“The compression molding technology is well suited to produce small to large-sized rubber parts for different applications. It allows manufacturers to leverage the properties of rubbers to create functional products.”
Among different methods of making elastic rubber parts, compression molding is a popular one. This molding method can shape the various rubber materials according to the geometry of the designed mold. Rubber Compression Molding produces components with high resilience, strength, and sealing properties for diverse industries, from automotive to consumer products.
This article will discuss the process, advantages, industrial applications, molding considerations, and other aspects. By the end, you will be able to decide whether it can fulfill your Rubber Moldings requirement or not.
What is Rubber Compression Molding?
It is a manufacturing process for rubber parts and products that involves molding the rubber material by placing and compressing the rubber into a heated mold. Meanwhile, the mold contains two halves, which can be opened to place the rubber and compressed to ensure the flow inside the mold. Both halves (upper halve and lower halve) of mold are connected with the compression mechanism, hydraulic, mechanical, or any other type.
However, it is no simple as it seems. The compression force, mold temperature, and even the weight of rubber material need to be precise to accomplish the process.
The temperature control is essential to make sure that the rubber placed inside the mold is activated and flow that compression can give the shape to melted rubber. Additionally, you might think that the material flash out from the position where two mold halves are met. You are correct, that is why placing the accurate weight on mold can only minimize material wastage.
Try Prolean Now!
What Rubbers Can be Compression Molded?
Now, what type of rubber materials are compatible with compression molding? The basic requirement is the rubber properties should support the b flow of rubber inside the mold during the process.
You can leverage the numerous rubber types in compression molding according to which rubber best fits the application requirements. Natural rubber, nitrile rubber, silicone rubber, and butyl rubber are the common ones. However, Silicone Compression Molding is the most popular due to its flexibility and set of properties.
Silicone rubber
ASTM Standard of Rubber Materials:
This standard verifies the physical and mechanical properties of rubber systematically. The ASTM Rubber Standards can also be used in the material selection for compression molded rubber parts.
For Example, ASTM D2000 provides a standardized method for describing rubber material properties.
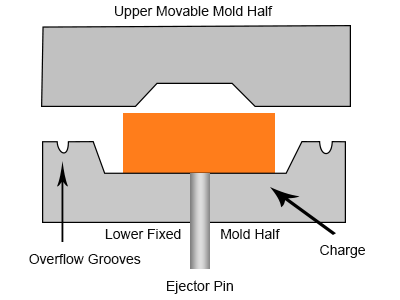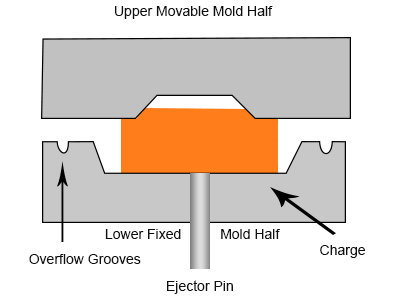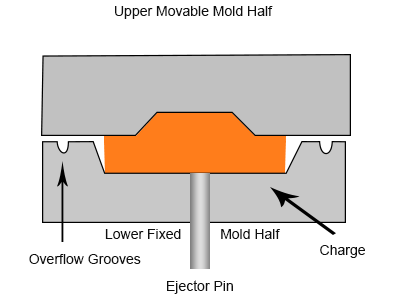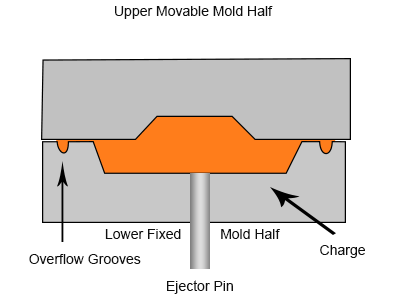
The Rubber Compression Molding Process
The process of molding rubber material requires precise control over temperature and pressure. Additionally, the right tool setup and curing are also equally important.
