“Copper may be the best conductor, but brass and bronze resist wear, withstand stress, and corrosive environments. It means choice relies on whether your parts require high conductivity or high mechanical performance”
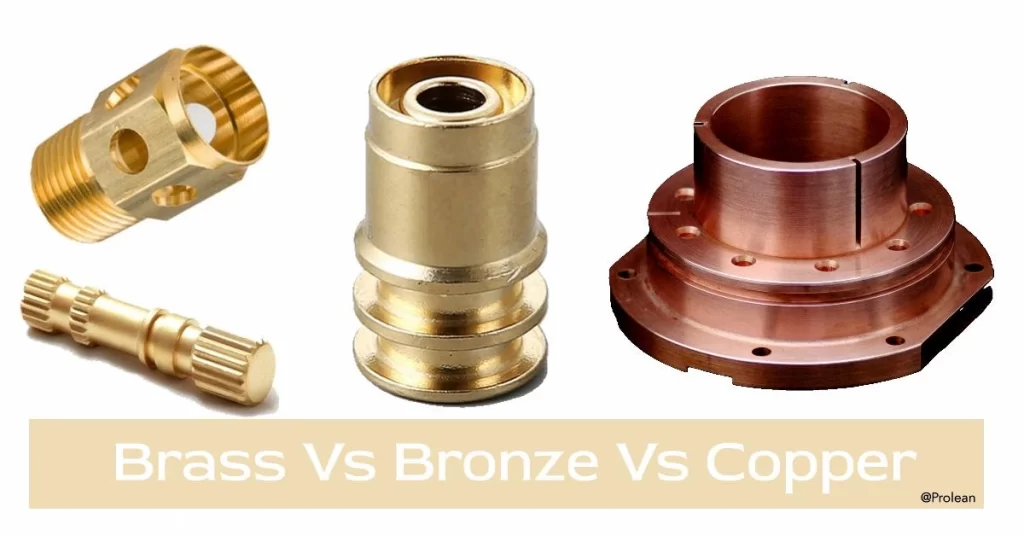

Copper is one of the most popular engineering materials used in numerous industrial and consumer applications. However, it has limitations regarding its strength and corrosion resistance. So, brass and bronze are two copper alloys made with copper and additional alloying elements that improve the physical, mechanical, and chemical properties. There are other differences in brass vs bronze vs copper also. For instance, their machinability, durability, and biocompatibility. Continue reading for a comparative elaboration of these three red metals.
What is Copper?
With excellent thermal and electrical conductivity, it has been a popular choice for engineers as a good material option for electronics and heat sink applications. Consequently, its antibacterial and biocompatible nature is beneficial for medical devices and implants.

Copper bars
The use of copper is not new, it has been an essential metal in human evolution; it all started with the copper age (3500 to 2300 BCE). From coins, jewelry, cooking pots, and tools to electrical batteries and aircraft in current times.
Natural ores like CuFeS2 ( Chalcopyrite), Cu9S5 (Digenite), and CuCO3·Cu(OH)2 (Azurite) are major resources for copper from where they are extracted and purified into applicable forms that we found in the market.
Furthermore, various copper machining grades are used in manufacturing, such as C81500(pure copper) and C81100(99% pure, 1% chromium).
Copper Properties

