Vespel machining
Vespel is a Polyimide Material developed and produced by a U.S.-based engineering company, DuPont de Nemours, Inc. This high-performance plastic is widely used in the automotive, aerospace, healthcare, and electronics industries. Vespel is an important material in plastic CNC machining due to its ability to retain strength at high temperatures, excellent wear resistance, and chemical stability.
Although Vespel material shows good machinability, certain machining factors must be carefully considered to prevent dimensional inaccuracies, manufacturing defects, and overhead costs. This requires an understanding of Vespel and its machining behaviour.
This article will elaborate on the properties, types, machining processes, and application preferences of Vespel plastic.
What is Vespel Plastic?
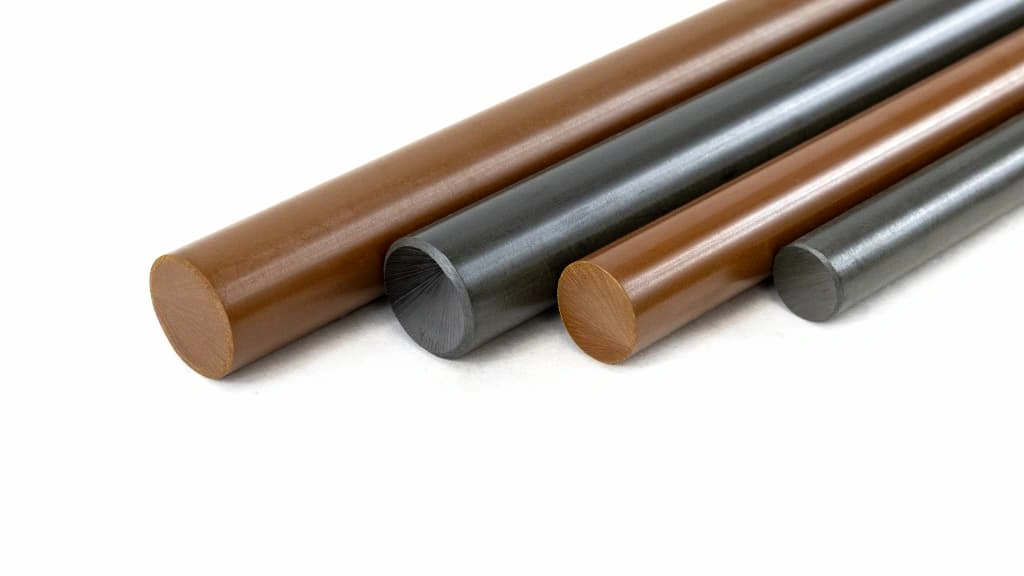
Vespel plastic
Vespel refers to a type of polyimide plastic engineered by DuPont; basically, it is a trademark (Vespel®). What makes it different from regular polyimide material is that Vespel achieves stronger molecular bonds during polymerization. Sometimes, fillers(graphite, molybdenum disulfide, etc.) are also used during formulation.
Due to the stable molecular chains, Vespel provides high strength, longer fatigue life, thermal stability (up to 300 °C), wear resistance, and chemical neutrality. These blends of properties make it a good material choice for plastic CNC machining when parts will be exposed to extreme heat (typically ≥250 °C), high stress, and need a long service life.
Furthermore, DuPont Vespel material is available in the following form.
- Bars
- Tubes
- Rods
- Rings
- Plaques, etc.
Vespel Plastic Properties
Although Vespel shows many characteristics of thermoplastics, it cannot be reshaped after melting. (You can read thermoset vs. thermoplastic here.) Other properties include strength, lubricity, and
- Thermal Stability: Compared to typical thermoplastics, Vespel withstands higher temperatures without losing physical & mechanical properties.
- Chemical Resistance: This material resists many solvents, acids, alkalies, oils, and organic chemical solutions.
- Dimensional Stability: Vespel offers good machinability, and it can be machined into complex shapes with tight precision.
- Outgassing: Vespel shows very low outgassing at high temperatures.
- Water Absorption: Vespel absorbs very little moisture and performs well under vacuum conditions.
- Lubricity: Vespel exhibits good lubricity, producing low friction when in contact with another part/material or under sliding action.
