“Reaction, thin wall, liquid silicone rubber (LSR), metal injection molding (MIM), and hot runner systems represent key types of injection molding. Each offers distinct advantages: from producing lightweight components to complex geometries”

Injection molding manufacturing is used in the low-cost production of thermoplastic parts across industries. But, what is injection molding? It is the process of shaping raw plastics( metal in some cases) by melting and injecting them into a mold cavity of the desired geometry. The best thing is that the mold is reusable for multiple cycles and maintains the dimensional consistency for each molded part. Moreover, this technology has various injection molding types, so you can choose the best one that can fully satisfy your parts requirements.
This article will guide you through six injection molding types and how to make the best choice.
The Fundamentals of Injection Molding
Molding is a simple but crucial technique that allows to achievement of diverse shapes by designing custom molds. The history of injection molding can be traced back to 1868 by John W. This formative process injects the molten material at high pressure in most methods, the pressure ensures the flow of liquid plastic inside the cavity and captures the details. Then, it is cooled and solidified, and part is ejected.
Modern injection molding machines can take direct pallets ( raw material) from the hopper to the barrel and melt them inside where a heated screw pushes and melts the material as it travels to the nozzle tip, a nozzle injects the materials into an injection mold. Meanwhile, the screw is typically operated with the hydraulic screwdriver ad gears.
| Parameter | Description |
| Pressure Requirements | Also known as clamp force, the injection pressure is between 10,000 to 30,000 psi. |
| Heat Transfer | The type of mold material and raw material inside determines the heat transfer rate and cooling period. |
| Flow and Solidification | The liquid polymer flows through the mold cavity with a high shear rate to fill intricate cavities |
Next, the common types of injection molding are;
- Gas-assisted Injection Molding
- Thin Wall Injection Molding
- LSR injection Molding
- Reaction Injection Molding
- Metal Injection Molding
- Hot and Cold Runner Injection Molding
Try Prolean Now!
1. Gas-assisted Injection Molding
The gas-assisted injection molding process uses a flow of inter gas (typically nitrogen) just after injecting the molten resins inside the mold. The channel of blowing air pushes the material towards the surface of cavity walls and makes hollow parts with thicker wall sizes. Next, it involves an auxiliary gas tank with a supply control panel beside the standard injection molding equipment.
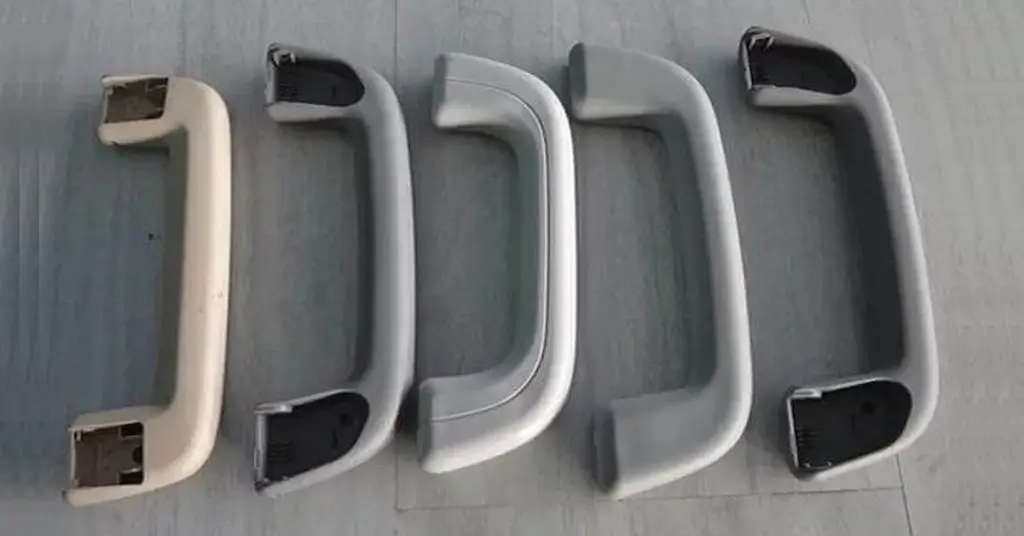

Gas-assisted injection molding parts
First, the molten material is injected into the mold, but not enough to fill the cavity, which could be 70, or 80%. As the injected material travels and solidifies its outer layers on the cavity walls, an inert gas stream pushes the material toward the walls and makes a channel for itself, leaving a hole in the solidified core.