Properties of copper
The following are the key copper properties;
-
- Electrical and Thermal Properties: High thermal and electrical conductivity among the common manufacturing metals.
- Antibacterial: Its antibacterial properties make it suitable for storage of drinking water, dentistry, and healthcare. Copper is also resistant to corrosion(moderate).
- Formability: The high formability allows for fabricating into complex shapes with different forming techniques, bending, stamping, drawing, welding, etc.
- Machinability: Even HSS and hardened steel tools can machine the C81100, while it is a bit challenging for the C81500.
Try Prolean Now!
What is Brass?
Brass, a common copper alloy, consists primarily of zinc as an additional element (approximately 35%) with other secondary alloying elements like phosphorus, silicon, manganese, and lead. These secondary metals aid in mechanical strength, ductility, wear resistance, machinability, and lifespan. These beneficial brass properties are suitable for electrical & electronics, musical items, jewelry, etc.
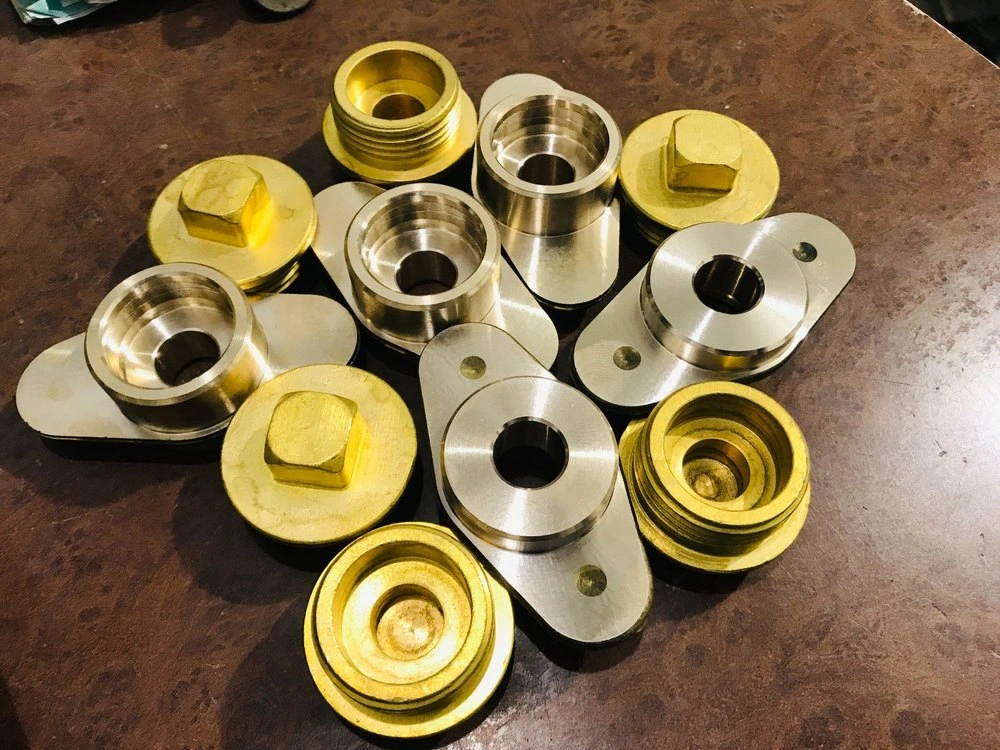

Custom brass parts
Consequently, the copper and alloying elements are forged or cast to form the industry-grade brass. Some common grades for brass CNC machining are alloy 260, 272, 330, 364, and 385. These grades contain slightly different zinc compositions from each other. Meanwhile, other minor alloying element % can also be different from one grade to another.
Brass Properties

Brass properties
- High Machinability than Copper: Copper vs brass– The added zinc and other elements like lead and aluminum in minor amounts facilitate the easy & smooth brass machining.
- Malleable and Formability: It can be cast, formed, and machined into diverse shapes and products.
- Corrosion Protection: It has a similar level of resistance as copper against corrosive & harsh environmental conditions.
- Appearance: The aesthetic brass properties are beneficial for architectural, decorative, jewelry, and other items. These alloys provide an eye-catching shiny yellowish tone.
What is Bronze?
Another common copper alloy is bronze, composed of 12% tin (approx.) and other alloying elements(phosphorus, manganese, silicone, etc. ) in tiny amounts. This particular alloy material improves the strength, corrosion resistance, brittleness, and relatively higher thermal stability.
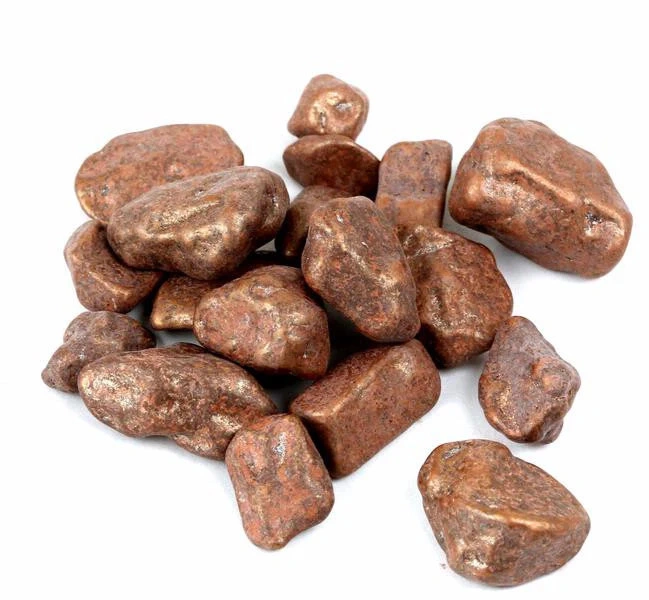