Types of Vespel Materials
Vespel has different types/grades, classified based on material composition, filler amount, and thermal capacity. Each type offers a slightly unique property; for example, Vespel SP-3 provides the lowest outgassing, and SP-21 is ideal for parts susceptible to high wear and tear.
Let’s further elaborate on common types of Vespel material, including SP-1, SP-3, SP-21, and SP-22.
Vespel® SP-1
SP-1 is a pure polyimide form without any fillers in the composition. This Vespel type provides excellent electrical and thermal insulation properties. Consequently, it is highly durable and beneficial for strength and toughness.
When to Use: When parts’ lifespan and structural strength are more essential than low friction.
Vespel® SP-3
The formulation of Vespel SP-3 contains approximately 15% molybdenum disulfide (MoS₂) by weight as a filler. Among different types of machining vespels, it offers minimal outgassing, which is beneficial in aerospace and industrial automation.
When to Use: Low-wear items for dry & vacuum conditions.
Vespel® SP-21
The graphite filling in Vespel SP-21 makes it highly wear & friction-resistant, beneficial for applications involving sliding mechanisms. Consequently, it maintains thermal stability with a high service life.
When to Use: When low friction is crucial for the application and performance of parts, or wear and tear is the primary concern.
Vespel® SP-22
Vespel SP 22 is the most common type in machining, containing a high amount of graphite filling (~40%), which further reduces friction. In fact, it provides a balance of wear resistance and thermal stability.
When to Use: When dimensional stability is a concern, i.e., tolerances matter for functionality & performance.
Other Types
Besides these, there are several other types of Vespel plastic, including SP-22, SP202, SP-211, ST2010, SCP50094, and SCP5000.
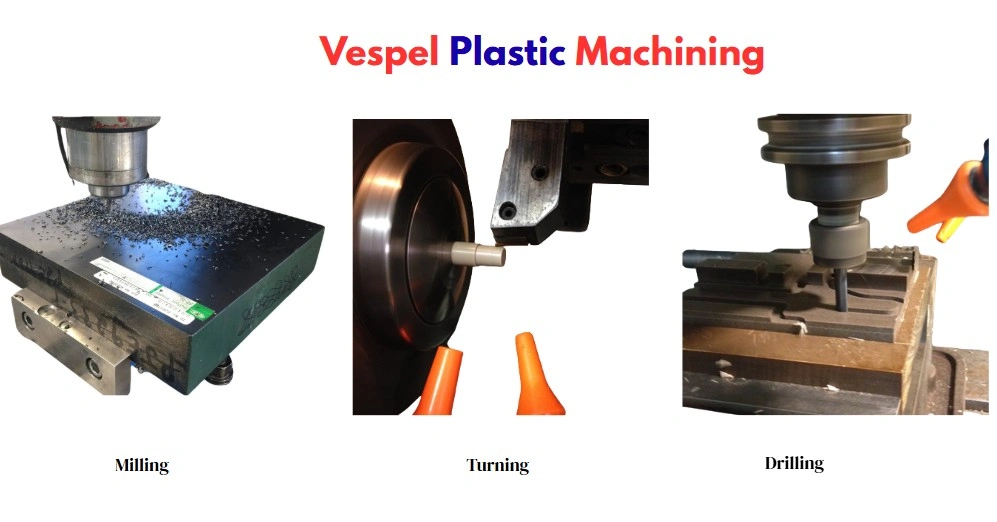
Vespel Machining Processes
Vespel machining processes
Based on the geometry, desired precision, and production requirements, one or more processes, including milling, turning, drilling, threading, and grinding, are utilized.
- Milling: CNC milling produces complex 3D shapes from raw Vespel. Climb milling is preferred for this material, and both cross & down feed are compatible. Choose the cutting speed around 40 to 50 SFM at moderate RPM.
- Turning: Turning is for machining symmetrical shapes, such as cylindrical bearings and seals. Consequently, turning also involves boring, facing, and partings.
- Drilling: The primary consideration during Vespel drilling is the risk of seizing, which occurs when the hole wall & tool become locked together. To tackle this, modified drills are recommended. You can use a standard twist drill, but the hole depth should be no more than half of its diameter.