Advantages
- The gas-assisted injection molding creates lightweight parts and also removes the internal stress on molded parts.
- As the gas pushes the molten material, it achieves a high degree of dimensional stability.
- Uses a lower amount of clamping force.
- It produces a smooth surface finish without any sink marks
Applications
Parts with small holes inside the structure like hollow columns. Here are some examples of applications;
- Handle covers for various applications, from cycles to sporting items.
- Housing for electrical components, wearable devices, etc.
- Air plates for Air conditioning systems
2. Thin Wall Injection Molding
Thin wall injection molding types are ideal for small-thickness parts compared to overall part size. Thin walls mean we are talking about 1-2mm thick molding parts. You can shape materials like PP, POM, nylon, polystyrene, etc. The process involves high-speed filling of the injection mold and maintaining sufficient structural strength regardless of small thickness.
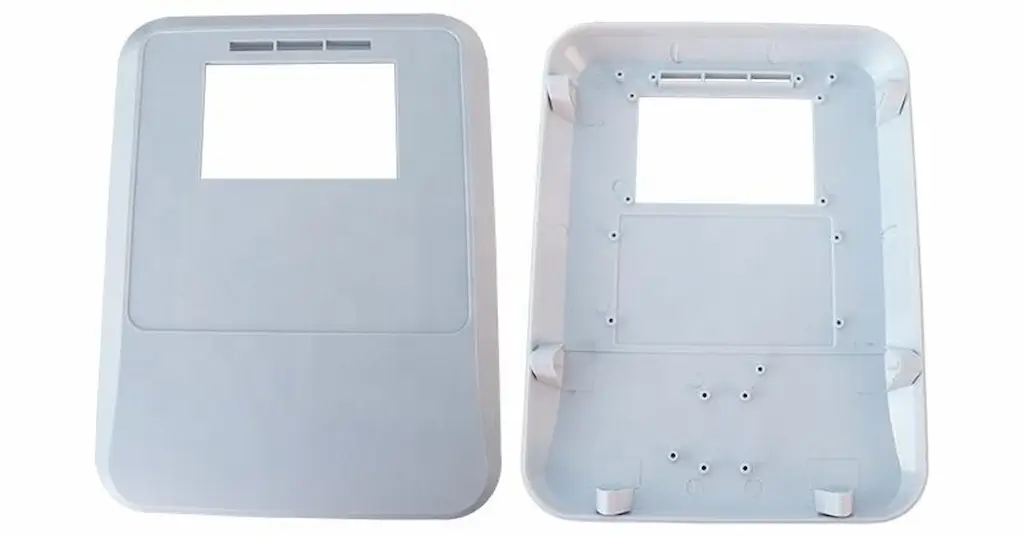

Thin wall injection molding parts
Advantages
- The material cost is almost reduced by 60 to 70%
- Significantly lower cycle times than standard injection molding and other injection molding types, fast and accurate process.
- Smooth surface finishes
Applications
The thin wall injection molding parts are used from packaging to components for automotive, electronics, aerospace, and other industries.
- Mobile phone and camera cases
- Food and medical packaging
- Housing and enclosures for electronics and electrical items
- Storage containers
- Plastic lids, etc.
3. Liquid Silicone Injection Molding
Liquid Silicone Injection Molding is the process of creating flexible rubber components using liquid silicone rubber( LSR). Typically, foam silicone liquid is injected inside the mold. As a result, the molded parts show a unique set of physical and mechanical properties.
