
Cast vs extruded acrylic
There are exciting acrylic products in the market, but not all acrylics are built the same. A common comparison is between cast acrylic and extruded acrylic, with the focus points being the manufacturing process, optical clarity, physical properties, and applications.
Cast acrylics are cell-casted, while extruded acrylics are made through a die process. The resulting difference in optical clarity is clear; cast acrylics are better in this area.
Regarding physical properties, extruded acrylics exhibit better thickness tolerance. Color variations tend to be more common with cast acrylic sheets than with extruded sheets, which are typically available in black, clear, or Opal colors.
In this post, you will learn about the properties, manufacturing processes, and applications of these types of acrylic sheets, culminating in a comparison between the two for more effective plastic CNC machining.
Are Acrylic and Perspex The Same?
The definition of Perspex is that it is a brand name for acrylic; it doesn’t wholly or generally refer to the material. The Perspex vs acrylic discussion is similar to comparing acrylic to other brand names, such as Acrylite or extruded Plexiglas.
All these materials refer to poly(methyl methacrylate). Users worldwide are understandably confused because Perspex has enjoyed market dominance for a long time.
What is the Difference Between Perspex and Acrylic?
As mentioned, Perspex and acrylic are not different, only that Perspex is a brand name for acrylic. PERSPEX® acrylic sheets are produced by 3A Composites GmbH, a globally-renowned producer of panels and sheets based in Germany.
What is Cast Acrylic?
Cast acrylic sheet
Cast acrylic is an aesthetically appealing synthetic plastic material manufactured from liquid polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA). It is produced when molten PMMA is introduced between glass sheets to create a mold.
This transparent thermoplastic is widely used as an alternative to glass, especially where shattering is to be avoided. It has wide industrial applications, including in cars, advertising displays, architectural applications, and smartphone displays.
Acrylics, in general, are soft, versatile, and transparent, properties that are more notable in the polycarbonate vs acrylic comparison. Unlike acrylics, polycarbonate is difficult to machine, often requiring specialized tooling.
Properties of Cast Acrylic
Cast acrylic exhibits distinct properties that are suitable for interior design, commercial displays, and other applications. The common cast acrylic characteristics are:
- High chemical resistance
- A hard surface that is resistant to scratches and wear
- High molecular weight of up to 2,000,000 g/mol or more
- Optical clarity of up to 92%
How Cast Acrylic is Made?
Cast acrylic manufacturing entails allowing liquid methyl methacrylate (MMA) monomer to solidify between a pair of glass plates over several hours. Röhm and Haas invented this slow polymerization method in the 1930s.
Here are the steps in brief.
Step 1: Raw Materials Mixing
Polymethyl Methacrylate Pellets, Methyl Methacrylate Monomer, and colorants are mixed.
Step 2: Pouring the Mixture
The mixture is poured into a mold, which is a sealed space between two glass sheets.
Step 3: Oven Heating
The mixture in the mold is then heated in a controlled oven to polymerize the methyl methacrylate monomer (MMA). This process is called casting.
Step 4: Slow Cooling
Slow cooling ensures the relief of internal stresses developed during the casting process. It prevents the development of brittleness in the material.

Cast acrylic production line
Advantages of Cast Acrylic
There are several advantages of cast acrylic in precision plastic CNC machining, including;
- Cleaner cut material edges
- Better heat resistance during manufacture and use
- Color variability
- Stress-crazing resistance when the material is exposed to chemicals
- Maintenance of tight tolerances during fabrication
What are the Disadvantages/Limitations of Cast Acrylic?
The biggest limitation of cast acrylic, in the light of the cast vs extruded acrylic comparison, is its relatively high cost. The material is usually about 20% more expensive than alternatives.
Other than that, the cast acrylic characteristics, stemming from its narrow forming temperature range, require manufacturers to handle the material with extra care during the thermoforming process.
Cast Acrylic Applications
Cast acrylic is widely used in applications where precision cutting and optical precision are highly valued. These include the following;
- Aquariums
- Furniture and interior design
- Signage
- Exhibitions
- Museum Displays
- Aircraft Canopies

Cast acrylic aquarium
What is Extruded Acrylic?
Extruded acrylic is a type of polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA) material produced when molten acrylic is forced through a die. The product is typically available as transparent sheets of uniform thickness.

