The heart of the car engine is the valve; it keeps the engine running smoothly through the controlled inflow of fresh air and expulsion of combustion gases. Without this component, the car engine would be unable to generate power.
There are two categories of car valves. The intake valve in the engine lets in the air-fuel mixture while the exhaust valve releases exhaust gases. Manufacturing a valve involves several processes, including CNC machining services.
Since this is a sensitive part of a car, ensuring it is in the best condition is critical. Choosing the best valve is only the first part; you must maintain and replace it when necessary. Considering the several challenges to having optimum performance from the valve, following expert performance tips can be helpful.
This handy guide looks at these and other aspects of the car engine valve. Please read on.
What are the types of car engine valves?
For someone who cherishes a car’s performance and is interested in learning how the car engine runs, starting with the engine valve types and designs is a good idea. The intake valve and exhaust valve are crucial in the controlled inflow of the air-fuel mixture and expulsion of exhaust gases respectively.
Intake valve
The intake valve allows the entry of an air-fuel mixture into the combustion chambers. During the intake stroke, a vacuum forms in the cylinder as the piston lowers. At the same time, the intake valve opens and lets in the air-fuel mixture from the intake manifold. The setup uses the camshaft to open the intake valve at the right time and speed.
The Exhaust Valve
The role of the exhaust valve is to ease the expulsion of exhaust gases from the chamber. As the piston forces the exhaust gases after the power stroke, the valve opens appropriately in synchrony with the camshaft.
Parts of a car engine valve
Before highlighting the different parts of auto engine parts and functions, it is noteworthy that there are several types of vehicle valves. The prominent types are:
- Poppet valve
- Sleeve valve
- Rotary valve
- Reed valve
The poppet valve is also called the mushroom valve because of its interesting shape. The valve face has a 30-degree or 45-degree face for tight closing fitting. These valves work in tandem with a camshaft.

Poppet Valves
For the sleeve valve, the shape is tubular. This shape is for quieter operation.
The rotating valve type has a rotating disc and a port. The positioning is such that as the disc rotates, the closure and opening of the inlet and exhaust sides alternate. With minimal stress and vibration, this valve design is ideal for high-speed car engines.
Finally, there is the reed valve, which is comparable to a check valve. The reed vehicle valves allow the entry of fresh air while blocking the exit of exhaust gas, and vice versa. You will mostly find this type in two-stroke engines.
Here are the main parts of a car engine valve:
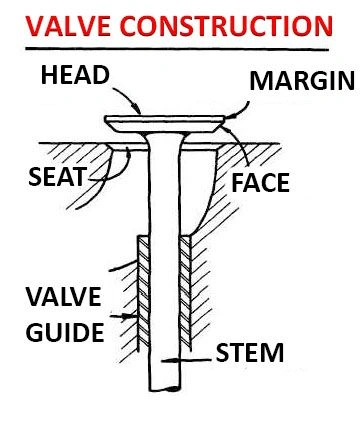
Engine valve components
Valve Head
The valve head is the flat part of the valve that looks like a disc. It perfectly aligns with the valve seat to form a tight seal, an important design property for perfect control of the flow of the air-fuel mixture.
Stem
The stem is the narrow cylindrical part of the valve. It runs from the valve head to the other tip of the valve.
Valve Seat
As the name suggests, the seat of the car engine valve is the part of the valve that provides the settling surface during the closing stage of the combustion cycle. The material for the seat is thermally conductive and wear-resistant.
Spring
This part of the car engine valve provides the necessary force to keep the valve closed during compression and power stroke. It closes the valve following the opening by the camshaft.
Valve Guide

