“DMLS 3D printing creates intricate metal parts with exceptional mechanical properties, including high heat resistance and durability. This method can print aluminum, titanium, stainless steel, and other metal parts from CAD design.”
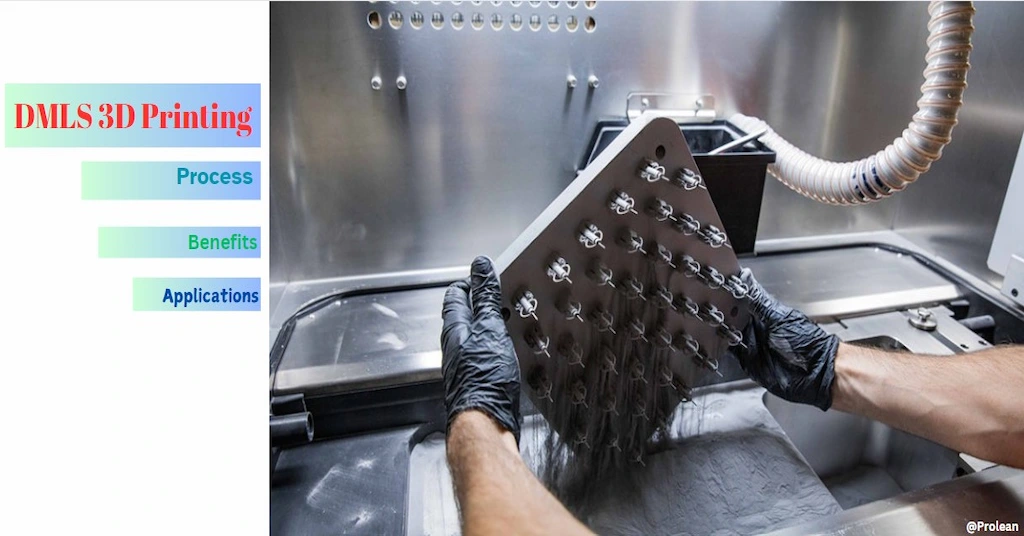

Tool access in complex machining areas limits additive manufacturing’s capability to create highly intricate features. Here comes the role of additive manufacturing processes like 3D Printing in making precise and complex geometries. It involves building the designed 3D model by adding the subsequent material layers. Manufacturers use various methods to print the desired part based on material type and required specifications. Direct Metal Laser Sintering, or DMLS 3D Printing, is a method for printing metallic parts.
The DMLS 3D printers use a laser beam that melts the metal powder and bonding agents and builds the liner layers to achieve the intended parts or products. This article will discuss how SMLS works, which metal and alloys can be printed, application examples, and other aspects of this 3D printing technology
.
What is Direct Metal Laser Sintering(DMLS) 3D Printing?
DMLS is a variation of 3D printing manufacturing that involves modifying the fine metal powder into a designed shape using a laser path. The laser moves in the instructed path and melts the selective areas fusing the powder to build the product. The history of using powder fusion to make metal parts can be traced back to 1971, Frenchman Pierre Ciraud.
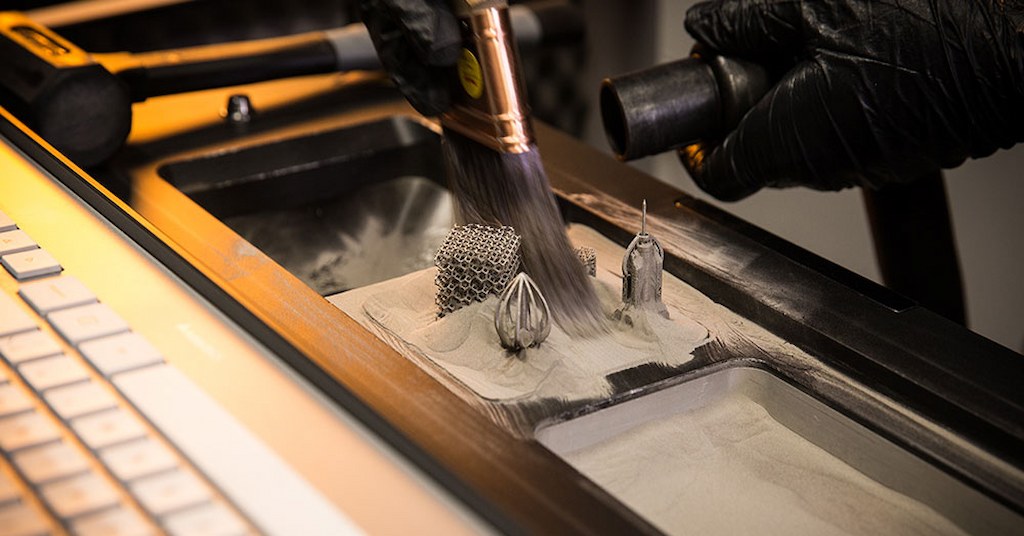

DMLS 3D printing
Unlike conventional manufacturing, it does not remove the material and eliminates mold tooling requirements. A DMLS laser printer simply creates the parts by fusing the powder grains according to the sliced layers of CAD designs.