Extruded acrylic sheets
Properties of Extruded Acrylic
The continuous manufacturing process gives extruded acrylic unique properties and performance capabilities, including the following;
- Higher thermoforming capabilities
- Easier fabrication due to a softer surface finish
- An optical clarity that suits many commercial applications
- High impact resistance
- Tolerance for consistent thickness
How Strong is Extruded Acrylic?
Extruded acrylic is relatively strong, with an impact resistance that exceeds that of many alternatives. The material does not break easily during machining and usage. Whether for formed parts or common load-bearing applications, this material demonstrates the required flexural characteristics and tensile strength.
How Extruded Acrylic is Made
Manufacturing this product involves a continuous extrusion process that begins with the melting of acrylic pellets at approximately 250°C. The molten material is then passed through special dies.
The next stage for the resulting sheets is polished rollers for calibration and cooling. Extrusion is a high-speed process with real-time surface treatment and thickness monitoring.
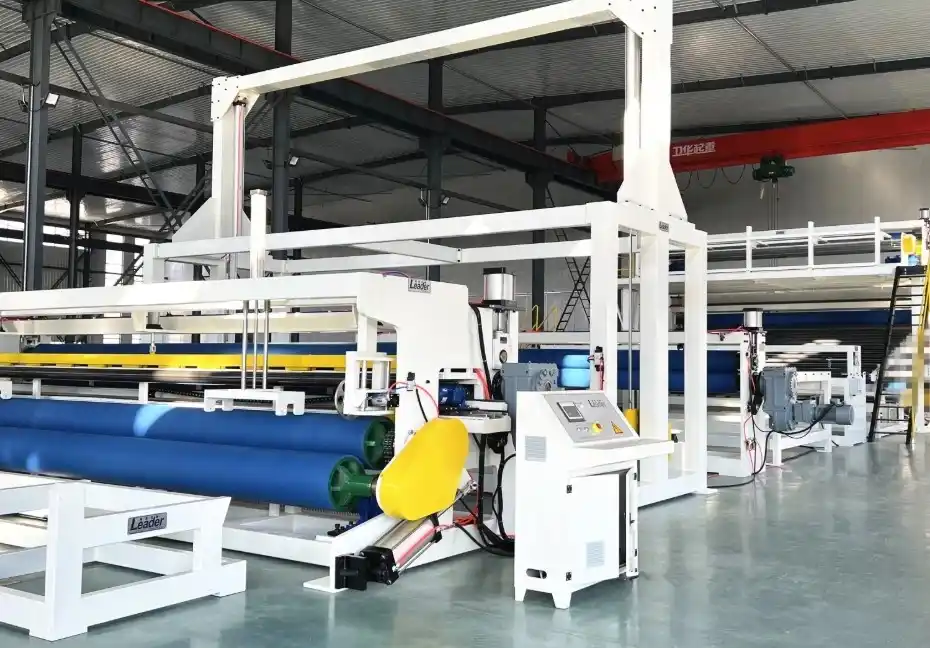

Acrylic sheet extrusion line
Advantages of Extruded Acrylic
Extruded acrylic delivers tangible benefits such as;
- Consistent thickness
- High impact resistance
- High-volume manufacturing capability
- Easier thermoforming
Limitations of Extruded Acrylic
The continuous manufacturing and the resulting extruded acrylic characteristics contribute to the following limitations;
- Uneven thermal expansion due to the molecular properties
- Mechanical stress causes crazing
- Polished edge finishes are difficult to achieve
- Material can warp where tight dimensional tolerances are required
Try Prolean Now!
Applications of Extruded Acrylic
Extruded acrylic sheets are widely used in various applications, including design & furniture, glazing, signage, and a range of industrial components.
Design and Furniture
The material’s high impact resistance and optical clarity are ideal for cabinets, glass decorations, and furniture.
Glazing Applications
Extruded acrylic roof glazing
The glass effect of this acrylic material works for glazing applications, such as sliding doors, sliding windows, and skylights.
Signage
The material is also used in signage applications, for instance, Point of Sale (POS) displays, directional signage, and outdoor signs.
Industrial Applications
In this segment, one of the most popular applications is in the automotive industry. Examples of parts include headlamp covers, instrument panels, and interior trims.