Valve Guides
These are cylindrical engine valve components that help align the valve in its path. The valve guide is also instrumental in minimizing the wear and tear of the stem.
Valve Lifter
The valve lifter rests on the camshaft and uses the cam lobe’s movement to operate the valves. It could be a solid lifter or a hydraulic lifter.
Valve retainer
This part of the car engine valve primarily keeps the valve step and spring together.
Try Prolean Now!
How the car engine valve works
When handling a car, have you ever wondered about the amazing interaction of engine parts that makes the car roar to life? As this section explains, it is all about the flawless operation of the engine valves in conjunction with other engine components.
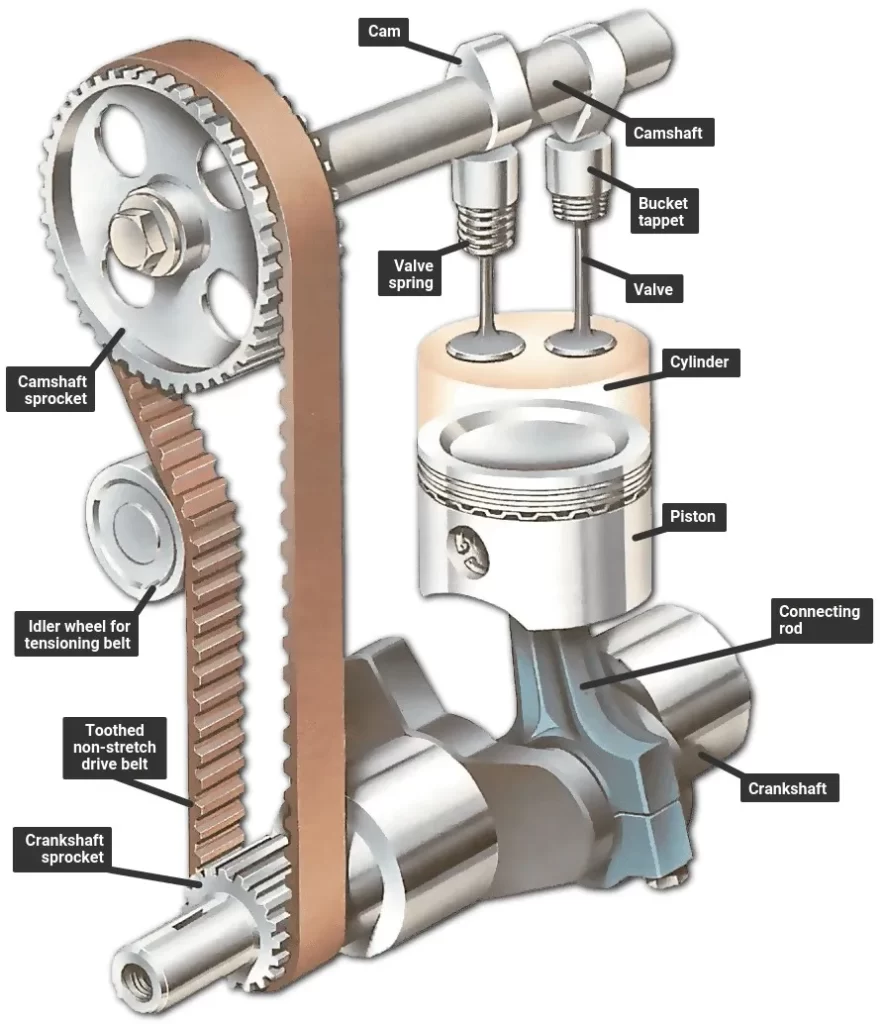
Diagram of the mechanism between crankshaft, camshaft, and valves
The camshaft controls the parts of the valve and is in synchrony with the crankshaft. Lobes connected to the camshaft push the vehicle valves in the designed sequence. The force is transmitted through intermediaries such as lifters and pushrods. The lobes close and open the valves in tandem with the rotating camshaft.
Engine valves
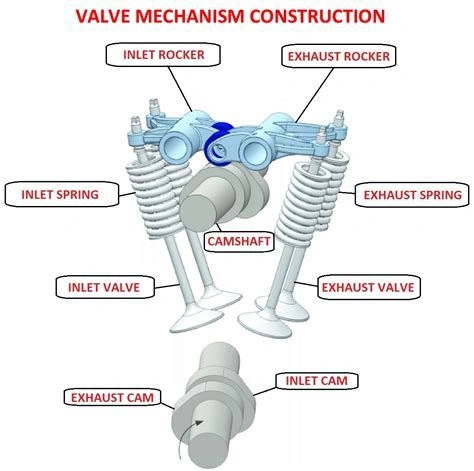
Valve interaction with camshaft
There are four engine strokes: Intake stroke, compression stroke, power stroke, and exhaust stroke.
The first step is the power supply to the crankshaft.
In the next step, the crankshaft, through its rotary motion, moves the camshaft, which controls the up-and-down movement of the car engine valve.
During the suction stroke, the camshaft forces the valve down, creating space for the air-fuel mixture in the combustion chamber.
During the next step, the piston changes direction and compresses the air-fuel mixture in the combustion chamber. At this time, the camshaft closes the engine valve. A spring mechanism ensures the valve remains in this closed position.
During the power stroke and as the piston moves downward, both the inlet and exhaust valves remain closed for some time to maintain pressure.
The exhaust stroke occurs with the piston moving upward and the exhaust valve opening to let out the exhaust gases.
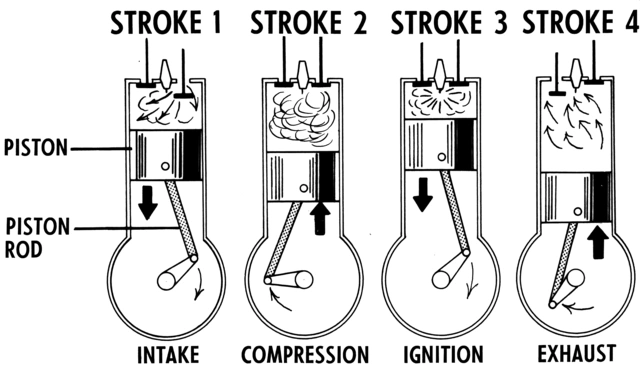
Diagrammatic representation of a four-stroke engine of a car
What do valves do in an engine?
Without valves, the engine would not come to life and no journey would happen. They are the lungs and heart of the car, and this is why:
They demarcate air and combustion chamber
This is the primary role of the car engine valve. A reliable seal between the air and the combustion chamber is essential to control the air-fuel intake in four-stroke engines. The lack of an intake channel in this type of engine means an efficient separation between the chamber and air is necessary.