Since this method builds a single item with all the necessary features, either no or minimal assembly is required. DMLS technology offers design flexibility, productivity, and complexity. Meanwhile, the DMLS printed parts are cost-effective for prototyping and small volumes as they do not require expensive setup and tooling.
You can use DMLS additive manufacturing for AiSiMg, Tool Steel MS1, Inconel 718, and numerous other metal and alloy powders.
Try Prolean Now!
How Does DMLS 3D Printing Work?
DMLs, SLM, direct metal laser sintering 3d printing, and all other powder bed fusion techniques work on the principle of metal powder fusion using intense heat. A concentrated laser beam sinters the foundation layer on the build chamber filled with fine powder and inert gas. The solidified layer reduces its thickness compared to the original powder level. Again metal powder is added and the laser builds another layer over it. The cycle continues until the process forms the desired shape.
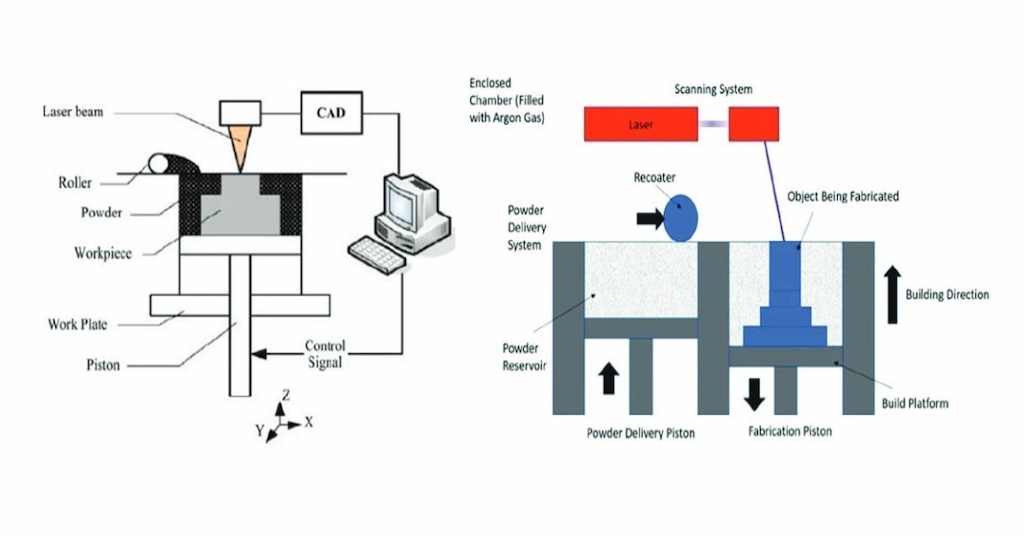
Process flow and schematic diagram of DLSM 3D printing
The building part requires support structures to maintain the correct positioning of layers and withstand the temperature difference between fused and remaining metal powder. A fabrication piston supports the building platform or chamber, meanwhile, another support structure works in the building direction.
Furthermore, here is the step-wise process of how you can convert your design into a physical form using DMLS 3D printing.
Design Preparation
Initially, a 3D model of the intended part is created with computer software. This design contains all the necessary information, such as geometry, features, dimensions, tolerances, etc. Next, slicer software is used to define the printing layers of the designed part. Slicing means converting the design into multiple layers and instructions for printing (G-codes).
Laser and Print Bed Setup
Next, the setup process includes positioning laser and concentrated lenses to facilitate the movement guiding, filling the metal powder in the build chamber with the correct thickness, setting filaments in the material supply, setting the powder supply from the reservoir to the build chamber, etc. Additionally, installing the support structure based on geometry and size is also essential.
Printing Stage
This is the actual DMLS printing stage, the laser follows the selective path of sintering in the powder layer according to uploaded G codes. The material supply piston continuously adds powder to the chamber. The process is repeated until the machine adds all the sliced layers one by one.
Ejection and Post Processing
After completing of printing, the support structures are removed and part is ejected from the printing chamber. The final parts might contain surface irregularities and minor marks. However, it does not leave visible layer lines. The finish quality is comparable with sand casting parts. The post-processing proceeds like machining, grinding, polishing, and plating, can be used to achieve the desired surface smoothness and aesthetic.
