Brass is an alloy of copper and zinc with a higher amount of copper, up to 80% in some grades. It is popular in manufacturing due to its high machinability and other various beneficial properties like corrosion resistance, thermal & electrical conductivity, antibacterial, and aesthetic. Consequently, different machining processes are used to convert raw brass material into functional items, and CNC turning is one of them. CNC turned parts have a critical role in sensors, hydraulics, motors, electronic control, and other areas contributing to diverse consumer and industrial applications.
Let’s overview the CNC turning of brass, suitable grades, benefits, and application examples.
Brass As an Engineering Material and CNC Turning
Brass is a copper alloy with zinc as the main alloying element, whereas other elements like iron, tin, lead, phosphorus, and nickel are added in minor amounts. Consequently, the exact composition and their proportions depend on the type of particular brass alloy.
Brass materials
The common machining grades are C300, C360, C335, C314, C230, C272, and C220. Meanwhile, C 3XXXseries are known as free-machining grades (Nearly 100% machinability)
The table below outlines the common machining grades, composition, and key properties. Source.
| Brass Alloy Grades | Copper (%) | Zinc (%) | Lead (%) | Additional Elements | Key Properties |
| C260 (Cartridge Brass) | 70 | 30 | – | – | High ductility, corrosion resistance, good strength |
| C280 (Muntz Metal) | 60 | 40 | – | Iron (minor amount) | High corrosion resistance and good for casting |
| C230 (Red Brass) | 85 | 5 | – | – | High corrosion resistance and decorative appeal |
| C360 (Free Machining Brass) | 60 | 35.5 | 3 | – | High machinability and good formability |
| C385 (Architectural Bronze) | 59 | 42 | Up to 3.5 | Excellent machinability and high-precision work | |
| C464 (Naval Brass) | 9 | 40 | – | 1% Tin | Marine corrosion resistance and durable |
What is CNC Turning?
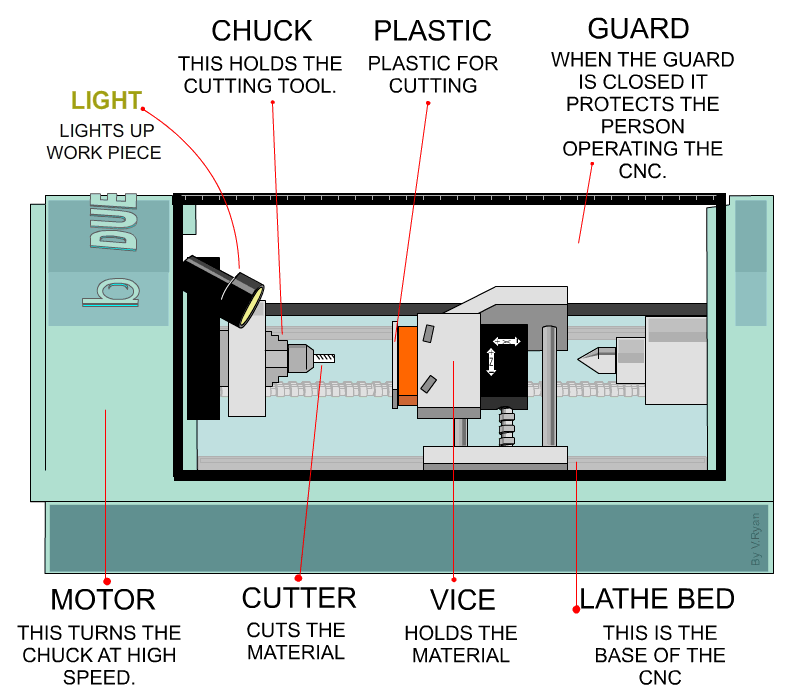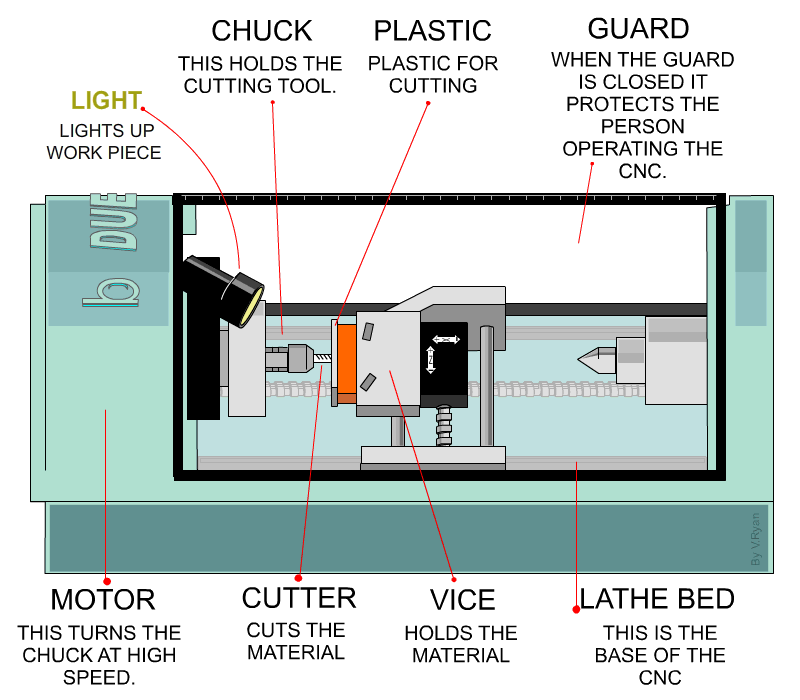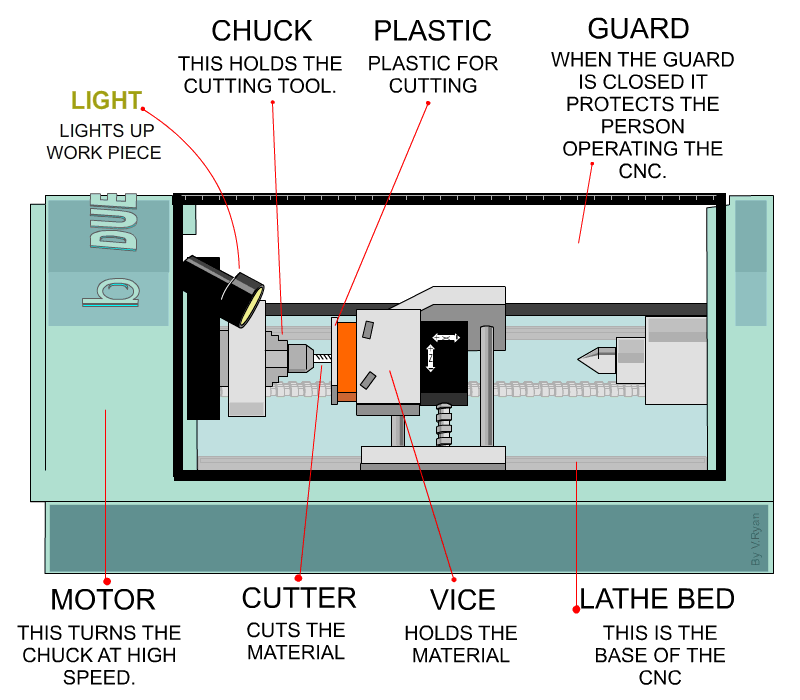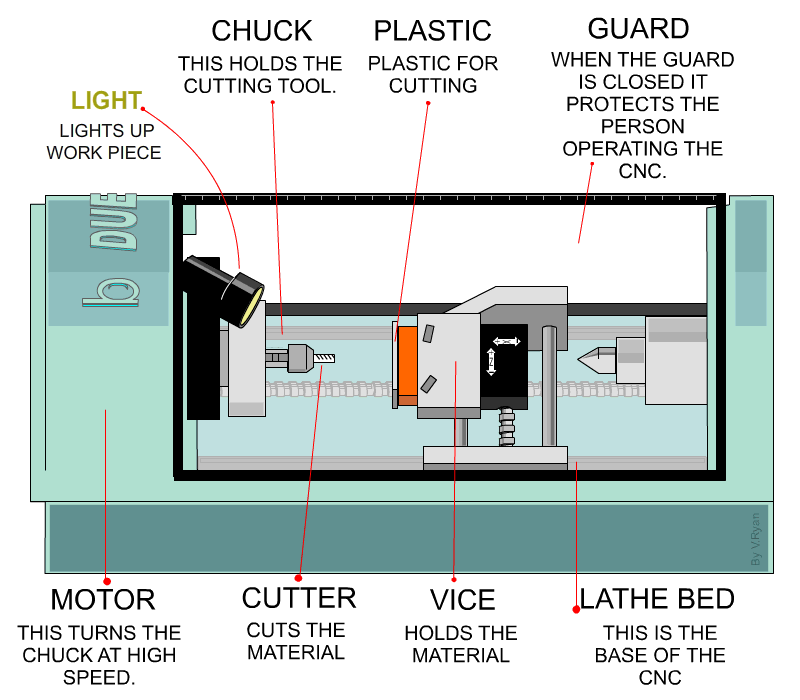
Next, CNC turning is a process of creating symmetrical parts from cylindrical workpieces through controlled material removal. During the process, turning tools feed the rotating workpieces, and the tool post/carriage controls the linear and vertical movement of the tool through G-codes.
