both the workpiece and the tools can spin following the demands of the CAD file and input instructions.
A mill-turn center machine is used for the Turning-milling machining, basically, a hybrid system that performs both Turning and milling operations simultaneously without switching the device. Because complex geometries require both processes, this approach eliminates the need for frequent machine switching and streamlines manufacturing compared to the normal CNC machining process.
Both milling and turning tools are included in CNC mill-turning machines, and they are set up so that they can be used simultaneously and quickly under input instructions from a computer.
Use of CNC turn-mill machine
The various components for the automotive, aerospace, defense, medical, and mechanical industry requires geometries that involve both turning and milling operation. The CNC Turn-mill machine is ideal for such cases. However, it might not be cost-effective to use it to manufacture items where one process is sufficient, and the operator might have to cope with a more complicated setup.We recommend the CNC turn-mill is ideal when the milling required on the part is less than 25 %.
Working Principle of CNC Turning Milling
The working bar is fastened to the chuck on the spindle and rotates rapidly when computer commands direct the turning operations. When milling operations are required, it becomes stationary, and the rotating tools begin to move to feed the material.
The CNC turn-mill machine can perform turning, milling, boring, facing, drilling, and many other operations. The rotational direction of the machine that commonly uses the milling head is referred to as the “B-axis” in turn-mill machines. The workpiece is fastened to the milling head, allowing various tool-to-workpiece angles.
There are four standard Axis of movement. X-axis: Movement perpendicular to the Axis of the workpiece, Y-Axis: movement using a live tool or separate milling head perpendicular to the Axis of the workpiece, Z- axis: Movement along the stock axis required when holes need to be drilled in the center of the workpiece, B- Axis: movement around the Axis of the workpiece.
The CAD file is first loaded onto the device, and the program is customized following the drawing. Before beginning the process, the turning-milling operation instructions are provided. Even after that, manual supervision is required to ensure quality. However, it doesn’t need different programming or education for each process—just one program will do.
See How Customers Dig Us
We were working on some stainless steel turning projects and contacted Polean to outsource a couple of parts. We sent our design and they made the parts. Those were exactly to needed specifications. Our factory will come back for other projects.
-Paul Campbell, TechFab Innovations
The ordered milling gears were as per our drawing. The surface treatment also looks nice. Once we get feedback from our vendors, I will contact you for subsequent batches. We might need to modify the teeth size and other parameters.
-Jennifer Baker, Senior R&D Engineer
ProleanTech's Mill Turn services have consistently delivered exceptional results for our custom heat sinks. We appreciate their professionalism and commitment to timely delivery.
-Jason Adams, Director of Operations at CastMaster Technologies
Their services of machining justify the name “ProLean” . Engineers and operators are pro at technology and seems like they have mastered the lean manufacturing principles. Thanks for cnc milling near me in savannah, GA.
-Hannah Murphy, Head of Tooling Engineering at PrecisionMold Works
Thank you. The engineers really go the extra step to set up the custom tooling for our Mechanical coupling components. We will also order some other CNC-turned parts for our new project.
-Richard Green, MachiningPro Labs
Proleantech CNC turning services exceeded my expectations. They send me to inspect my small steel parts before the full-scale run. The precision and exact specifications of the final pieces were flawless. I'll recommend and return.
-Victoria Harris, Product Development Engineer
Turning Milling FAQs
What materials are best suited for turn milling?
What is the smallest thickness I may incorporate into my design to prevent warpage during the turning-milling process?
What are the Advantages of Using the Turning-milling process?
What parts can be made with the Turning-milling process?
What is the key difference between CNC milling and Turning?
Get Your Parts Made Today
All uploads are secure and confidential.