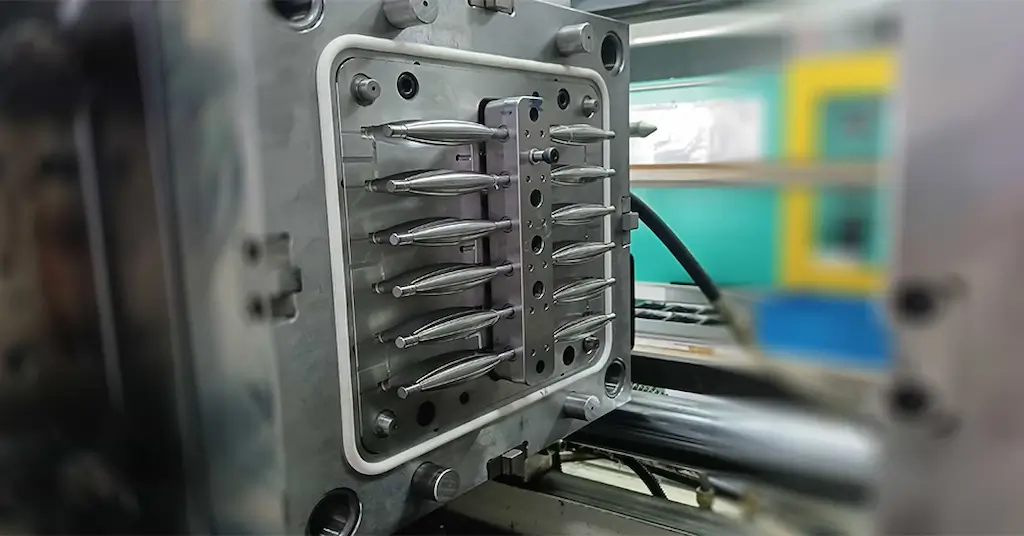
LSR injection molding
The silicone rubber parts are critical in sealing applications for medical manufacturing. It serves the need for elastic and flexible components. Furthermore, LSR molding is also known as foam injection molding, the end parts are strong and lightweight structural components for various uses. In this special type of liquid silicone injection molding, liquid silicone rubber with blowing agents is injected.
Advantages
- Direct Liquid Silicone can be used in the process instead of pellets or other forms.
- High strength, durability, thermal & chemical resistance, and precise parts
- Food grade and Bio-compatible
- Structural foam molding variation is also possible
Applications
- Medical components and devices
- Seals, gaskets, tubing, and other similar components
- Water-proof housing and enclosures
- Infant care and kitchenware items
- Electrical insulators and covers
4. Reaction Injection Molding(RIM)
It is among the advanced and relatively modern injection molding types. As the name says, reaction injection molding involves mixing two different material liquids in a mixing chamber and injecting them into a mold. The constituent molten liquid reacts and forms newly characterized parts upon solidification. The materials are continuously re-circulated inside the mixing tank, whereas a low-pressure pump supplies mixed solution to the mold cavity. Meanwhile, the two materials are separately injected one by one in some cases without the use of a mixing chamber/tank.
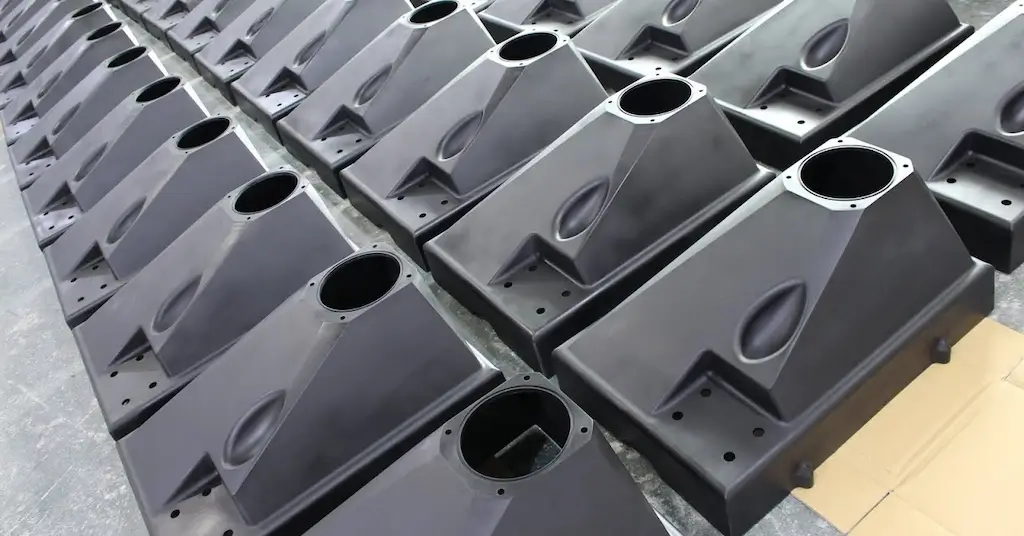

Reaction injection molding parts
Typically, the reactive elements are polyol and isocyanate. Their mixing (reaction) generates heat and formulation can produce foamed, solid, or other structures.