DMLS Metal 3D Printing Materials
Although all 3D printing materials materials not compatible with DMLS, almost every metal is suitable for this. Aluminum alloys, stainless steel, cobalt, chrome, copper, and other various metal and alloy powders can be used to print the design parts using DMLS additive manufacturing.
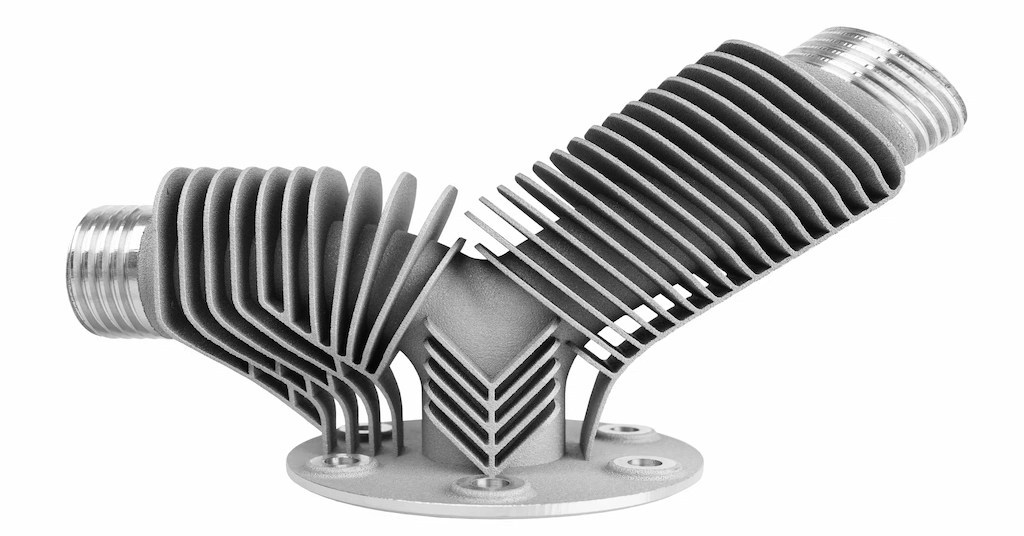
DMLS 3D print aluminum part
Here is a brief description of some common DMLS Materials in 3D printing;
Aluminum Powder
Aluminum is a good mechanical strength and corrosion-resistive material used in 3D printing. Various electronics, automotive, and aerospace parts rely on aluminum DMLS 3D printing for various components. AlSi10Mg is a typical aluminum alloy powder. However, AlF357, Al2139 AM, and other aluminum are also used.
Stainless Steel Powder
It is among the one of the high-strength and durable DMLS materials. The sufficient hardness and fatigue resistance make stainless steel suitable for various industrial items. Some of the common stainless steel powders include 254, 316L, duplex steel, and steel 17-4PH1.
Nickel Alloy Powder
These are known as high-performance alloys that offer a combination of strength, durability, and thermal stability. The 3D-printed nickel alloy parts are applicable in energy, aerospace, defense, and many other industries. Consequently, the common nickel alloy powders used in DMLS 3D printing are IN625,718, 939, etc.
Incole 718 Powder
It is also a high perforce alloy made with chromium and nickel. Incole printing parts are mainly popular in applications with high mechanical and thermal stress. Consequently, incole parts can be aged with AMS 5663 solution.
Titanium Powder
Titanium powder is used to print the high-strength and low-weight components. Its biocompatibility, hardness, tensile strength, and other mechanical properties are also beneficial. Titanium powder options for direct metal laser sintering 3d printing are Ti6, Ti64, TiCP, their combinations, etc.
What Are the Advantages of DMLS 3D Printing?
If we simply compare it with other conventional processes, material wastage, simple tooling, and straightforward production are the key benefits.
- Complex Features: As there is no such thing as tool access areas, more complex designs can be manufactured with 3D printing.
- Minimal waste: The unsintered metal power can be reused immediately. So, DMLS 3D printing produces almost zero material waste.
- Difficult-to-Machine Alloys: Titanium, Incole, and Nickel alloys, and other such difficult-to-machine materials are easily compatible with 3D print manufacturing.
- Rapid Prototyping: It does not require cutting tools or molds that take high initial costs and production speed is also faster. So, the DMLS method is suitable for rapid prototypes.
- Strength: The DMLS print metal parts do not lose the original properties like traditional plastic 3D printing.
- Lightweight Components: The lower thickness build-size and capability of micro-features allow DMLS technology to print lightweight components from titanium, Incole, and Nickel powders.