They cool the engine
The harmonious operation of the intake and exhaust valves is instrumental in keeping the engine cool. As one valve expels hot air, another lets in cool fresh air. A steady flow of air ensures the engine’s coolness and safety.
They minimize engine noise
The two types of vehicle valves open and close smoothly. The timing of these operations is precise, leading to a perfect flow of air and fuel. Consequently, pressure disruptions are prevented. The car engine valves dampen any sound waves that may emanate from the combustion process.
They get rid of gas
When ignited, the air-fuel mixture generates power that forces the piston to move. After the power stroke, the piston changes direction and prompts the exhaust valve to open. This in turn leads to the expulsion of the exhaust gases. The exhaust valve is designed to open at the exact time to remove all the gases. This readies the chamber for fresh air entry for the start of another cycle.
They protect the engine against backflow
Backflow can be detrimental to the car engine in several ways. Apart from reducing the engine’s efficiency, backflow can cause overheating of engine components, which could lead to damage. Poor combustion and increased emissions are also likely repercussions of backflow.
A good car engine valve prevents this problem by forming a reliable barrier against the free entry and re-entry of gases. The camshaft is also instrumental in enhancing this role because it ensures the synchronized opening and closing of the intake and exhaust valves.
Try Prolean Now!
Materials for making car engine valves
You will agree that the resilience of the car engine valve is unmatched. The monumental pressure and temperature in the engine requires a tough component. Manufacturing engine valves using the following materials ensures smooth performance for long:
Titanium alloys
Titanium has a high strength-to-weight ratio. Experts in rapid prototyping in China alloy this strong metal with copper, molybdenum, and other metals to make it more suitable for valve performance.
Stainless steel
Stainless steel automobile valves are available in different grades. However, the most common preference is EV8, particularly for high performance. Manufacturers use this material in varying ways. For instance, some use it for the intake valve in engine only while others use it for both types of valves.
High-speed Steel
High-speed steel’s working temperature can be as high as 600°C, so this material is unique and applicable in the hot combustion engine environment. The X45CrSi93 valves are common in the automotive industry for their durability and heat resistance.