Raw bronze material
The bronze is used in marine, hardware, fittings, and other areas due to its resistance to salt water & moisture. For example, ship components, plumbing items, valves, bushings, and hydraulic machinery parts.
The bronze grades for machining, fabrication, and other manufacturing processes are C95400, B-10, and MTEK 375.
Bronze Properties

Properties of bronze
-
- Saltwater Resistance: Bronze alloy is resistant to saltwater and does not develop corrosion while operating on seas and other saltwater conditions.
- Conductivity: High thermal conductivity than brass and melting point is highest among brass vs bronze vs copper.
- Durability: The resistance against corrosion, wear, and surface degradation increases the lifespan of bronze parts and products.
- Ductility: Bronze grades are ductile and can be formed into desired shapes and geometries with the use of forming techniques.
Brass vs Bronze vs Copper: Physical and Mechanical Properties
“Copper is a go-to option when electrical or thermal conductivity is essential for end application, whereas brass and bronze perform well under stress and are more suitable for structural uses”

Brass machining
After individual discussion, let’s discuss the head-to-head comparison of brass vs bronze vs copper in various aspects. Their composition, physical & mechanical properties, uses, etc.
- Alloying Composition
The copper is 99.3% pure, and its market forms are available with minor additions of chromium(approx. 1%). The brass contains 34-35% of zinc, 65% copper, and other minor constituents. On the other hand, bronze is 12-12.5% tin, 88 % approx pure copper, and others in negligible proportion.
- Performance Under Mechanical Stress
Among these three options, bronze performs well under impact forces, continuous loads, vibration, and forming stress due to the toughness and strength of tin in it. Then, brass and copper come after bronze.
- Corrosion Resistance
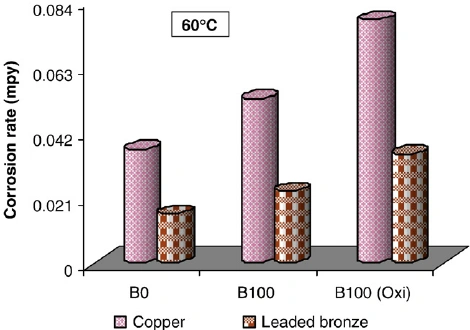
Corrosion rate in copper and bronze. Source
As discussed before, all three materials can protect the rust & corrosion under normal environmental conditions like water & moisture. But, bronze & brass have higher resistance against the marie (salt water) resistance.
- Mechanical Strength
Again, bronze is superior to copper and brass in terms of yield strength. However, it has a slightly higher ultimate tensile strength compared to the other two.
If you consider their weight relative to their strength, brass has comparatively low weight with respect to their densities.
- Physical Appearance
Pure copper has a lustrous reddish-orange physical appearance that tends to become greenish spots when exposed to environments(oxidation occurs). Next, brass offers a yellow-gold appearance, and bronze dull & reddish-brown.
- Hardness and Machinability
Copper CNC machining
Bronze(40 to 420 HB) is more tough and brittle than brass and copper. So, it has relatively lower machinability and can be cracked if the machining variables are not optimized. However, the rockness hardness can be customized by adjusting the alloy composition.
Subsequently, brass and bronze have lower machinability than copper due to the addition of tough & high-strength metals.
- Thermal and Electrical Conductivity
The ranking for conductivity goes from copper to brass and bronze respectively. Pure copper conducts current and heat more effectively than others.
Try Prolean Now!
Chemical Properties of Copper vs Brass vs Bronze
Copper is more reactive towards oxygen and acidic environments compared to bronze and brass. On the other hand, bronze has more inertness against any acidic and alkaline conditions.