- Threading: External threads can be made with thread-cutting tools (single-point carbide cutter), whereas internal threads can be made with tapping.
- Grinding: Grinding removes minor material from the surface of the machine parts with an abrasive wheel. You can use centreless or double disc grinders with aluminium oxide abrasive( H8, 46 grit) to grind Vespel.
Try Prolean Now!
Benefits of Vespel Plastic Machining
From machinability to metal-like performance, Vespel offers several benefits, making it a preferred choice for engineered plastic machining parts across industries. It is one of the plastic materials with low outgassing and high creep strength. Consequently, Vespel also has excellent wear resistance and durability.
Let’s look at the key Vespel machining benefits below.
Low Outgassing
It refers to the minimal emission of volatile compounds during machining and in various application environments, which is essential for health and operational safety.
Dimensional Stability
The thermal properties of Vespel are not only beneficial for end-use applications but also for the machining process itself. Vespel does not expand with the heat generated by the friction of the tool and workpiece, so it loses its dimensional consistency. Meanwhile, machined Vespel parts also retain the dimensional accuracy over time.
Wear and Chemical Resistance
The rigid and thermally stable molecular chains in Vespel result in high resistance towards wear, tear, abrasion, and corrosion, even under high stress and rotational loads. Next, Vespel does not react with several chemicals, including oils, fuels, some acids & alkalies, alcohols, and organic solvents.
High Creep Strength
Vespel offers excellent creep strength, which means it resists deformation caused by high pressure. This is beneficial in high-performance applications where components face continuous loads, such as engine seals and compressor parts. When the operating condition is changed, it does not lose the original physical & mechanical properties.
Lubricity
The stable polymer matrix and fillers in Vespel provide high lubricity, even under continuous sliding contact. In some conditions, it does not need any external lubrication.
Durability & Resistance to High Temperature
Although the lifespan of Vespel material widely varies, standard Vespel grades (hard/rigid) can last for 20+ years. Additionally, it has higher temperature resistance and retains properties like flexural strength and tensile strength up to 260°C.
Applications of Vespel Machining
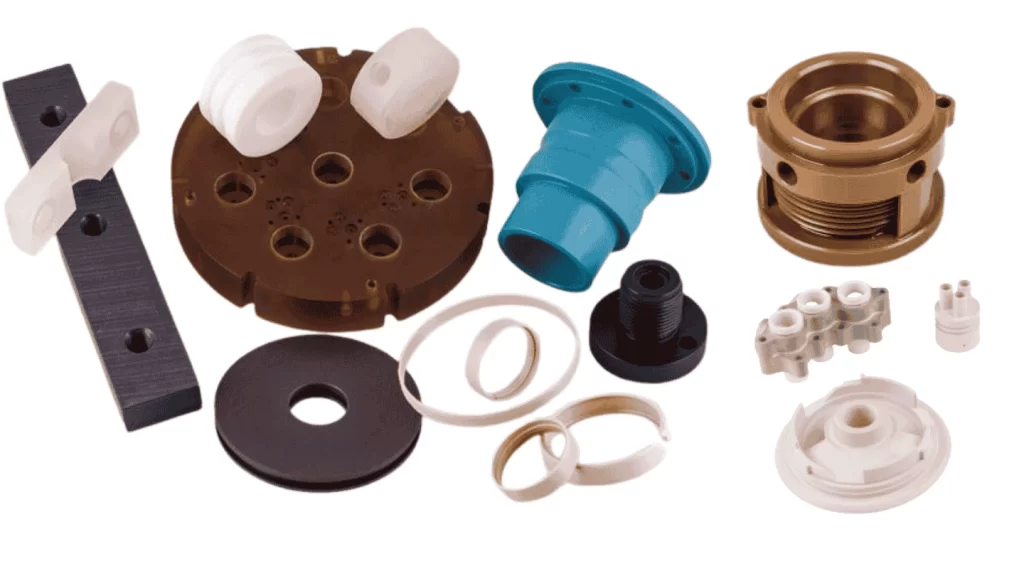
Machined Vespel parts
Vespel is a durable and low-friction material. Meanwhile, CNC-machined Vespel parts perform smoothly when subjected to high mechanical stress, thermal stress, dry running, or vacuum conditions. Therefore, multiple industries use Vespel material.