Headlamp cover
Is Extruded or Cast Acrylic Better?
Your choice of cast vs extruded acrylic for your projects depends on factors such as production volume, surface finish, durability, and cost. For instance, if you are focused on the budget, extruded plexiglass, with its lower raw material cost and faster processing, is relatively cost-effective.
Acrylic machining in large volumes is also better done with extruded acrylic because of the speed and cost-efficiency.
Cast Acrylic and Extruded Acrylic Sheet Colours, Finishes and Textures
You can tell the difference between cast vs extruded acrylic from the surface quality and optical clarity. Cast acrylic sheets are optically clearer, but when you look at extruded acrylic, some distortions are often evident. Also, cast acrylic has more color variations than extruded acrylic does.
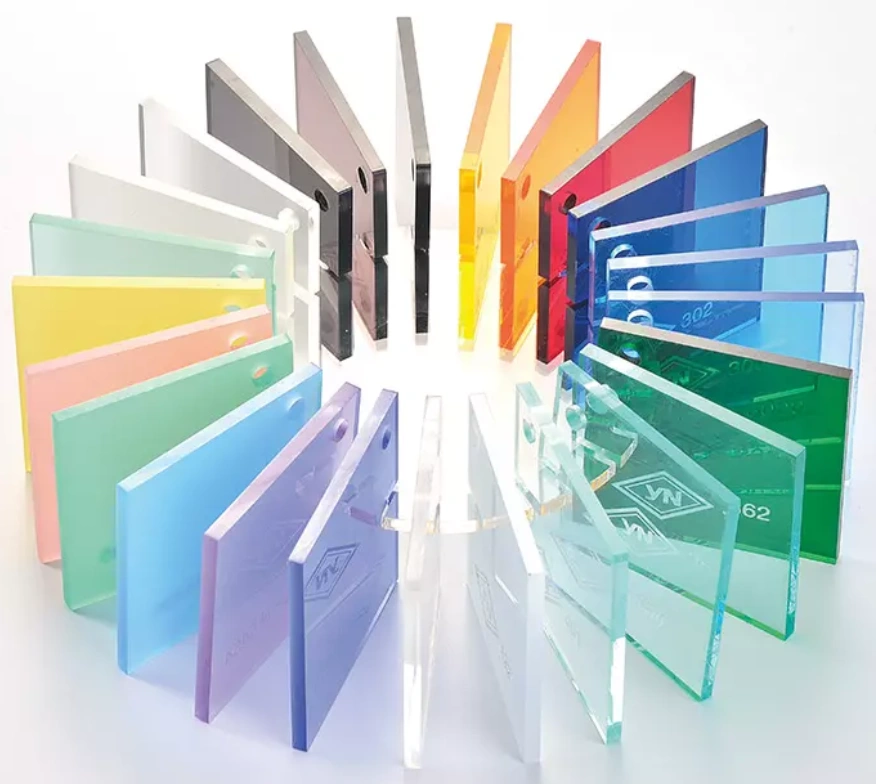

Cast acrylic color variations
Expectedly, from the above point, cast acrylic is smoother with fewer surface imperfections. The results of the extrusion process can be shown in the form of flow lines.
Performance During Laser Cutting/Cutting Speeds
Cast and extruded acrylic perform differently in laser cutting operations, mainly due to their different molecular structures.
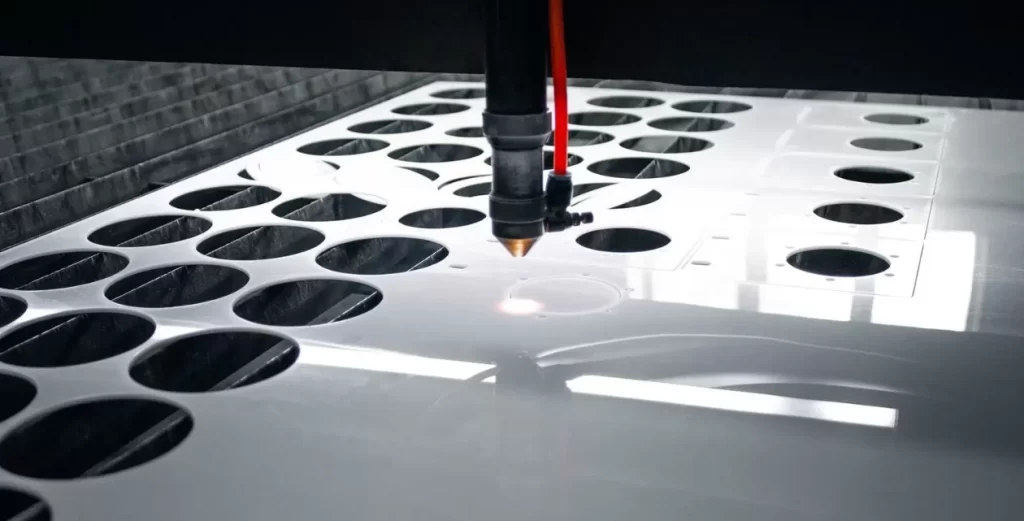

