Phenolic plastic CNC machining is done through techniques such as turning, milling, drilling, and routing. Seasoned CNC machining service providers use well-chosen sets of tools and machining methods to produce clean, accurate cuts.
This is critical because this thermoset plastic can splinter, build up heat, and wear the tool fast. Countermeasures include adequate cooling, optimized cutting, and rigid support for the workpiece.
Whether cloth-based, paper-based, or glass-based, phenolic machined parts have vast industrial uses – washers, gaskets, terminal blocks, structural parts, and much more.
Manufacturers and users value the corrosion resistance, heat resistance, and low thermal expansion.
For more on the structure, benefits, and applications of machining phenolic material, read on.
What is Phenolic Material?
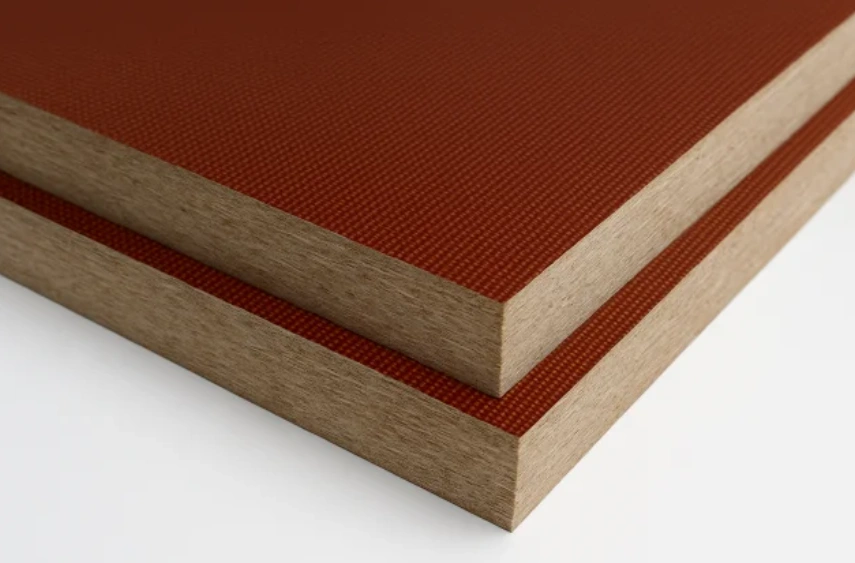

Phenolic material
Phenolic material is a type of thermoset plastic manufactured from the combination of formaldehyde and phenol under heat and pressure. Fundamental chemistry shows that phenol molecules crosslinked by formaldehyde produce a 3D network structure.
This structure gives phenolic material its characteristic dimensional stability, chemical resistance, heat resistance, electrical insulation, and moisture resistance.
Phenolic first appeared commercially in 1907 as Bakelite. It was first used for electronics, but it now has widespread use in gears, rollers, insulators, bushings, and many other areas.
You can read more about the properties of thermosets from this comparison:
Different Types of Phenolic Materials
Phenolic materials are broadly categorized as phenolic composite materials and phenolic encapsulation materials. Since CNC machining mostly focuses on reinforced laminates, this article limits itself to phenolic composite materials.
Phenolic composite materials can be broken down into cloth-based, glass-based, and paper-based types.
Here are more details about these types.