Advantages
- The low pressure makes the mold more durable compared to other injection molding types.
- Reaction injection molding requires less heat, which means less energy.
- Simple and cost-effective setup( equipment & tooling)
- It allows for the customization of final properties by mixing suitable additives.
- The thermal stability of polyurethane resins is beneficial for high-temperature applications are reaction molding.
Applications
RIM produces high-impact resistant parts with a variety of thicknesses and sizes for various applications. Some examples are;
- Automotive bumpers, steering wheels, dashboards, etc.
- Electrical insulators and covers
- Overmold or Encapsulated parts
- Medical diagnostic device enclosures
- Sports items and safety gear
Try Prolean Now!
5. Metal Injection Molding
Not only the thermoplastics but metal & alloys are also injection moldable. You can mold aluminum, nickel, ferrous alloys, and other metals into intricate and complex shapes with the use of mold. Metal Injection Molding utilizes the feedstock of metal powder and binders. The binder can be ceramic, wax, polymer, or organic material-based, depending on the raw metal types.
This feedstock is injected into the barrel, where the screw melts and injects the feed into the mold. Inside the mold cavity, the liquid feed flows and takes the shape. Then, the binder is separated from solidified parts after it is ejected from the mold. Furthermore, the molded metal parts may need grinding, polishing, and further treatments to eliminate the porosity and finish the surface.
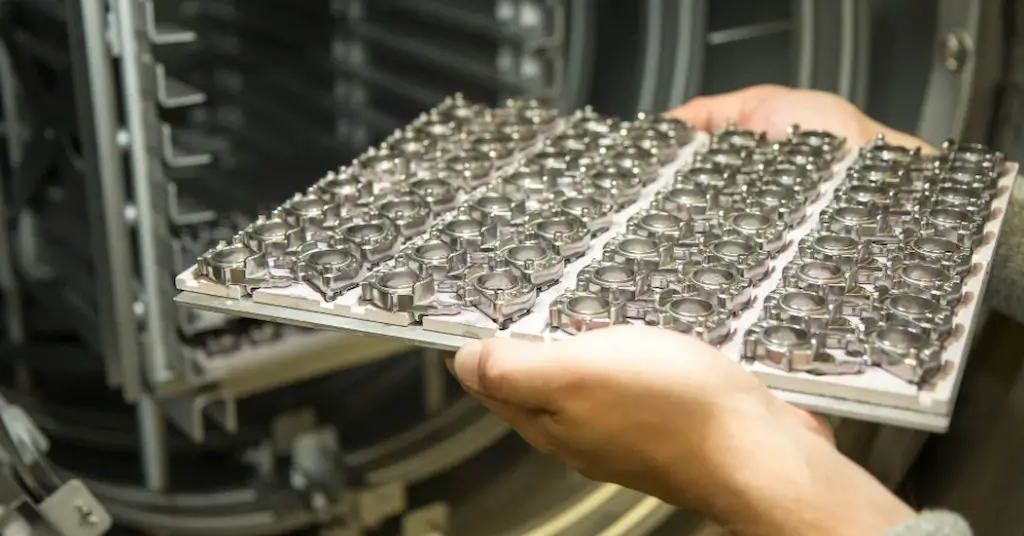

Metal injection molding
Advantages
- Molding allows to creation of intricate features like undercuts, deep channels, and internal cavities that are challenging with conventional manufacturing processes.
- Excellent repeatability and dimensional consistency across the production batches
- Almost zero material waste, significant benefits compared to machining.
- Low cost for high volume production of identical items.
Applications
- Automotive transmission components; small gears and precision components.