CNC turning mechanism
The machining of CNC turned parts can make the following shapes;
- Cylindrical and Conical Shapes
- Grooves, Tapers, and Steps
- Flanges and Recesses
- Slots
- Chamfer and Ridges
- Fillet, Knurls, etc.
Furthermore, manual lathes, CNC lathes, and Turning centers are the machines that execute turning operations on brass workpieces. Manual lathes are suitable for small volumes and custom turned parts, whereas CNC lathes and turning centers are more precise and fast. Turning centers especially handle highly complex designs.
Try Prolean Now!
Applications of Brass Turned Parts
The key industries that use brass turned parts are as follows;
Plumbing and Fittings
Brass plumbing and fitting items
Brass is a comparatively lightweight and highly corrosion-resistant copper alloy. Its durability and resistance against harsh conditions make it suitable for various plumbing fixtures and fittings.
- Valves
- Water heater elements
- Joints and faucet
Architectural and Decorative Items
Architectural brass components made with CNC turning
Brass’s bright goldish appearance makes it ideal for various architectural and decorative items. Additionally, its aesthetic quality does not fade over time.
- Door hardware like knobs and handles
- Roofing facades
- Lanterns
- Luxury furniture and artworks
- Water pump components
Automotive Industry
Brass turned auto parts
The precision of brass CNC turning and the mechanical properties of brass grades allow brass turned parts manufacturers to make various high-performance auto parts. Consequently, they can withstand the harsh environments.
- Low-friction bearings and bushings
- Sensors
- Low surface friction bearings and bushes
- Radiator elements
- Trims and emblems
- Fasteners
Electrical and Electronics Industry
Brass turned parts for the electrical industry
The electrical conductivity and rust protection properties of brass are beneficial for electrical and electronic components. Different electrical equipment and devices use brass turned parts.
- Electrical connectors and terminals
- Changing and connecting plugs
- Busbars for MCCs
- PCB Board parts
- Switchgear elements
Other Industries
Besides these, music, sport, jewelry, defense, and aerospace also use brass CNC turned components.
CNC Turning Methods for Brass Components
Brass CNC turning process
There are three main options for Brass CNC Turning; lathe machining, CNC turning centers, and Swiss turning. Each of them has distinct capabilities and work preferences.
CNC Lathe Machining
Lathes are most common for custom brass turned parts, they use a chuck and tool carriage for work holding and tool setup respectively. A single-point cutting tool removes the material that shapes the brass workpiece. Consequently, CNC lathe machining includes different operations that can be controlled through uploaded CAM files, such as taper turning, threading, knurling, and grooving.
Machining with CNC Turning Centres
Turning centers on action
These are more advanced turning machines with diverse machining capabilities in addition to turning operations. They can also mill, drill, grind, and tap the cylindrical works. You can perform several turning operations in CNC turn centers with precision and speed with CNC turning centers. Additionally, they might have 3, 4, 5, or even higher-axes capabilities.
CNC Swiss Turning
Swiss turning of brass parts
It is a precision turning method specialized for small-sized and complex parts. CNC Swiss Turning produces brass turned parts like avionic connectors, surgical instruments, antennas, small fasteners, etc. A guide bushing mechanism for the workpiece helps to minimize vibration and deflection during the machining of tiny items.