Cloth-Based Phenolic Materials
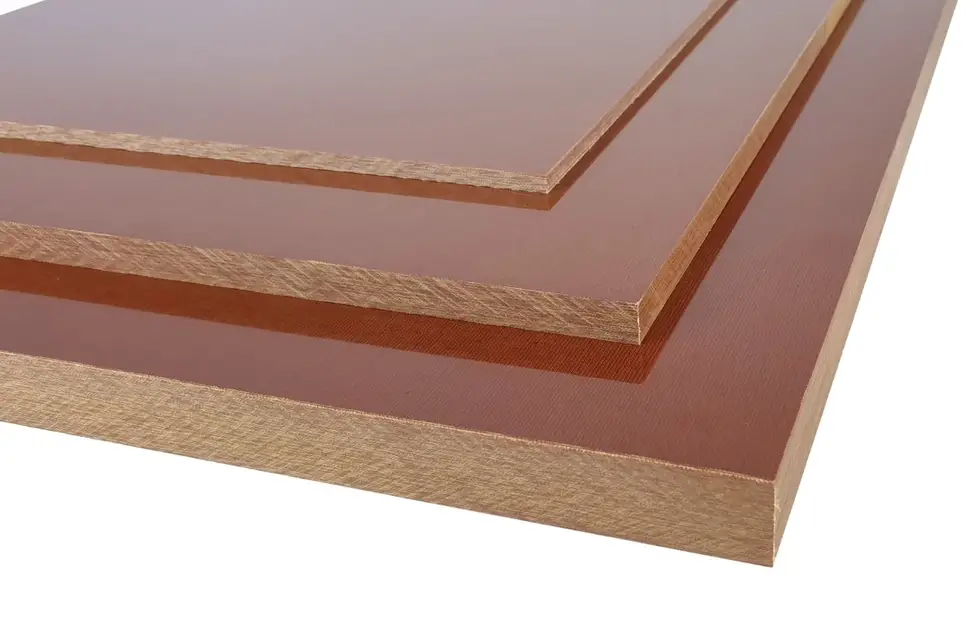
Cloth-based phenolic resins
Cloth-based phenolic resins are also called phenolic cotton board or phenolic cotton cloth lamination sheet. These materials are formed from the heated and pressurized combination of phenolic resin and cotton fabric.
These composites have good machinability and dimensional stability.
Glass-Based Phenolic Materials
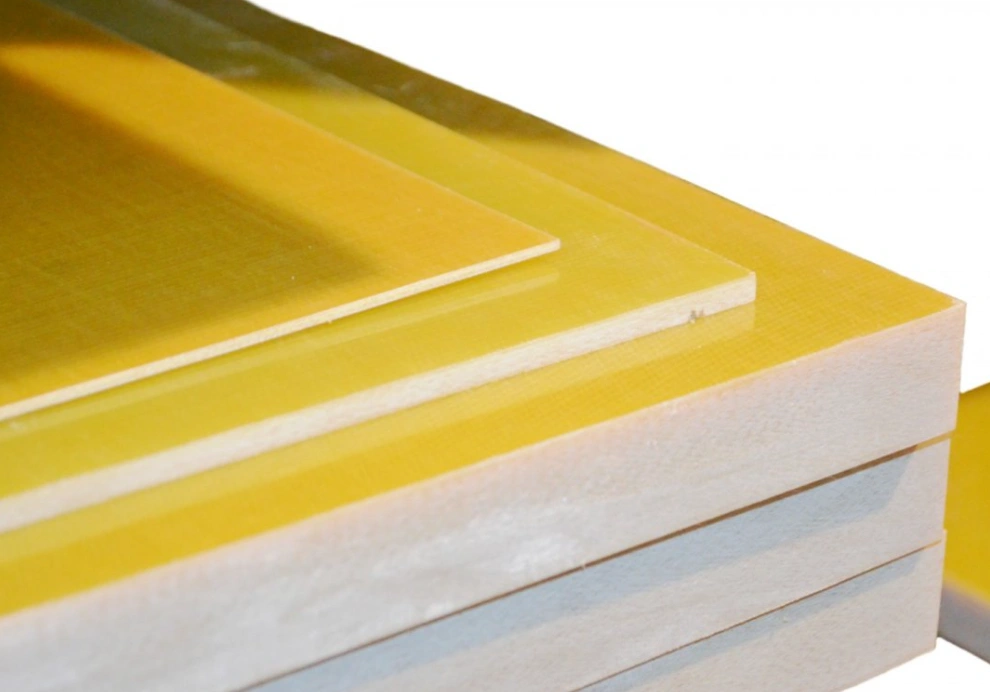

Glass-based phenolic resins
Glass-based phenolic parts have superior heat resistance and mechanical strength. Their phenolic parts are also renowned for suitable electrical properties compared to the alternatives.
With our extensive experience in epoxy glass laminates machining, we can provide the accurately machined components you are looking for.