- Surgical tools and medical device components
- Firearm parts like trigger components
- Hinges and other small parts for mobile
- Connectors and housing components for aerospace
- Watch components including cases, gears, and clasps
6. Hot Runner and Cold Runner Injection Molding
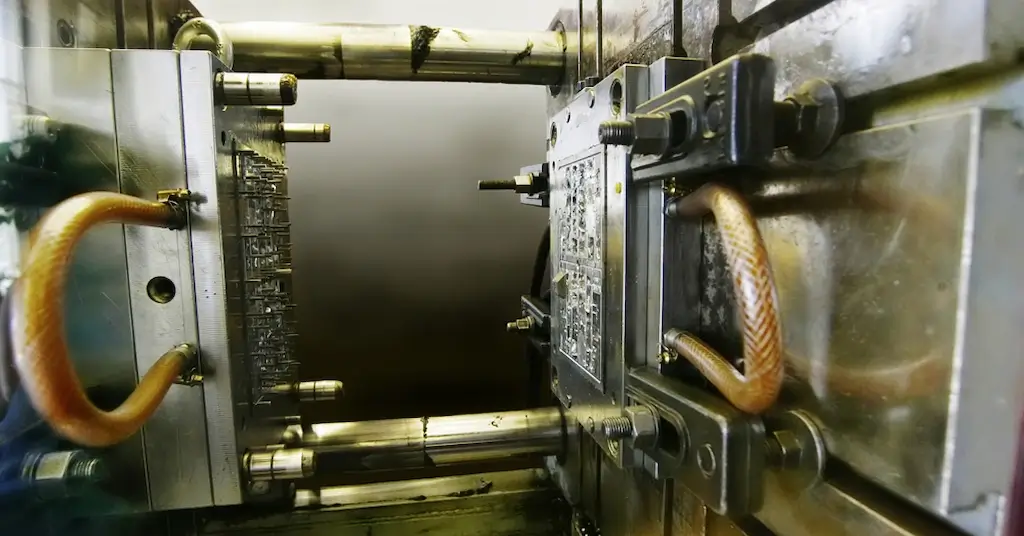
Hot runner injection Molding
These injection molding types are classified based on whether the process used a hot or cold runner to transfer the material into the mold cavity. The hot runner injection molding uses a heated runner that maintains the uniform temperature and viscosity of the flowing material. On the other hand, cold runner injection molding does not use the heated runner, instead a runner at room temperature.
The heated runner is especially used for the requirement of highly precise and structurally intact parts. It is suitable for rapid injection molding and eliminates the risk of premature cooling or inconsistent solidification.
| Hot Runner Systems | Cold Runner Systems |
| Heated runners keep plastic molten and improve overall quality. | The cold channels cause more waste but are simpler and cheaper. |
| Higher initial cost and complex maintenance. | Lower initial cost and easier maintenance. |
| Ideal for high-volume production and intricate designs. | Suitable for low-volume production and frequent color changes. |
| Fast cycles due to reduced cooling needs. | Slower cycle times |
| Used for automotive parts, medical devices, electronics housings, bottle caps, etc. | Prototypes, low-volume custom parts, toys, simple packaging, disposable cutlery, etc. |
Injection Molding vs. Compression Molding
Besides various injection molding types, other molding techniques are also popular in manufacturing. Blow molding, compression molding, rotation molding, and extrusion molding are a few to name.
The blow molding process involves a heated plastic parison (tube of plastic) inflated in the shape of the mod. It is typically used for hollow items like containers, pipes, and bottles.
Compression molding directly puts the heated plastic materials into an open mold. Then, the plunger compresses them to liquidity and forces the flow inside the cavity. This process is suitable for large-size thermoset components. Furthermore, you can read more details in the compression molding vs injection molding article here.
In rotational molding, the plastic powder is placed inside a heated mold that can rotate around two perpendicular axes. Meanwhile, the heat supply is continuous to the mold. The rotational motion leads to the coating of the mold’s interior surface uniformly.
Try Prolean Now!
We Help you to Choose the Right Type of Injection Molding
Are you still confused about which injection molding type to choose for your project? Well, it entirely depends on the specified features of your design and end requirements. You must consider, your raw material type, size, intricacies, production volume, budget, and other factors to choose the right match for your design.
ProleanTech is an On-demand manufacturing company providing injection molding service and other various manufacturing solutions. Our engineers have experience in handling various metal and thermoplastic injection molding projects across all industries. So, they have expertise in all injection molding types and how to achieve optimal results on them.
Our engineers and research team can help you find the best injection molding technology that can ensure all the specifications and requirements. Furthermore, we have an advanced injection molding facility with automated equipment to execute your chosen injection molding method.
Send us your design, our engineer will get back to you with all further information and an accurate quote.
Key Takeaways;
- There are different injection molding types, you need to choose the right one by matching the process capability and your requirements.
- Common types include gas-assisted, thin wall, liquid silicone, reaction, hot runner, and cold runner injection molding.
- Each of the methods has its own special capabilities and benefits in precision manufacturing.

0 Comments