Furthermore, if you want to read the comparative advantages, check 3D printing vs injection molding and 3D printing vs CNC machining here.
DMLS 3D Printing Applications
Automotive, aerospace, defense, energy, electronics, and other many industries use DMLS 3D printing to create precise components and products in the shortest possible time. For example, 3D printing automotive parts are favored for complex internal structures, medical implants for precision, etc. Additionally, metal 3D printing prototyping uses DMLS and other metal powder fusion techniques.
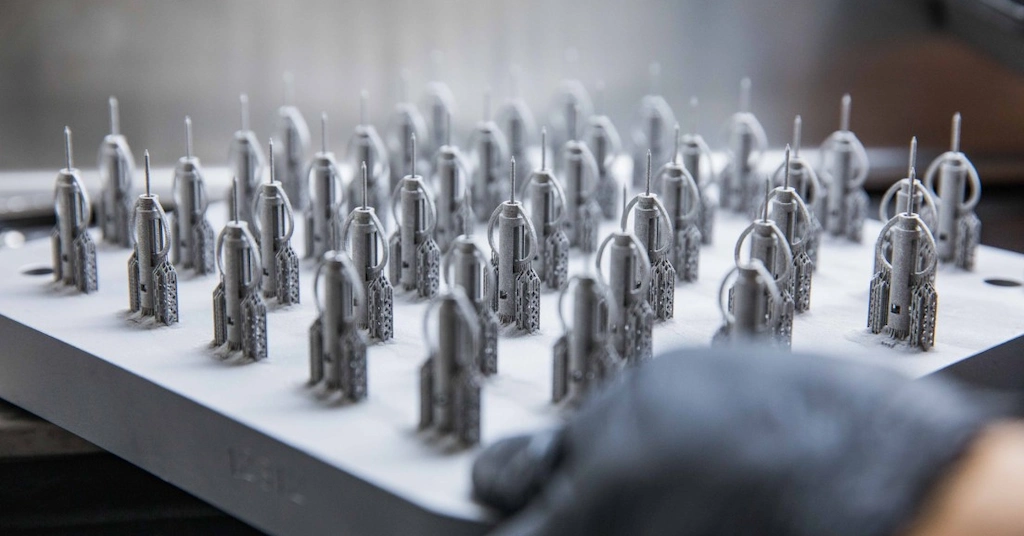

DMLS printing applications
The table below shows the applications across different sectors with examples;
| Industry | Why Use DMLS? | Application Examples |
| Aerospace |
– Lightweight and complex geometries – High strength-to-weight ratio – Material performance at high temperatures |
– Turbine blades – Engine components – Structural brackets |
| Automotive |
– Design flexibility – Rapid prototyping – Customization possibilities |
– Exhaust manifolds – Engine pistons – Gearbox components |
| Medical |
– Biocompatibility – Patient-specific implants – Complex internal structures |
– Orthopedic implants – Dental crowns – Surgical tools |
| Tooling & Molds |
– Reduced lead times – Complex cooling channels – Material durability |
– Injection mold inserts – Die-casting molds – Tooling fixtures |
| Energy |
– High-temperature resistance – Corrosion resistance – Custom geometries |
– Turbine parts – Heat exchangers – Pump components |
| Jewelry |
– Intricate designs – Customization – Material versatility |
– Rings – Bracelets – Custom metal piece |
Try Prolean Now!
Summing Up
Overall, DMLS 3D printing is ideal for prototyping and small-volume production of various metallic components across industries. The selective fusion of metal powder bed with optical laser maintains the structural integrity and original properties. You can use this manufacturing method for precise, complex, and compact designs. However, the expertise of engineers and the capability of 3D printing machines equally influence the final quality.
If you are looking for 3D printing metal prototypes and parts, our 3D printing service can be the best option for you. We have advanced 3D printing facilities with a pool of experienced engineers in the field of additive manufacturing. Our low-cost yet fast and precise 3D printing solutions can help you to grow your business.
FAQs
Can I 3D print metals?
Yes, metals can be 3D printed using technologies like Direct Metal Laser Sintering (DMLS) or Selective Laser Melting (SLM). These processes allow for the creation of complex metal parts directly from digital designs.
How does DMLS 3D printing build the parts?
DMLS builds parts layer by layer by sintering metal powder with a high-powered laser. The laser selectively fuses the powder according to the digital design.
What materials can I use for DMLS printing?
DMLS can use various metal powders, including stainless steel, titanium, aluminum, cobalt-chrome, and nickel alloys.
Is DMLS technology expensive?
DMLS can be expensive for simple designs that can be manufactured with conventional machining. However, it becomes cost-efficient for rapid prototypes and complex geometries.


0 Comments