An X45CrSi93 car engine valve
Inconel
Nickel-based superalloys (Inconel) are highly resistant to corrosion and oxidation. This material is ideal for automobile valves used in high-performance cars.
Popular manufacturing processes for car valves
To provide reliable performance to the car, a car engine valve undergoes a series of manufacturing processes before it is ready for use. Here is a brief description of the main processes.
a. Cutting

It starts with cutting a metal stock to size.
The raw material of stainless steel, inconel, titanium, or another relevant material is initially in the form of bars. The machinist reduces the stock to the desired diameter based on the envisaged size of the car engine valve. A CNC lathe may be used for this process.
b. Joining
Sometimes, the stem and valve head must be of different materials. This is because of the unique temperature resistance requirement for the head and tensile strength requirement for the stem. The two metal pieces are joined through friction welding.
c.Upsetting
At this stage, the initial shape of the car engine valve is generated in readiness for the forging step. The goal of upsetting is to reduce the height and increase the diameter, so the piece is compressed using a pair of dies. The component is often heated at this stage to make it malleable.
d.Forging

Forging is essential for valve mechanical properties
This step entails heating the metal piece to a specified temperature and then forming it mechanically. While this process helps attain the desired shape of the car engine valve, it also enhances the part’s mechanical properties. Closed-die forging is the preferred method.
e.Heat treatment
Heat treatment of the valve is a three-pronged process of reducing the metal’s crystallinity and brittleness.
f. Surface treatment and finishing
Borrowing from this coverage on metal prototype manufacturing methods explained, the finishing steps are as crucial as the other stages.
Surface treatment and finishing are the finishing procedures of the car valve manufacturing process. Surface treatment cleans the part’s surface while surface finishing refines the shape. By adding hard chrome plating, surface finishing also helps increase the valve’s durability.
An engine with chrome-plated parts
How do I know if my car valve is bad?
A struggling car valve will always communicate. From troubling engine noises to leaks, knowing how to identify signs of a malfunction can help solve car valve issues in a timely manner. Below is a highlight of the common signs of faulty automobile valves:
1. Leaks
A leaking valve cannot seal the combustion chamber fully. This causes a loss in engine efficiency due to compression loss. Some common causes of leaks include a misplaced valve seat, a broken valve spring, a dislodged retainer set, and a faulty timing belt. Identifying the specific issue and repairing or replacing the part should stop the leak.
2. Car valve burnout
This challenge results from the valve being subjected to high heat for a long time. The indication of burnout is engine power loss. Since the most common cause is the valve being incorrectly aligned to the valve seat, it is important to address this issue promptly.

Burnt valve and valve seat
3. Car engine sticky valves
When carbon and dirt collect around the valve, they can interfere with the smooth opening and closing process. Engine misfires and poor acceleration often occur due to sticky valves. Using quality fuel is often an effective solution for sticky valves.
Conclusion
As we reiterate at Prolean Tech, the heart of a car’s engine is the engine valve. Understanding the auto engine parts and functions is fundamental to maintaining optimal engine performance.
Since the car valve regulates combustion in the engine, it is necessary to understand how it works and accord it the necessary care and maintenance. The best strategy involves using the right car valve from the start.
Do you want to get more insights and ideas about how a car valve affects a car’s performance? Contact us today and ask us about your project needs to ensure optimal valve performance.
FAQ
What is the valve on a car?
This is a mechanical device that works in synchrony with the engine’s camshaft and other components to allow fresh air in or remove exhaust gases from the cylinder.
How much does it cost to replace a car valve?
On average, a full valve replacement will cost between $900 and $2,000, while replacing one valve can cost up to $200.
What is the car valve called?
The car valve is sometimes called a valve. Some mechanics also refer to it as a “poppet valve”, which is the name of one of the main car valve types commonly used.



0 Comments