Copper after oxidation
Next, PH level is another criterial to compare brass vs bronze vs copper chemical properties. The bonze grades show higher chemical inertness or stability across a wide range of PH values than the other two. It also contributes to fighting against rust formation and material degradation.
Bronze parts are used in marine and alkaline conditions due to their neutrality toward them. Additionally, secondary coatings like chrome or adhesive paintings can be applied to protect against harsh & chemical exposures.
Another chemical properties is associated with an antibacterial nature. Typically, copper is the best choice for applications requiring antibacterial and hygiene.
Which Costs More? Brass Vs Bronze vs Copper
The cost of pure copper grades is higher and justifies the prices if conductivity, flexibility, and anti-bacterial properties are the critical requirements. Next, the bronze cost is moderate and brass is the least expensive among the three.
The general prices of brass vs bronze vs copper internal market can range; from $ 8 to 10 /kg for copper, $ 3 to 5 for brass, and $ 5 to 8 for copper. However, the exact cost varies on market availability, purchasing volume, and geographical locations. For instance, the costs in Asian regions like China, Vietnam, Indonesia, and India are lower compared to the US & Europe. The reason is the low labor cost for processing and the advantage of metallurgy extraction technologies.
Considerations for Choosing between Brass, Bronze, and Copper
Which is best: brass vs bronze vs copper? It depends on your requirements and application. It means which properties are essential for functionality & performance. Consequently, aesthetics can be another factor in some cases.
It is also about how flexible you are with your requirements. Some high-performance applications like electronic chips might require very strict specifications, while it is much more flexible when choosing plumbing items.
Let’s look at the individual steps involved in the selection process and how they impact the choice.
| SN | Step | Elaboration |
| 1 | Identify the Application | What is the end use? (e.g., decorative, structural, electronic) |
| 2 | Assess Required Properties | Check for thermal/electrical conductivity, strength, corrosion resistance, and machinability. |
| 3 | Environmental Factors | Determine exposure to elements like saltwater or heat. |
| 5 | Consider Material Cost | Not just about cheap prices, but balancing cost and performance |
| 5 | Finalize Choice | Weigh all factors and choose the optimal material (specific grade). |
Try Prolean Now!
Summing Up
Brass, bronze, and copper all are among the popular manufacturing materials. Copper being a pure form provides high conductivity and anti-bacterial benefits, while the other two alloys are suitable for applications requiring more strength, toughness, and flexibility. Additionally, copper & brass are more resistant to corrosion. These differences in characteristics require distinct considerations in CNC machining & forming operations.
At ProleanTech, we have a specialized team of engineers and material scientists for the machining service of metal and alloys. Our engineers understand the requirements of clients and guide the operators to meet the desired quality and precision.
FAQs
Why is brass cheaper than copper and bronze?
The zinc content of bronze is the main reason behind the cost-effectiveness of brass. The low price of zinc also contributes to the reduction of overall costs.
Which longer lasts? Brass, Copper, or Bronze
Copper has a lower lifespan in its pure form. Meanwhile, alloying elements make brass and bronze durable. Also, bronze is even more durable than brass.
Which tools are best for brass and bronze machining?
Both brass and bronze can be machined with CNC machining tools (end mills, turners, drills, boring inserts, etc). Meanwhile. he suitable tooling materials are carbide and high-speed steel.
What to consider while choosing between brass vs bronze vs copper?
First, properties for the functionality of your parts matter most. So, consider strength, thermal & electrical conductivity, corrosion resistance, and toughness. Then, analyze their cost benefits.



0 Comments