Rubber Compression molding process
Let’s break down the process of Rubber Compression Molding into individual steps. So, it will be easy to understand.
1. Die Creation
The first step is design and manufacturing the compression molding die. The design contains all the information like dimension, tolerance, and other specifications. Meanwhile, EDM or CNC machining prepares the doe according to the design.
2. Machine and Tooling
The machine setup involves arranging the die in the machine and setting a proper compression system to the mold. It could be with a hydraulic system on compression plates, plates connected with lower and upper halves, and can opened and closed according to requirement.
3. Placing the Rubber in an Open-Die
Next, the rubber in suitable sizes goes into the open mold, which could be done either manually or automatically. Here, the mold and rubber are both preheated. Another thing is that the material should be weighed before placing it inside the mold.
4. Compression and Curing
The mold temperature is maintained between 140°C to 200°C. during the competition. While the compression force depends on the different factors;
Next, curing is done for 3-5 minutes, where the material flows inside the cavities to fill the details after applying the pressure on heated rubbers.
5. Part Ejection and Post-processing
Once the rubber part, solidifies inside the compression mold. The ejection mechanism opens the mold halve. The advanced machine consists of automatic ejection, whereas conventional compressional molding involves careful ejection of parts by hand.
Then, machining or other processes remove the flash and excess material at the joining position of the mold halves. Consequently, further processing like polish can help to achieve the desired aesthetic requirements.
Advantages of Rubber Compression Molding
First, the rubber part or products made with compression molding show good strength, durability, and cost advantage. Next, it also suits all kinds of volumes, from small batches to large runs. In fact, the per-part cost decreases on every subsequent batch.
Large Size Parts
First, compression molding allows to creation of large-size and weighted rubber parts while maintaining the original properties intact. It can also create more thicker parts as compared to injection molding.
Simple Tooling
The tooling is also simple and cost-effective. The reason is simple and cheaper Mold making and other tooling arrangements. Meanwhile, the compression molding machine is also less complex.
Minimal Material Wastage
The correct weight of raw material significantly reduces material wastage, which also helps to lower the overall cost. It might seem insignificant in small runs, but you can see the impact in large runs.
Suited for Rubber Prototypes
The low tooling cost of Rubber Compression Molding provides cost advantages in the product development of several rubber components. At the same time, it offers the required precision also.
Disadvantages of Rubber Compression Molding
This method has some limitations too. The common Rubber Compression Molding Disadvantage is the part’s complexity and inclusion of intricate features like long and short corners or undercuts.
Another drawback is its cycle time. The compression and curing contribute to the longer production time.
Furthermore, the flash or excess rubber at the parting line demands further processing to remove that excess material.
- Limited complex features
- Slower production
- Post-processing is required in many cases
Try Prolean Now!
Are there Alternatives to Rubber Compression Molding?
Yes! There are two other popular methods to shape rubber materials: Rubber Injection Molding and custom extrusion. These processes have their own advantages in specific scenarios.
1. Rubber Injection Molding
The process involves injecting the mixture of molten rubber polymer, additives, catalysts, and pigments into an injection mold at high pressure.
- Rapid cycle time
- Smooth finish of molded rubber part
- Capability of complex features and shapes
- Highly cot-efficient for mass production
If you need intricate rubber parts injection molding could be a better choice. Additionally, it is also suitable for Liquid Silicone Rubber Molding.
2. Custom Extrusion
Next, the extrusion method works by forcing the rubber material into an extrusion die to shape it. It creates custom shapes(linear mainly) and can also extrude multiple types of rubber to produce a singular item. Therefore, it is popular in different applications. For example, Custom Silicone Extrusion has a significant role in medical tubing.
What are the Possible Rubber Compression Molding Defects?
Defective Rubber Parts
Some material composition errors and minor machine or tooling deviations can result in defective rubber parts. However, considering some precautions can easily avoid the risk of defects on molded rubber parts.
For example, at the separation line of mold halves, the flash material can directly affect the dimension of the intended part and it can avoid precise control of the compression process.