Paper-Based Phenolic Materials
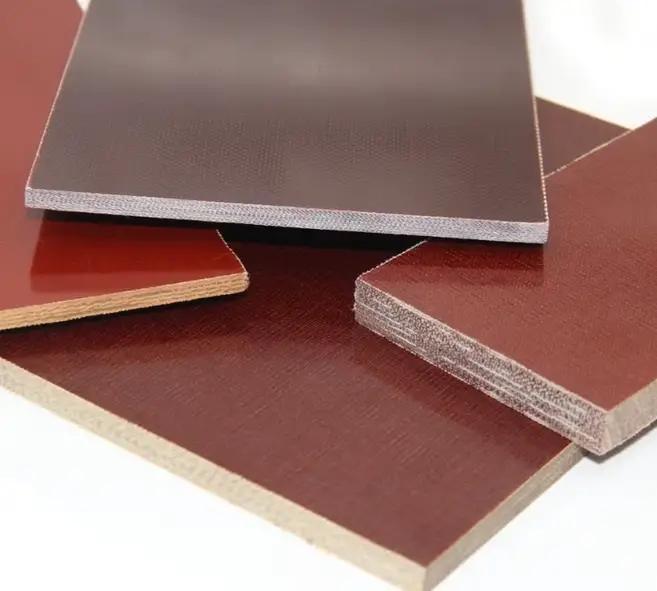

Bakelite
Paper laminates, also called Bakelite in the common language, use paper for reinforcement. The paper-based material provides the characteristic insulation and mechanical properties of this phenolic type. These laminates are also highly cost-effective.
Try Prolean Now!
Advantages of Machined Phenolic Parts
Machined phenolic parts offer several advantages, including the following;
- superior electrical insulation
- resistance to chemical degradation
- reliable performance at high temperatures
- extended wear resistance, and
- precise machining tolerances
Limitations of Machined Phenolic Parts
Here are the main limitations of machined phenolic parts.
- Brittleness – The material is more brittle than engineering thermoplastics and metals. Its parts can easily fail in demanding mechanical applications.
- Higher Cost – The raw materials for phenolic production are typically costlier than for standard plastics.
- Tool Wear – The filler component of phenolic materials is abrasive and can lead to faster tool wear.
- Color Limitation – The aesthetic aspect is absent or limited in phenolic materials; predominantly brown.
Application of Machined Phenolic Parts
Machined phenolic parts are widely used in aerospace interiors, electrical applications, industrial tooling, automotive parts, and thermal management.
The details of these applications are as outlined next.
Aerospace Interiors 
Aircraft interior
Some phenolic grades make excellent parts for aerospace interior components. Their high strength-to-weight ratio suits parts such as panels, fittings, and fixtures.
The design freedom and durability of these parts are also definitely good value for the aerospace industry.
Electrical and Electronic Applications
Phenolic machined parts are extensively used in the electrical industry. These laminates offer the arc resistance and dielectric characteristics necessary for these components. The insulation properties are also valuable.
Examples of electrical and electronic parts/components are;

PCB material
- Printed circuit boards (PCBs)
- Circuit breaker insulators
- Distribution panels
- Transformer parts
- LED lighting
Industrial Tooling
These laminates have suitable properties related to part weight, corrosion resistance, and insulation requirements in industrial settings. Maintenance-wise, self-lubrication of the laminates is a big cost-optimizer in mechanical systems.
Specific applications of phenolic parts in equipment and machinery include wear plates, bearings, and gears.
Automotive Parts
Phenolic properties are suitable for a wide range of car parts, including dashboard parts, electrical connectors, and brake pads. These laminates are strong candidates wherever heat resistance is necessary.
The material also offers good dimensional stability, so it can be made into quality, accurate automotive parts.
Thermal Management
By minimizing thermal conductivity, phenolic parts offer excellent temperature control suitable for various applications. Some notable applications are motor bearing cages, heat shields for car exhausts, and pump impellers in corrosive environments.
Try Prolean Now!
Is it Difficult to Machine Phenolic?
Phenolic materials are more difficult to machine than soft plastics. The difficulty does not exceed that of the materials commonly considered hard. The abrasive fillers in these thermosets cause tool wear.
Interestingly, phenolic materials machine more cleanly than fiberglass. Phenolics also beat many thermoplastics in terms of tolerance reliably.