Try Prolean Now!
Tips for Brass CNC Turning
Brass grades are highly ductile and easy to machining, including the turning process. However, there are some concerns about tooling, turning variables, and operation handling.
The following are some tips for precise and high-quality brass CNC turned components based on industry practices;
- Ensure a Secure Work Holding
Secure your brass workpiece into the chuck and ensure that it is perfectly centered with head and tail stock. Additionally, too-tight holding can also leave marks on the surface.
- Coolants
Not all brass turning operations need coolants, but it is essential for large works and deep cuts. Coolants counters the heat buildup in the tool during the turning process.
- Air Stream in the Machining Area
It is for process safety, air pushes the brass chips or dust away from the operator’s body and minimizes the heat buildup.
- Use Sharp Tools with Minimum Hanging
Common tools for CNC turning of brass are bars, inserts, or other single-point cutters. Ensure they do not overhang and securly positioned in the tool post. Additionally, avoid the excessive winding of the cross-slide.
- Tungsten or Caride Tip
The tuning tool material for brass work is typically High-Speed Steel(HSS) with tungsten or carbide tips.
- Check the Conditions of Tooling
Ensure that chuck jaws, loose bearing, gins, saddle, and cutting tools do not have any wear and they perform well under desired conditions.
- CNC Turning Variables
RPM, cutting depth, and feed rate are three critical variables in CNC turning. They directly affect the dimensional accuracy and production speed of brass turned parts. The depth can be 4 to 10 times of tip diameter, the feed is 300 to 400 feet per minute, and the RPM of 500 to 9,000. The exact value depends on the diameter of the workpiece and the type of grade.
Brass Machining: CNC Milling Vs Turning
Another CNC process to craft brass parts is Milling, which involves a rotating tool attached to a spindle. The main difference between CNC milling vs turning is about kinds of shapes they create. Milling is preferred for flat and complex contours, whereas turning is best for cylindrical geometries.
Brass turning vs milling
The table below outlines the key differences between milling and turning in the context of brass workpieces;
| Criteria | CNC Milling | CNC Turning |
| Process | The cutting tool rotates against the stationary workpiece | Rotating work and stationary tool |
| Applications | Complex shapes with multiple axes | Cylindrical or conical parts |
| Brass Fit For | Best for detailed engravings or contours | Ideal for shafts, bushings, and threads |
| Material Waste | Fast material removal, but also higher waste | Efficient material use and minimal waste |
| Setup Time | Longer for multi-axis precision work | Quicker for repetitive symmetrical parts |
Do You Need CNC Turned Brass Parts?
If you are looking for any standard industrial or custom brass parts, don’t go anywhere; ProleanTech is a viable option. The muti-axis CNC lathes and Turning centers can produce complex turning parts with utmost accuracy. Additionally, our experienced team of engineers is ready to tackle unique and complex designs.
✔ 10 + Brass Grades
✔ 15 + CNC Turning Operations
✔ ISO 9001:2015 Certified
✔ 10 + Years of Track Record in CNC Machining
✔ Assistance in Design Optimization for Manufacturability
Upload your design and, request a quote for our Turning Services today! Our engineers will get back to you about how we can proceed with your project and an accurate estimation.
Try Prolean Now!
Conclusion
The use of brass turned parts is widespread, from high-performance automotive components to surgical instruments in the medical industry. Different properties(physical, mechanical, chemical, electrical) and high machinability are the main reasons behind this popularity. You can use CNC brass turning for your applications, but remember to choose the right alloy type and turning method according to end requirements.
FAQs
Are brass turned parts durable?
Although the exact life span of CNC turned brass parts depends on the particular application scenarios, they are durable and can last up to 25 years. The corrosion resistance against harsh environments and salt water, low surface friction, and thermal stability make brass parts durable.
What is meant by CNC turned components?
CNC turned parts or components are axially symmetrical items produced with CNC turning operations, where the cutter removes the material from the rotating workpiece until the desired shape is achieved.
What are the examples of turned brass?
Some examples of brass CNC turning parts are bushings, connectors, valve stems, threaded rods, nozzles, and couplings.















0 Comments