Table: Defects & Prevention of Rubber Compression Molding Parts
| Defect | Reason | Prevention |
| Flow Lines | Excess heat or premature cooling | Uniform mold temperature and smooth cavities to increase the flowability. |
| Blister | The expansion of trapped air (or volatile at the time of curing. | Mold venting & pre-heating of raw material. |
| Chips | Improper mold design | Optimize the mold for smooth rounded corners |
| Shrinkage | Material contraction due to cooling and curing processes. | Accommodate shrinkage compensation during mold design and adjust curing conditions. |
The Cost of Rubber Parts Made from Compression Molding
The cost basically depends on the four major factors, tooling, material, labor, and complexity. Also, the production volume impacts the per-unit cost of rubber parts significantly.
Thus, it is hard to exactly point out the cost. But, typically, short-run production of small-size rubber parts ( Eg. 20 cm X 15 cm) might cost around $2000 to $5000.
Here is the table showing the cost variables and their influence on overall production cost:
| Cost Factor | How does it impact? | Impact |
| Tooling | Die material, precision, wall finish quality, etc. | $$$ |
| Material | The cost of raw rubber for compression molding. | $$$ |
| Labor | Operator and other workers involved in production | $$ |
| Complexity | Do parts contain intricate features? | $$ |
| Production Volume | The per-unit cost is significantly less in mass production. | $$ |
The compression molded rubber parts play a significant role in sealing components for different equipment or systems. They are also used for vibration damping. The reason behind the countless applications is the flexibility and durability of the rubber materials.
Here are the common applications of rubber compression molding;
- Rubber gaskets and seals
- Rubber bushings
- O-rings
- Diaphragms
- Anti-vibration mounts
- Bumpers and shock absorbers
- Keypads for electronics
- Handles and grips
- Electrical insulators
- Rubber rollers
- Foot pads
- Battery seals
- Medical device components
Where to Mold Rubber Parts?
As we discussed, several factors affect the quality of rubber molding parts. What kind of machine or tool do you use? , quality control, the right curing, and more
At ProleanTech, we address all the requirements needed to deliver the intended rubber parts. Our Compression Molding Service and Injection Molding Services have an advanced production factory with an automatic control system for pressure and temperature optimization. Subsequently, our strong supply chain of rubber material will provide you with several rubber material options.
You can upload your design here with additional specifications. We will get back to you with an accurate quote for your Rubber Compression Molding Project.
Try Prolean Now!
Summing Up
Compression molding has several benefits in molding rubber materials. Meanwhile, the use of molded rubber parts is also vast. Its application spans several industries, from consumer items to automotive components. The only thing is that you need to ensure the right tooling and control parameters according to the project requirements.
Furthermore, choosing the right manufacturer is equally important in Rubber Compression Molding. Only experienced manufacturers with advanced production facilities can meet your design specifications.
FAQs
Q1- How Compression Molding Rubber Works?
The compression molding of rubber works by heating the die and applying pressure for a specific time, which cures the rubber and fills the e mold cavity. Meanwhile, a pre-measured amount of rubber is placed on the mold initially.
Q-2. How to Compare Rubber Compression Molding vs. Injection Molding?
Rubber Compression Molding requires simple tooling and has a longer cycle time. On the other hand, Rubber Injection Molding suits to produce more complex shapes in a shorter time.
Q-3. What is a Rubber Compression Molding Machine?
It is a molding equipment that typically consists of a heated platen or table and a hydraulic press mechanism.
Q-4. What are the Examples of Industrial Rubber Parts?
Some common industrial rubber parts made through compression molding include:
- Seals and gaskets
- Vibration dampening applications
- Rubber pads for machinery
- Hose and tubing connectors
Q-5. Why Compression Molded Rubber Prototypes are Cost-effective?
Compression-molded rubber prototypes are cost-effective because the compression molding process offers low tooling costs and flexibility in design changes.







0 Comments