Acrylic sheet laser cutting
Why Laser Cutting Enthusiasts Prefer Cast Acrylic
Laser cutting enthusiasts are fond of cast acrylic because of its superior edge quality. Since the material has a more uniform molecular structure, it tends to cut more cleanly. This material doesn’t necessarily require secondary processes because its edge finish is naturally polished. Yes, the two types of materials can be laser cut, but cast acrylic gives cleaner and easier cuts.
For extruded acrylic, laser cutting causes stress cracking, which is evident in rough edges. A laser-cut extruded sheet may require post-processing to improve the edge quality. If you are cutting for larger jobs where edge quality is not a top priority, the faster cutting of extruded acrylic may be worthwhile.

Smooth-cut acrylic
Applications in Routing & Engraving
Routing and engraving jobs are defined by precise, clean cutting. Cast acrylic sheets are the better option for these applications because of their minimal surface and edge defects.
Thermal Stability
Manufacturing items for heat-prone applications requires consideration of this property. Again, cast acrylic characteristics are better suited for these applications. The material has better heat resistance. This analysis becomes clearer from the comparison of cast vs extruded acrylic perspectives presented in the table below.
Try Prolean Now!
Table for characteristics comparison for Cast vs Extruded Acrylic
|
Element |
Cast Acrylic |
Extruded Acrylic |
Conclusion |
|
Manufacturing method |
Liquid material is slowly solidified in a mold |
Particles are melted and extruded in a die |
Extrusion suits assembly setup while casting is relatively slow |
|
Optical clarity |
No internal stress, so higher optical clarity |
Optical clarity is enough for most applications, but minor surface variations are visible |
Choose cast acrylic for perfect optical clarity |
|
Dimensional tolerance |
Cast acrylic sheets have tighter tolerances and more consistent thicknesses |
Some thickness variations, but still useful in many applications |
Cast acrylic is more suitable for precision projects due to its tighter dimensional tolerance |
|
Material cost |
Higher due to manufacturing cost |
Lower because of manufacturing efficiency |
Extruded acrylic is a more economical option |
|
Thermoforming |
Typically develops surface marks and stress whitening when thermoformed |
Smooth forming with little or no stress marks. The extrusion process makes the material’s molecular orientation more uniform |
Cast acrylic is ideal for clean bends in detailed forming works, while extruded acrylic works for simpler forming |
|
Machinability |
Easy to machine with less chipping and a minimal requirement for secondary processes |
It machines well, but it produces rough edges. Stress cracking and higher chipping. |
Cast acrylic generally machines better, with extruded acrylic requiring extra processes to achieve similar cleanness |
|
Chemical resistance |
More resistant to chemical and solvent reactions due to higher molecular weight |
More prone to cracking and solvent corrosion |
Cast acrylic is likely to last longer in chemical exposure |
|
Young`s modulus of acrylic |
Higher due to higher molecular weight |
Slightly lower |
Cast acrylic is stiffer than extruded acrylic |
In Conclusion
Both cast and extruded acrylic have their standout pros and applications. While extruded acrylic suits affordability and availability, cast acrylic is the go-to thermoplastic for optical clarity and precision machining. The choice of cast vs extruded acrylic depends on your project, specifically the type of product you want.
ProleanTech’s CNC machining services will deliver unmatched results regardless of the material. With our advanced machinery and experienced workforce, you can get exciting acrylic products at affordable rates.





0 Comments