Methods for Machining Phenolic Materials
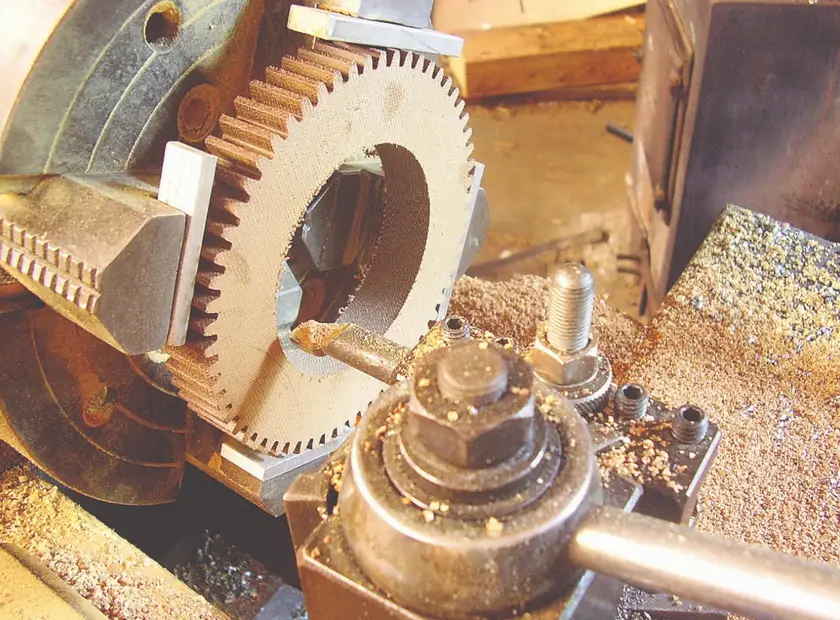

Machining phenolic material
Phenolic stock can be effectively machined using usual machining methods – turning, milling, drilling, routing, and others. Provided the machinist knows dynamics such as thermoset vs. thermoplastic and applies the right tooling and machining strategies, phenolic is easy to process.
More about these methods is below.
Turning
Bushings, insulators, and sleeves are common phenolic parts made by CNC turning. The cylindrical components are made to tight tolerances and excellent surface finishes.
Machining phenolic material this way is possible with optimized feed rates and quality tooling.
Milling
CNC milling is for flat surfaces and complex profiles, which are necessary for various industrial applications. Phenolic machining experts use the technology to make popular parts such as enclosures and terminal blocks.
Drilling
Assembly features and fasteners in phenolic materials require precisely made holes, which are commonly made by drilling. Provided the process takes care of potential chipping on the edges and the tool design matches, the results are excellent.
Routing
Phenolic panels and gaskets are effectively manufactured through CNC routing. This technique thrives in the cost-effective production of cutouts, slots, and other intricate features.
Some Best Practices/Guidelines for Phenolic Machining
Tips for phenolic machining include effective dust extraction, using diamond or carbide-tipped tools, and balancing between cutting speed and feed rate.
Other strategies involve part geometry, cutting tool geometry, and machining tolerances.
Tool Material
Phenolic fillers are tough, so the cutting tool must be equally combative. Since the regular HSS tools will wear out fast, manufacturers almost entirely use diamond and carbide-tipped tools.
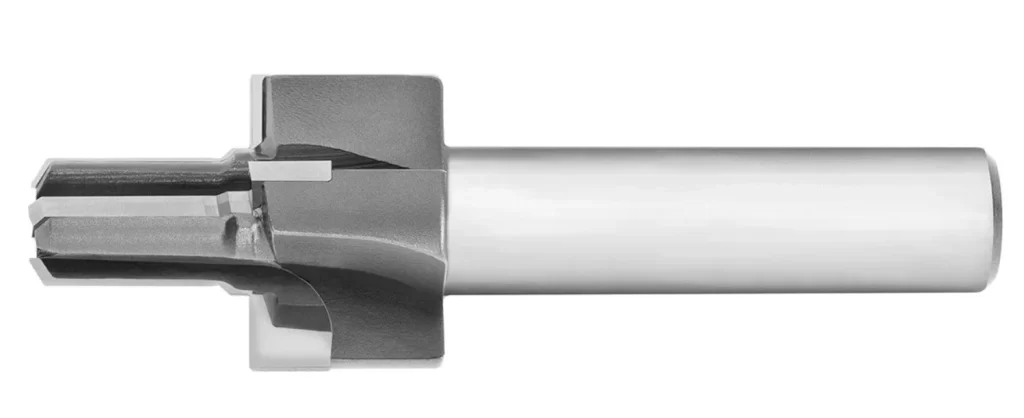
Carbide-tipped tool
While the premium tools cost more, they are cost-effective over the long term because they don’t require regular replacements. They also deliver better surface finishes.