The table below outlines industries that use Vespel machining and application examples, including aerospace, automotive, energy, industrial automation, electronics, semiconductor, and defense.
| Industry | Application Examples |
| Aerospace | Wear pads, electrical insulators, fuel system seals, thrust washers, and valve seats. |
| Automotive | Seal rings, valve guides, clutch spacers, transmission bushings |
| Energy | Used for both renewable & conventional; insulation spacers, valves, wear strips, thrust washers, and piston rings. |
| Industrial Automation | Robotic joint bearings, conveyor wear strips, indexing table rollers, custom fixtures, and molding system accessories. |
| Electronics & Semiconductor | Vacuum seals, insulator rings, and wafer clamps. |
| Defense | Turret system bearings, launch system bushings, RF communication mounts, and UAV actuator components. |
| Injection Molds and Systems | Thermal separator, guide components, mold inserts, insulation cap, sprue bushing |
What Are the Challenges of Vespel Machining?
Although Vespel has high machinability, there are some challenges in machining this material. It includes machining contamination, excessive material wastage, heat buildup at the cutting edge, and dimensional stability.
Let’s look at key Vespel machining challenges.
Machining Contamination
Due to the active electrostatic nature, Vespel can trap microscopic particles during machining, such as coolant residues and dust.
Material Wastage
Since Vespel is an expensive polymer, excessive material wastage significantly impacts the final cost of manufactured items. Therefore, optimize the tool path in the CAM program to reduce the material wastage.
Thermal Management
The low conductivity of Vespel does not allow for efficient dissipation of the heat from the machining area. This causes heat build-up at the cutting edge.
Dimensional Stability
Especially while machining thin-wall complex parts, it can show stress-induced distortions. Therefore, vespespel must be machined and stabilized properly.
Try Prolean Now!
Best Practices for Machining Vespel Material
Vespel CNC machining
To tackle the Vespel machining challenges and avoid potential defects, you must follow some specific strategies, such as correct workholding, use of the right tooling, coolant application, rake angle adjustments, and lip clearance in drilling.
The following are some Vespel machining practices based on industry experience and DuPont™ recommendations (the material producer itself).
- Workholding Force: You can use OD & ID collets for Vespel holding, but ensure it is not too tight; otherwise, it will deform.
- Tool Material: Use Tungsten carbide for small runs and diamond tooling for high-volume Vespel machining.
- Heat Generation: Choose the correct feeds and speeds to avoid overheating of the workpiece.
- Thin-wall Turning: While turning Vespel thin-wall shapes, set the rake angle to positive 0–5°.
- Tool Nose Radius: While turning, the nose radius of the tool should be in the range of 0.08 to 0.20 mm.
- Milling Depth: For finish passes in Vespel milling, set the depth of cut to a maximum of 0.5 mm.
- Deburring: Use rotating or vibratory deburring setups to remove minor chips and imperfections.
- Deep-hole Drilling: If the required hole depth is higher than half of the drill diameter, choose modified drills with a lip clearance of 30°.
Read More: Thermoplastics CNC Machining
Summing Up
Although Vespel has several benefits & industrial applications, it is definitely not an easy material to machine. If needed, follow tooling, feed, post-processing, and other considerations during machining processes to avoid potential challenges and defects. Additionally, there are many types of machining Vespel, and it is essential to choose the right one that meets your application requirements.
If you need precise and high-quality Vespel machined parts, ProleanTech can be the best partner to collaborate with for your project. Our CNC machining services are designed to provide one-stop solutions, everything from DFM feedback to post-machining operations.
FAQ’s
How hard is Vespel?
Vespel is considered a hard polymer; SP-1 grade offers hardness of approximately Rockwell E45–60.
Does Vespel absorb water?
Yes, but at a very minimal rate. Vespel is a material with a low water absorption property, making it compatible with humid conditions.
Why is Vespel so expensive?
The costing of Vespel is associated with its manufacturing process, which involves complex powder chemistry and sintering at high temperatures.







0 Comments