Tool Geometry
Machining phenolic grades is prone to chip formation and cracking. Popular countermeasures are optimizing rake angles and clearance angles. Plastic CNC machining with the least cutting force possible also helps.
Cutting Parameters
Optimized cutting speeds and feed rates are critical for the assurance of dimensional stability and surface quality on phenolic parts.
As this material is notorious for generating heat and dust during cutting, a balance of average cutting speeds and slightly higher feed rates is recommended. Apart from ensuring high-quality parts, the strategy also helps extend tool life.
Part Geometry
Part geometry elements, such as corner radii and wall thickness, are critical because they directly affect a part’s usability and safety from fracture. Getting design-for-manufacturing service is the best way to ensure the most effective phenolic part geometry.
With ProleanTech design input and manufacturing service, you are guaranteed parts that survive real-world applications.
Dust Management
Phenolic machining is typically accompanied by dust and particulate production. Dust management strategies are available to ward off respiratory effects and ensure excellent surface finishes.
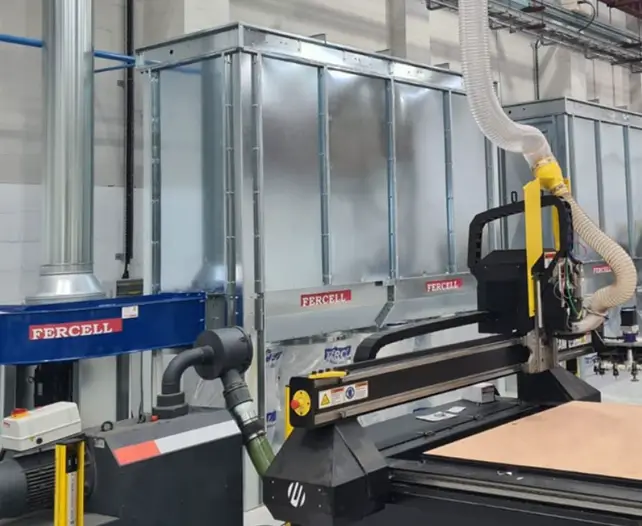

Dust extraction system
Process-Specific Parameters
For the unique phenolic properties, expect every machining process – turning, drilling, milling, and others – to require specific feed rates, cutting speeds, and other specifications.
These distinctions are summarized in the table below.
Table of Process-Specific Parameters for Phenolic
| Type of Process | Requirement for Phenolic Machining |
| CNC Drilling | |
| Cutting Speed (m/min) | 90-180 |
| Clearance angle (degrees) | 10-15 |
| Rake angle (degrees) | 0 – +5 |
| Feed rate (mm/rev) | 0.05 – 0.25 |
| CNC Turning | |
| Cutting Speed (m/min) | 120-300 |
| Clearance angle (degrees) | 10-20 |
| Rake angle (degrees) | 0 – +10° |
| Feed rate (mm/rev) | 0.10 – 0.40 |
| CNC Milling | |
| Cutting Speed (m/min) | 150-400 |
| Clearance angle (degrees) | 10-15 |
| Rake angle (degrees) | +5 – +15 |
In Conclusion
Mastering phenolic machining, that is, producing high-quality, crack-free parts, demands top expertise involving the best tools, machining techniques, and machinery.
The best machining companies implement best practices for cost-effectiveness, durability, and top performance.
With ProleanTech’s CNC machining services, you can get the best out of phenolic sheets. Contact us for world-class machined parts for your industry.




0 Comments